A Study of the Foreign Trade Department of Bank Asia Limited
Bank has always been described as a financial institution that collects deposits from individuals and organizations and provides loans to those who need it. However, at present day banks do not only have to collect and disburse money to various entities, but are also required to provide various services to various entities which facilitate their business operations. A foreign trade department of a bank is one of those services that not only facilitates the business of the businessmen but also contributes to the development of the economy as a whole. Foreign exchange is described as the system or process by which one country’s currency can be converted into another country’s currency. Foreign exchange is the means and methods by which rights to wealth in a country’s currency are converted into rights to wealth in another country’s currency. Foreign exchange department of banks plays significant roles through providing different services for the customers.
Objectives of the Study
General Objectives:
- To apply theoretical knowledge in the practical field.
- To observe the working environment in commercial banks.
- To get an overall idea of foreign trade activities.
- To get familiar with rules, regulations theories and practices of a bank.
- To be acquainted with the banking guidelines and gather idea about operational procedures.
Specific Objectives:
- To analyze the foreign trade activities (export, import and foreign remittance).
- To learn about Letter of Credit (L/C).
- To know how to issue and advise Letter of Credit (L/C).
- To be acquainted with the documents required for Export and Import.
- The consequences process of Transmitting L/C, L/C amendment & Lodgment systems.
- To get a practical knowledge about Export procedure and the system of foreign remittance.
- To acquire a synopsis of the problems in Foreign Trade department of Bank Asia Limited.
- To know about the company and its products/services.
- To generate suitable recommendations that might help to reduce the problems in Foreign Trade department of Bank Asia Limited.
- To complete my internship program and prepare an internship report.
History of Bank Asia
Bank Asia Limited has been established on 27th November, 1999 under the Banking Company Act 1991. It is third generation bank and scheduled commercial bank in the private sector. It has been incorporated as a public limited company under the Company Act 1994 in Bangladesh to carry out banking business. A group of successful entrepreneurs initiated the journey of Bank Asia Limited. The management of the bank is comprised a team led by senior bankers with vast experience in both national and international market. The bank has confirmed its position in the banking sector as one of the fastest growing. Presently it has more than 91 branches all over the Bangladesh. At the beginning of its initiation in 1999, it achieved a milestone by acquiring the Bangladesh operations of the Bank of Nova Scotia of Canada, which is the first in the banking history of Bangladesh. Later on in 2002, the bank acquired the Bangladesh operations of Muslim Commercial Bank Ltd. (MCB). In 2003 the bank went public by offering shares to the general investor and was listed with the stock exchange in 2004. The bank it’s most appreciated Islamic banking operation in 2008 by offering strict Shariah based products. On March 16, 2011 the bank established its 1st subsidiary company named “Bank Asia Securities Limited” and within the same year it opened another subsidiary company “BA Exchange Company (UK) Limited” in the United Kingdom. Currently the bank is rendering services through its 91 Branches, 5 Islamic Windows, 10 SME Service Centers, 1 Off-shore Banking Unit, and 2 Subsidiary companies.
DEPARTMENT OVERVIEW (FOREIGN EXCHANGE)
According to Foreign Exchange Regulation Act (FERA) 1947, “Anything that conveys the right to wealth in another country is foreign exchange. Foreign exchange means and includes all deposits, credits and balances payable in foreign currency as well as foreign currency instruments such as drafts, TCs, bill of exchange, Promissory Notes and Letters of Credit payable in any foreign currency.” In accordance with this definition any business activities related to Import, Export, Outward and Inward Remittances, buying and selling of foreign commissions, etc. fall under the concept of foreign exchange business.
Therefore a foreign exchange can be described as the system or process by which one country’s currency can be converted into another country’s currency. It can also be defined as the exchange of currency in terms of goods from one country to another country. This division of a bank is one of those services that not only facilitates the business of the businessmen but also contributes to the development of the economy as a whole. Foreign exchange department of banks plays a significant part through providing different services to the customers. This division can be categorized into two parts:
- Foreign Trade Department
- Foreign Remittance Department
Foreign Trade Department of Bank Asia Limited (Corporate Branch)
Previously it has been mentioned that foreign trade means the exchange of foreign currency between two countries for the purpose to trade. In other words, foreign trade deals with foreign financial transactions related to trade or business. The Foreign Trade Department of a bank assists and enhances the global trade by providing different services to both importers and exporters of Bangladesh. In order for a bank to have a foreign exchange department it needs to be an authorized dealer approved by Bangladesh Bank which is the central bank for Bangladesh. In today’s world a bank not only supports the foreign trade of the business organizations of Bangladesh, but also connect the buyer to the seller who unknown to one another and are boundaries apart.
Foreign Remittance Department of Bank Asia Limited (Corporate Branch)
The purchase and sale of freely convertible foreign currencies is known as foreign remittance under the Foreign Exchange Regulations Act (FERA) 1947. Foreign remittance as a whole considers all sale and purchase of foreign currencies paid for import, export, travel and other purposes. Nevertheless, this department specifically manages the sale and purchase of foreign currencies for any purpose except for export and import.
Concepts of Foreign Exchange Department
In relation to UCPDC (Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credit) 600, the concepts are mentioned below: abide
Applicant/Opener/Importer/Buyer: Applicant (importer) is referred to the person/business organization who requests the bank to issue Letter of Credit (L/C) in support of the applicant corresponding to the terms and conditions mentioned in the sales contract or pro forma invoice between the buyer and seller.
Opening Bank/Issuing Bank: An issuing bank is referred to a bank that issues Letter of Credit on behalf of the applicant, who is the client of the bank, to the exporter (beneficiary).
Exporter/Seller/Beneficiary: An exporter is also known as the beneficiary in support of whom the Letter of Credit has been issued.
Advising bank: An advising bank is the exporter’s bank that accepts a Letter of Credit (L/C) issued by the issuing bank on favor of the exporter. The advising bank also authenticates the L/C and informs the exporter, i.e., the beneficiary.
Nominated bank: A bank specified in the Letter of Credit (L/C) that has the authority to pay or receive payments. Usually the nominated bank is the exporter’s bank, i.e., the advising bankun less any other bank is mentioned in the Letter of Credit.
Confirming Bank: A confirming bank is a third bank that adds its confirmation at the request of the issuing bank. This bank guarantees payment to the exporter that if terms and conditions mentioned in the Letter of Credit will be abided by completely. In other word, the confirming bank at the request of the issuing bank gives confirmation to the Letter of Credit.
Payment Practices in Foreign Trade
Increased global competition has forced both the buyers (importers) and sellers (exporters) to agree to different payment methods that will facilitate them equally. Even though it will be beneficial for the exporters to receive payments before or right after shipment, it might not be advantageous for the importers. Therefore the exporters and importers are in an agreement for appropriate payment mode. In general there are four major payment practices in foreign transactions that have been discussed below:
Advance Payment: In this case the importer pays the exporter in advance through T.T before the exporter ship the goods, implying that exporter receives the payment before the importer gains possession of the goods. This process of payment is profitable for the exporters since the risk for receiving the payment is zero or minimal. However this payment practice is least advantageous for the importers due to the risk of not receiving the shipment. Therefore the importers impose some conditions in the Letter of Credit to make sure that they are secured. Generally, the condition is that the exporter cannot receive the payment in their account until they submit the exporter documents, such as the bill of exchange, bill of lading, commercial invoice, certificate of origin, etc. to the exporter’s bank.
Consignment Payment: According to this mode of payment, exporter receives the payment only when the importer sells the goods to his/her end customers. For example, the exporter exports raw materials to the importer. The importer will use the raw materials to produce the finished goods and sell it to his/her customers. After the importer gets his payments, he will make the payments to his/her exporter. Although the exporters have the possession of the goods until it is sold, this process is extremely risky for the exporters because payment is not guaranteed and exporter might have to wait to receive payment. Therefore the exporters enforce some conditions to reduce the risk.
Documentary Collections: Sometimes importers may perhaps be worried about the exporter’s credibility. Advance payment or consignment payment might not be the appropriate option for these importers. The payment process called documentary collections look after the benefit of both importer and exporter. This payment process is carried out through the banks. In accordance with this method, the exporter requires to submit export documents, such as bill of exchange, bill of lading, commercial invoice, packing list, certificate of origin, etc., to his/her bank in order to receive the payment from the importer. Once the importer’s bank receives the documents, it is mandatory for the importer to pay the face amount written on the bill of exchange either at sight, i.e., payment is made right after documents are received, or on a specified date, i.e., the importer’s bank will give acceptance and payment will be made on the date specified in the agreement. This process is practiced under the rules set by ICC Uniform Rules for Collections (URC) that guide bankers, exporter and importers in the collections process.
