Formula on Mensuration
Mensuration is the branch of mathematics which deals with the study of Geometric shapes, their area, volume and related parameters.
It is based on the use of algebraic equations and geometric calculations to provide measurement data regarding the width, depth and volume of a given object or group of objects. While the measurement results obtained by the use of mensuration are estimates rather than actual physical measurements, the calculations are usually considered very accurate.
Prism
(i) Area of the lateral faces of a right prism = perimeter of the base × height.
(ii) Area of the whole surface of a right prism = Area of the lateral faces + 2 × area of the base.
(iii) Volume of a right prism = area of the base × height.
Pyramid
(i) Area of the lateral faces of a right pyramid = ½ × perimeter of the base x slant height.
(ii) Area of whole surface of a right pyramid = area of the lateral faces + area of the base.
(iii) Volume of a right pyramid = 1/3 × area of the base × height.
Tetrahedron
If a be the length of an edge of a regular tetrahedron then
(i) the area of its slant sides = 3√3/4 a2 sq. units;
(ii) the area of its whole surface = √3a2 sq. units
(iii) the volume of the tetrahedron = √2/12 a3 cu. units.
Mensuration Formulas for Rectangle
Area of Rectangle = Length × Breadth.
Perimeter of a Rectangle = 2 × (Length + Breadth)
Length of the Diagonal = √(Length2 + Breadth2)
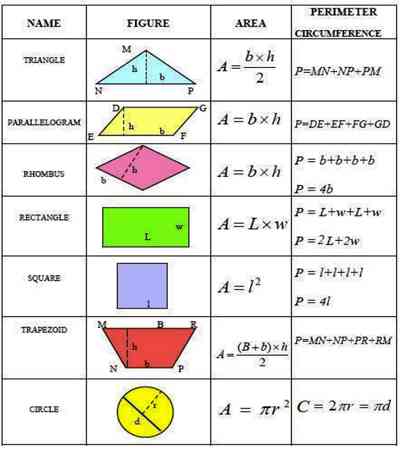
Mensuration Formulas for Square
Area of a Square = Length × Length = (Length)2
Perimeter of a square = 4 × Length
Length of the Diagonal = √2 × Length
Trapezium
Area = 1/2h(a+b)
Perimeter = Sum of all sides
Rhombus
Area = d1 × d2/2
Perimeter = 4l
Quadrilateral
Area =1/2 × Diagonal × (Sum of offsets)
Kite
Area = d1×d2/2
Perimeter = 2 × Sum on non-adjacent sides
Circle
Area = πr^2 or πd^2/4
Circumference = 2πr or πd
Area of sector of a circle = (θπr^2 )/360
Information Source-