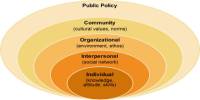
Globalization is a process of interaction and integration among the people, companies, and governments of different nations, a process driven by international trade and investment and aided by technology. This process has effects on the environment, on Culture, on political systems, on economic development and prosperity, and on human physical well-being in societies around the world.
It was not until the 1960s that the term globalization began to be widely used by economists and other social scientists. It had achieved widespread use in the mainstream press by the later half of the 1980s. Since its inception, the concept of globalization has inspired numerous competing definitions.
Globalization expands and accelerates the movement and exchange of ideas and commodities over vast distances. It is common to discuss the phenomenon from an abstract, global perspective, but in fact globalization’s most important impacts are often highly localized. This page explores the various manifestations of interconnectedness in the world, noting how globalization affects real people and places.
A historical and sociological approach to political economy with a belief in the importance of interdependency and the global systemic structure and connected processes. There is only one world system, and the claims by Stalin in The Economic Problems of Socialism shortly before his death in 1953 and others still since then that there are now “two world systems,” one capitalist and another socialist, were an optical illusion.
History of globalization is a subject of on-going debate but believed to be stretched over:
- Ancient Greek culture that stretched from India to Spain
- Roman Empire, the Parthian Empire
- The Islamic Golden Age
- Mongol Empire (middle east and china)
- European era
- The 19th century Industrialization (modern form)
Effects of globalization
Industrial, Financial, Economic, Political, Informational, Language, Competition, Ecological, Cultural, Social, Ethical, etc.Religious
Negative effects
- Spread some of the deadliest infectious diseases
- Richer countries driving talent away
- Booming economies are shaping the global biosphere .
- Rise in global food prices
- Global drug trade increases
- Increased black market animal trading
- Increased women and child trading
Advantages of Globalization
- goods and people are transported with more easiness and speed
- the possibility of war between the developed countries decreases
- free trade between countries increases
- global mass media connects all the people in the world
- as the cultural barriers reduce, the global village dream becomes more realistic
- as the liquidity of capital increases, developed countries can invest in developing ones
- the flexibility of corporations to operate across borders increases
- the communication between the individuals and corporations in the world increases
- environmental protection in developed countries increases.
Disadvantages of Globalization
- Developed countries can stifle development of undeveloped and under-developed countries.
- Economic depression in one country can trigger adverse reaction across the globe.
- It can increase spread of communicable diseases.
- Companies face much greater competition. This can put smaller companies, at a disadvantage as they do not have resources to compete at global scale.
Information Source: