Doxycycline (Uses and Effects)
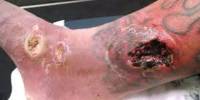
Definition: Doxycycline (oral tablet) is a prescription antibiotic medication that is used in the treatment of a number of types of infections caused by bacteria and protozoa. It’s used to treat infections such as chest infections, skin infections, rosacea, dental infections and sexually transmitted infections (STIs), as well as a lot of other rare infections.
It is useful for bacterial pneumonia, acne, chlamydia infections, early Lyme disease, cholera, and syphilis. It is also useful for the treatment of malaria when used with quinine and for the prevention of malaria. Doxycycline is available on prescription. It comes as capsules. It can be used either by mouth or intravenously.
Doxycycline was patented in 1957 and came into commercial use in 1967. It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.
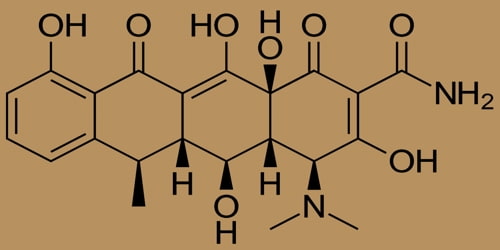
Key facts:
- For most infections, people will start to feel better in a few days but it is important to finish the course of medicine.
- The most common side effects of doxycycline are headaches, feeling sick or being sick. It can also make people’s skin sensitive to the sun.
- Doxycycline can affect growing teeth so it’s not prescribed for children under 12 years old or given to pregnant and breastfeeding women.
- Do not drink alcohol while taking doxycycline. There are also some common medicines people should not mix with it.
- Doxycycline can also be called by the brand name Vibramycin-D.
Doxycycline belongs to a class of drugs called tetracyclines. A class of drugs is a group of medications that work in a similar way. These drugs are often used to treat similar conditions. This drug works by blocking a bacterial protein from being made. It does this by binding to certain units of the protein. This stops the protein from growing and treats our infection.
Doxycycline is available as a generic medicine and is generally inexpensive. The wholesale cost in the developing world is between 0.01 and 0.04 USD per pill. In the United States 10 days of treatment is about 14 USD; however, some in 2014 were selling it for more than 3.00 to 10.00 USD per pill.

Uses and Dosage of Doxycycline: Doxycycline oral tablet can interact with other medications, vitamins, or herbs you may be taking. An interaction is when a substance changes the way a drug works. This can be harmful or prevent the drug from working well.
In addition to the general indications for all members of the tetracycline antibiotics group, doxycycline is frequently used to treat Lyme disease, chronic prostatitis, sinusitis, pelvic inflammatory disease, acne, rosacea, and rickettsial infections.
Doxycycline is available under the following different brand names: Vibramycin, Monodox, Acticlate, Atridox, Avidoxy, Doxy, Doxycin, Doryx, Oracea, Periostat, Adoxa, Ocudox, and Doryx MPC.
Doxycycline can be taken by adults and children over 12 years old. It isn’t suitable for some people. To make sure this medicine is safe for people, tell the doctor if people have:
- Ever had an allergic reaction to doxycycline or any other medicine in the past
- Kidney problems
- Liver problems
- An inflamed food pipe (oesophagitis)
- Lupus, an autoimmune disease
- Myasthenia gravis, an illness that causes severe muscle wasting
Do not use these drugs with doxycycline. Doing so can cause dangerous effects in people’s body. Examples of these drugs include:
- Penicillin. Doxycycline may interfere with how penicillin kills bacteria.
- Isotretinoin. Taking isotretinoin and doxycycline together can increase people’s risk of intracranial hypertension.
General Dosage –
- Initial: 200 mg/day divided twice daily orally/intravenously (IV) on the first day (IV may be given once/day), THEN
- Maintenance: 100-200 mg/day once/day or divided once every 12 hours orally/intravenously (IV) (IV may be given once/day)
Specific dosing varies depending on the condition being treated; consult the doctor.
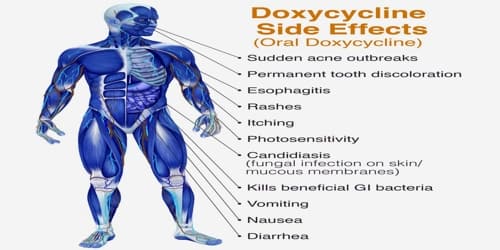
Effects of Doxycycline: Like all medicines, doxycycline can cause side effects, although not everyone gets them.
Side effects of doxycycline include:
- Diarrhea
- Difficulty swallowing
- Drug rash
- Esophageal ulcer
- Esophagitis
- Facial redness
- Headache
- Hives
- Inflammation of the small intestine and colon (enterocolitis)
- Lesions on the genitals or anus
- Loss of appetite
- Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
- Low levels of white blood cells or platelets
- Skin hyperpigmentation
- Skin peeling (exfoliative dermatitis)
- Tongue swelling
- Tooth discoloration
- Upper abdominal pain
Serious side effects of doxycycline include –
- Drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms
- Exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus
- Hemolytic anemia
- Hepatotoxicity
- Low platelet count (thrombocytopenia)
- Low white blood cell count (neutropenia)
- Intracranial hypertension
- Pericarditis
- Serum sickness
- Toxic epidermal necrolysis
Allergic reactions to doxycycline are common and occur in more than 1 in 100 people. In rare cases, doxycycline can cause a serious allergic reaction.
Doxycycline, like other tetracycline antibiotics, is bacteriostatic. It works by preventing bacteria from reproducing through the inhibition of protein synthesis.
Information Source: