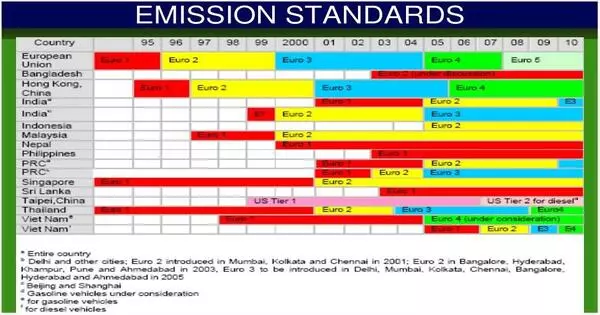
Emission standards are the regulatory rules that govern the emission of air pollutants into the atmosphere. It refers to regulations and recommendations established by governments or international agencies to limit the amount of pollutants and greenhouse gases that can be emitted into the environment from a variety of sources, including cars, industrial activities, and power plants. These regulations are in place to protect human health and the environment by lowering air pollution and mitigating climate change.
Emission standards establish quantitative restrictions on the amount of specified air pollutants that may be released from specific sources over specific time periods. They are primarily intended to meet air quality regulations while also protecting human life. Vehicle emission rules vary between areas and countries.
Here are some common examples of emission standards:
- Vehicle Emission Standards: Governments set limits on the amount of pollutants that can be emitted by vehicles, including cars, trucks, and buses. These standards often include limits on exhaust emissions (e.g., CO, NOx, and PM) and greenhouse gas emissions (e.g., CO2).
- Industrial Emission Standards: Regulations may require industrial facilities to control emissions from processes such as combustion, chemical production, and waste incineration. Limits are set on various pollutants depending on the industry.
- Power Plant Emission Standards: Power plants, especially those that burn fossil fuels like coal or natural gas, must adhere to emission limits for pollutants like SO2, NOx, and mercury.
- Marine and Aviation Emission Standards: Ships and aircraft are subject to emission limitations in order to minimise the environmental impact of their operations, particularly in terms of air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
- Renewable Energy and Energy Efficiency Standards: To minimize greenhouse gas emissions, certain guidelines promote greener energy sources and improve energy efficiency.
There may be rules in agriculture to limit methane emissions from animals or ammonia emissions from fertilizer application. Emission limits are frequently applied to landfills and waste incineration facilities in order to control the release of toxic gases and odors. There are certain restrictions in place to reduce emissions from construction equipment and building materials.
Compliance with emission requirements frequently necessitates the deployment of pollution control devices, adjustments to production processes, cleaner fuels, and regular emission monitoring and reporting. Violations of these standards may result in fines, legal action, or operational restrictions until compliance is reached.
Emission regulations are an important instrument in the fight against air pollution, protecting public health, and addressing climate change by lowering greenhouse gas emissions. They differ greatly between regions, based on local environmental circumstances, economic activity, and governmental priorities. International organizations such as the United Nations and the European Union also help to define and harmonize emission limits across countries and regions.