Letter of Credit (L/C): This mode of payment is the most widely used in the foreign trade. A Letter of Credit is a bank’s promise signifying that if the exporter fulfills all the terms and conditions mentioned in the L/C, then the bank is obliged to pay the exporter even if the importer fails to pay. Both the issuing bank and advising bank act a liaison through the L/C between the importer and the exporter and manages the documents only. The issuing bank verifies whether all the export documents have been sent as mentioned in the L/C. If any documents have not been sent by the exporter then the issuing bank informs the importer and through discussion with the importer may give a discrepancy. If discrepancy exists, then the exporter will not receive payment unless he/she meet the requirements to dismiss the discrepancy. A Letter of Credit is issued under the rules and regulations set by Uniforms Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP) that is regulated by the International Chamber of Commerce and Industries (ICC).
Categories of Letter of Credit
Bank Asia Corporate offers three categories of L/C and they are:
- Sight L/C: In this case payment has to be made within five working days after the bank receives the documents from the advising bank.
- Deferred L/C: In such case the payment is made afterwards, i.e., after the due date. Due date is considered from the date of shipment. It is usually issued for 60 days, 90 days, 120 days as per the terms and conditions mentioned.
- Back to Back L/C: It is opened by an importer who requires raw materials or additional materials to produce his/her goods that will be exported. The value of this L/C can go up to 80% of the master L/C.
IMPORT PROCEDURE OF BANK ASIA LIMITED
A country import goods that cannot be produced locally as efficiently or at a cheaper rate as those goods can be produced in another country. Moreover industries in a country may need to import raw materials or commodities that are not readily available within the country to produce finished goods. Therefore a country needs to import to meet the demand of its people along with positive or stable balance of trade.
According to Import and Export (Control) Act, 1950, any importer and exporter needs to have Import Registration Certificate (IRC) and Export Registration Certificate (ERC) respectively provided by the Office of the Chief Controller of Imports & Exports(CC I & E). This certificate will allow the importer or exporter to import or export any permissible item of any value and without any restrictions on quantity imported or exported and no further permission from any other authority is required.
An importer or exporter can obtain Import Registration Certificate (IRC) or Export Registration Certificate (ERC) by submitting the following documents:
- Trade License
- Membership Certificate from recognized Chamber/Trade Association
- Tax Identification Number
- Bank Certificate
- Memorandum and Articles of Association and Certificate of Incorporation (in case of Limited Company).
After an importer obtains IRC, he/she is a qualified importer. In order to open a L/C the importer will require acquiring Letter of Credit Authorization Form (LCAF) from his/her bank. When the importer fills out the LCAF and submits it with other required documents such as pro forma invoice, sales contract, insurance cover note, etc, the bank will issue an L/C, where the importer will be the applicant and the exporter will be the beneficiary.
An importer can import goods under two types of LCAF:
- Commercial: When an importer imports commercial goods, such as bags, toys, shoes, etc., he/she needs acquire commercial LCAF.
- Industrial: When an importer imports industrial goods, such as capital machineries, industrial raw materials (dyeing chemicals, yarn, etc.), etc., he/she needs to acquire industrial LCAF.
Step-1:
Firstly, the importer and exporter join in a sales contract with the intention to do business. The contract specifies the details of the goods such as the value of the goods, quantity required, latest date of shipment, payment method, shipment mode, etc. An L/C is issued on these conditions mentioned in the contract.
Once both the importer and exporter agrees to terms and conditions of the contract, the importer needs to submit required documents to the bank in order to issue a L/C. The documents required are given below:
- Letter of Credit application form that contains the information of the applicant and beneficiary.
The form also contains the total L/C amount, country of origin of goods, mode and type of payment, port of shipment, and latest date of shipment. It also includes the draft amount, exchange rate, equivalent BDT amount, margin, commission, stamp and other charges.
- Pro forma invoice copy or sales contract.
- Insurance cover note policy must be submitted to make sure that the security of the goods is covered by insurance.
Step 1
- Submitting required documents for opening the L/C
- Verification of the documents
Step 2
- Issuing L/C and trnsmitting the L/C to the advising bank
Step 3
- Verification of Export Documents
Step 4
- Lodgment
Step 5
- Retirement and reports.
- IMP form containing the signature and seal of the authorized personnel of the company.
- Letter of Credit Authorization Form (LCAF) mentioning the H.S code (Harmonized System Code) that represents the category of goods, quantity of goods, invoice value, IRC number, LCAF number.
- Agreement form that includes details contract between the parties.
- Charge Document.
Along with the above mentioned documents the importer requires to submit the following documents:
- Trade License.
- Import Registration Certificate (IRC).
- Income Tax Declaration of TIN no.
- Membership Certificate.
- Memorandum of Association (Only for Limited companies).
- Registered Deed (Only for Partnership firms).
When the importer submits all the documents, the bank verifies the documents.
Step-2:
If the documents submitted by the importers are accurate then a L/C is issued and needs to be transmitted to the advising bank. There are three ways of transmission:
- Telex
- Courier
- SWIFT (Society for worldwide inter telecommunication network).
Bank Asia Ltd. transmits its L/C through the SWIFT. After the L/C has been transmitted and acknowledged by the SWIFT arrangement of the advising bank, the issuing bank gives one copy to the importer and keeps another copy as the office copy.
Upon receiving the L/C, the exporter produces the goods and ships the goods as per the latest date of shipment.
In case the importer and exporter want to make changes in the terms and conditions of the L/C then the importer requires the issuing bank to issue an amendment. Amendment means modifying any terms and conditions in the L/C.
According to the guideline for Foreign Exchange amendments include:
- Extension of shipment date or expiry date.
- Increase or decrease of invoice value within L/C limit.
- Alteration of any specifications, such as price or quantity to be imported.
Step-3:
When the exporter produces the goods and ships them, a number of documents must be prepared and submitted to the advising bank that forwards the document to the issuing bank. The documents required to be submitted are mentioned in the L/C. The required documents include:
- Bill of exchange
- Bill of Lading
- Insurance policy
- Inspection certificate
- Commercial invoice
- Packing list
The instant the issuing bank receives the above mentioned documents they verify these documents to check whether all the documents as per the L/C have been forwarded.
Step-4: Lodgment
Once the importer gives approval that the import documents are proper, the issuing bank transmits a an acceptance message through the SWIFT to the advising bank notifying that the documents have been accepted and payment will be made to the exporter within the maturity date. Moreover the issuing bank enters the records of the import bill into its register. In case the importer feels that the documents are insufficient, he/she requests the issuing bank to issue a discrepancy and sent it to the advising bank through the SWIFT. The payment is stopped until the exporter dismisses the discrepancy.
Step-5: Retirement & Reports:
Once the issuing bank pays the import bills, it issues vouchers of the bill for the importer. The voucher includes the detailed transaction information, mentioning the bank’ charges, margins, etc. The retirement process includes the following steps:
- Interest calculation (if any).
- Register entry.
- Endorsement on the bill of exchange.
At the end of the month the completed original IMP form attached with a copy of the commercial invoice and pro forma invoice is reported to the Bangladesh Bank. The duplicate IMP form along with a commercial invoice is kept with the bank as an office copy. After recording in the IMP form the particulars of the remittance the original copy of the IMP. Moreover, the returns of the bill lodged are also reported to Bangladesh Bank.
According to Bangladesh Bank guidelines for Foreign Exchange, every bank also needs to report the information of the L/C in the Bangladesh Bank Online import Monitoring System.
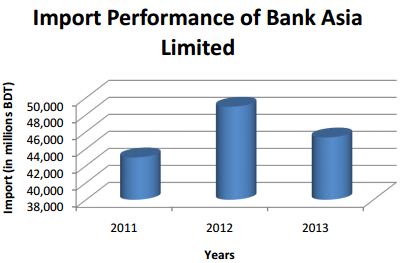
The graph above shows that the import of Bank Asia Limited has improved from 2011 to 2012. The total import was 42,983 million BDT in 2011. However in 2013 import decreased to 45,330 million BDT. The political instability was the major reason behind the declination.
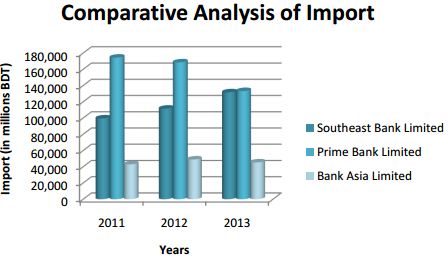
In order to have an overall viewpoint of the import of Bangladesh, I have compared the import of Bank Asia with that of Southeast Bank limited and Prime Bank Limited. From the graph above it can be observed that both the banks’ performances are better in comparison to Bank Asia Limited. One of the reasons is that both the banks are in operation longer than that of Bank Asia. As a result they are more visible in the market. The graph also represents that the overall import of Bangladesh improved in 2011 and 2012. Most importantly, import of all the three banks decreased in 2013.
Findings
While preparing the report and analyzing the data, I have identified some major findings. I have only worked at the Corporate Branch of Bank Asia Limited. Therefore if the practices and corporate culture of Bank Asia as a whole is believed to be the same as at the Corporate Branch, then the following are the findings of my report:
- The employees of most departments are not satisfied with the management regarding the amount of work that they have to do. Moreover they have to put up with a lot of difficulty to apply for the annual leave (LFA) even though they apply for the leave on due time.
- There is observable manpower shortage in the foreign exchange department of Bank Asia Limited. Consequently the work load is extremely high compared to any other departments. This also leads to accumulation of work that the employees must complete within the deadline. For example, in the year 2014, most of the inland Letters of Credit opened at this branch were not updated in the Bangladesh Bank Online Import Monitoring System. A few days back Bangladesh Bank sent a query showing that approximately 675 Letters of Credit were overdue. Bangladesh Bank gave a time frame of one month within which all these Letters of Credit must be updated. In addition there were more than 700 EXP forms from last year that were not entered in the Bangladesh Bank Online Export Monitoring System. All these forms needed to be entered within three weeks time as stated by Bangladesh Bank.
- Bank Asia Limited is a customer-oriented bank where the customer is given the priority. Therefore whenever a corporate client of the foreign exchange asks for a service, such as to issue a L/C or to provide PRC (proceed realization certificate), the employee must provide it within a short span of time. This happens repeatedly disturbing the normal workflow of the employee.
- Bank Asia Limited tends to follow the instructions of Bangladesh Bank. However due to the immense pressure of the clients, the employee has to provide a service that is against the rule and might be risky. For example, a client must take the EXP form from the Bank after providing the commercial invoice. However in reality the clients take EXP books in advance from the bank. They then take the EXP number from the bank over the phone and submit the EXP later.
- The employees are unhappy with some of the actions taken by the management. For example, an employee is transferred from the foreign exchange department to another department within the branch. The transfer takes place within a span of one to two days which is a very short time for the foreign exchange employee to train his/her replacement. This is a disturbance for other foreign exchange employees because they have to train a new employee and after sometime the same incident is repeated.
- Bank Asia Limited provides extensive training facilities to its employees to develop their skills and knowledge about the entire banking system. However with the existing manpower shortage, an employee is sent to training without any replacements. This increases the work pressure for other employees and leads to customer dissatisfaction due to delay of work.
- The internet facility of Bank Asia limited is extremely poor. Recently this is a major issue because it is mandatory by Bangladesh Bank to input EXP and L/C information online as soon as they are issued. Due to slow internet connections it becomes difficult for the employees to input the information online. This also adds to customer dissatisfaction because if the information is not entered into Bangladesh Bank Online System then the customer cannot release or ship goods.
- Lack of space is another problem for the foreign exchange department. Since the department needs to keep all the files of five years in addition to the recent year’s files, the storage has become a major issue. The files are scattered here and there hampering the image of Bank Asia Limited.
- The import is higher than that of export, therefore giving a negative trade of balance.
Recommendations
The internship experience has provided me an insight of the foreign exchange department. Bank Asia Limited is a leading commercial bank and is bound to have problems. However these problems must be resolved in order to progress. Therefore I provided the following recommendations to the above mentioned findings to reduce the problems and to move forward towards progress:
- The management of the bank should try to resolve disputes and dissatisfaction amongst the employees.
- The management should reduce the manpower shortage by appointing skilled and dedicated employees.
- The bank must look after the customer since it is a service organization. However, it should reduce the practices such as issuing EXP number over the phone to avoid any kind of problems in future.
- The bank should use latest software to fast forward their jobs. Moreover, the internet facilities have to be looked into so that they can provide faster services.
- The management must work in coordination with the branches and thus plan the training programs accordingly.
- If required they should rent bigger office space to reduce the storage problem. In this case the management needs to work swiftly to take any decisions if they do not want to compromise their standards.
- The import and export volume must be monitored. At present, import is greater than export causing the balance of trade to be negative. The bank must try to increase export volume and also to reduce the gap to increase profitability and stability.
CONCLUSION
With the increase in the economic development in Bangladesh, the financial institutions’ roles are extremely crucial. Bank Asia Limited is a third generation Bank that is also contributing to the socioeconomic development of the country. Although Bank Asia Limited has some issues to be resolved, yet it is progressing and has a greater prospect to develop further once the problems are resolved.
Internship is vital for us because we have only acquired theoretical knowledge. This program gives us the opportunity to have the practical knowledge so that we can match the theories to the reality. I am fortunate enough to complete my internship at bank Asia Limited, Corporate Branch. Moreover I got the chance to work in the foreign trade department which is considered to be one of the core departments of a bank. Although the internship period is extremely short to learn or acquire in-depth knowledge, yet it gave me a taste of the corporate world.
Bank Asia Limited is working tremendously to become one of the pioneers in banking. The members management are well-educated and it about time that the bank achieve its goals. However the bank must introduce advanced software and technologies to provide faster service to its customers. If they can ensure their customers about the service quality it will give them the opportunity to attract new and bigger clients.