Researchers at the Garvan Institute of Medical Research discovered that an epigenetic modification known as DNA methylation can explain endocrine resistance, which is a primary cause of breast cancer deaths. In patient-derived animal models, the team was able to successfully reverse this methylation and limit cancer progression.
Using a low dose of the epigenetic treatment chemical decitabine, which is presently used to treat some blood malignancies, the researchers were able to effectively limit the growth of endocrine-resistant breast tumors in mice while increasing survival by 90%. The discovery, which will be tested in a future Phase I clinical trial, has the potential to transform the lives of almost 4,000 Australians diagnosed with endocrine-resistant breast cancer each year.
“This research has uncovered a completely new approach to treating endocrine-resistant breast cancer. In our study, we have not only pinpointed a new molecular mechanism that explains how endocrine resistance might develop – we have identified a treatment currently used in the clinic that can target this mechanism precisely,” says Professor Susan Clark, Head of the Cancer Epigenetics Laboratory at Garvan and senior author of the paper published in Nature Structural & Molecular Biology.
This research has uncovered a completely new approach to treating endocrine-resistant breast cancer. In our study, we have not only pinpointed a new molecular mechanism that explains how endocrine resistance might develop – we have identified a treatment currently used in the clinic that can target this mechanism precisely.
Professor Susan Clark
Epigenetic change drives breast cancer treatment resistance
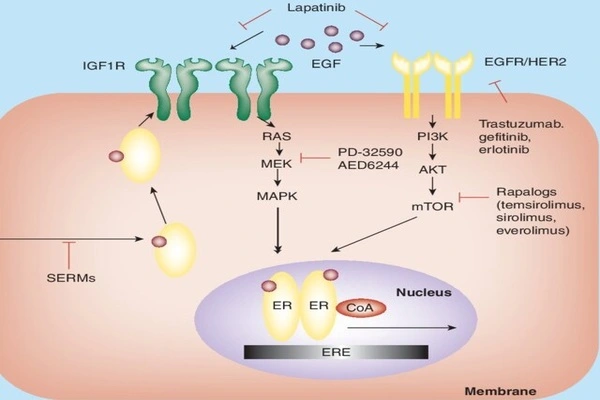
An estimated 70% of all diagnosed breast cancers are oestrogen receptor-positive (ER+), which means their growth is activated by oestrogen — a hormone that plays a key role in sexual and reproductive health in women. While endocrine therapy that suppresses oestrogen in the body can slow or stop the growth of these tumours, more than 30% of patients develop resistance, with their tumours no longer requiring oestrogen to grow.
In a 2020 study, the Garvan team investigated endocrine-resistant cancer’s epigenome, the layer of instructions that organises and regulates DNA’s activity, and revealed that endocrine resistance is linked to methyl groups attaching to regulatory regions of DNA and changing the 3D structure of DNA inside cancer cells.
New approach to breast cancer therapy
“In this current study, we set out to reverse the abnormal methylation patterns and restore the 3D DNA structure in the endocrine-resistant ER+ breast cancers using epigenetic therapy,” says first author Dr Joanna Achinger-Kawecka, Head of the 3D Epigenome in Cancer Group at Garvan. “We found that decitabine removed methyl groups at specific DNA regulatory regions, rewiring the 3D structure of DNA to not only reactivate the production of oestrogen receptors, but also activate tumour suppressor genes that can reduce cancer growth.”
“After treating patient-derived endocrine resistant breast cancer tumours with decitabine alone, we were surprised to see cancer growth significantly reduced in mice,” says co-first author Associate Professor Clare Stirzaker, Head of the Epigenetic Biomarker Group. “This highlights the importance of studying fundamental molecular mechanisms to best guide targeted treatments.”
Decitabine is an FDA- and TGA-approved epigenetic therapy currently used to successfully treat certain blood cell cancers, including myelodysplastic syndromes, but there are limited studies in other cancers. While the current study focused on ER+ breast cancer, the researchers say the drug may also have potential for other endocrine-resistant cancers driven by epigenetic changes.
“The next stage of our research will be to test decitabine together with endocrine therapy, which could be even more effectively target this difficult-to-treat cancer,” says Professor Clark. “We hope that such a combination approach is a turning point that enables significantly better clinical outcomes.”