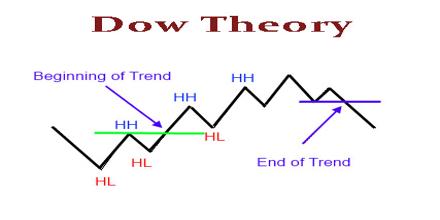
This article talks about Dow Theory, which is an approach to trading developed by Charles H. Dow, who with Edward Jones and Charles Bergstresser founded Dow Jones & Company Inc. and developed the Dow Jones Industrial Average. The theory argues that since the first index reflects the productive capacity and the second the volume of goods distributed, as long as they rise or fall together the economic trend will be maintained. The theory has undergone further developments in its 100-plus year history, including contributions by William Hamilton in the 1920s, Robert Rhea in the 1930s, and E. George Shaefer and Richard Russell in the 1960s.
Dow Theory