Ferro-actinolite is the ferrous iron-rich endmember of the actinolite-tremolite continuous solid solution series of the double chain calcareous amphibole group of inosilicate minerals. It is a form of Actinolite where the magnesium is wholly replaced by iron. Ferro-actinolite is scientifically regarded as a distinct mineral species. All the series members belong to the monoclinic crystal system.
The following formula comparison indicates the position of individual well-known members within the series:
- tremolite: ☐Ca2(Mg0-4.5Fe2+0.0-.5)Si8O22(OH)2
- actinolite: ☐Ca2(Mg0-2.5Fe2+0.0-2.5)Si8O22(OH)2
- ferro-actinolite: ☐Ca2(Mg5-0.0Fe2+2.5-5)Si8O22(OH)2
Some other substitute cations that may replace either Ca, Mg, or Fe include potassium (K), aluminum (Al), manganese (Mn), titanium (Ti), and chromium (Cr). A fluorine (F) anion may partially replace the hydroxyl (OH).
General information
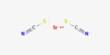
- Formula: ☐{Ca2}{Fe52+}(SiO22)(OH)2
- Color: black-green, dark green
- Crystal System: Monoclinic
- Member of: Tremolite-Actinolite Series Group

Fig: Ferro-actinolite
Properties
Ferroactinolite prisms are much darker in color than actinolite due to their higher iron content affecting opacity, but may be dark green in thin slices or around the edges. Its crystals are brittle, with a hardness of 5-6 on the Mohs scale, and have a white streak. Ferroactinolite is pleochroic and has a higher refractive index and surface relief than actinolite.
- Diaphaneity: Transparent to Translucent
- Hardness: 5-6 – Between Apatite and Orthoclase
- Luster: Vitreous – Dull
- Cleavage: Distinct/Good on {110}
Occurrence: In iron-rich greenschist and blueschist facies metamorphic rocks; in metamorphosed iron formations; as part of a vein assemblage cutting Ca-Fe-Si tactites.
Association: Hedenbergite (replacement), andradite, ilvaite (contact metamorphic); cummingtonite, quartz, magnetite, riebeckite, biotite, hematite (iron formations).
Information Source: