The Fahrenheit hydrometer is a device that measures the density of a liquid. It was invented by Daniel Gabriel Fahrenheit (1686-1736), who is best known for his thermometry work. A hydrometer is a device used to determine the density of a liquid. When the density of the liquid is compared to that of water, the specific gravity can also be determined. Before reading the hydrometer, ensure that both the hydrometer and the liquid are steady and not in motion. The reading is taken where the liquid touches the hydrometer stem.
Operation
A hydrometer is a gadget that determines the density or specific gravity of a liquid in comparison to water. A hydrometer is constructed from a calibrated glass tube. It contains a bulb at the bottom that is weighted and filled with air to ensure that it stands upright when submerged in liquid. It features a narrow tube that extends from the bulb with the scale on it. The hydrometer will descend so that the density may be displayed on the scale. The tube falls deeper as the density of the liquid it is immersed in decreases.
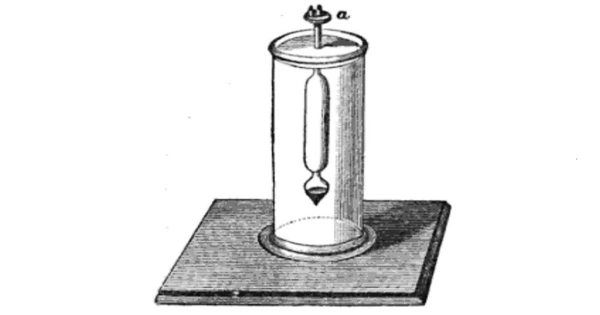
The Fahrenheit hydrometer is a constant-volume instrument that floats in water. In this illustration, the hydrometer is floating vertically in a cylinder filled with liquid. A weighted bulb sits at the bottom of the hydrometer, while a pan holds small weights at the top. To use the hydrometer, first correctly measure its weight (W) while it is dry.
Next, the gadget is immersed in water, and a weight (w) sufficient to sink a marked point on the rod to the water’s edge is placed on the pan. At that point, the weight of water displaced by the instrument is equal to W + W. The hydrometer is then withdrawn, cleaned dry, and immersed in the liquid whose density is to be measured. A weight (x) sufficient to sink the hydrometer to the same marked point is placed in the pan. The density (D) of the second liquid is then given by D = (W + x) / (W + w).
The Fahrenheit hydrometer can be made of either glass or metal.
The Nicholson hydrometer is similar in design, but instead of a weighted bulb at the bottom there is a small container (“basket”) into which a sample can be placed.