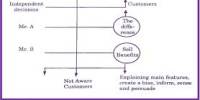
Distribution strategy of Reckitt Benckiser Bangladesh Limited:
Reckitt Benckiser Bangladesh Limited has specific distribution policy. Its target is divided into two mechanical strategies those are product push strategy and customer pull strategy.
Products push strategy
Here product push strategy is such devices where the distribution people follow “pro-actively influence sell-in” of Reckitt’s product that is they actively influence the buyer to buy Reckitt’s product.
The key challenges they face here are as follows.
- Direct coverage expansion.
- Driving passive distribution.
- Right service frequency
- Selecting the right distribution partners.
Customers pull strategy
Here the customer pull strategy is such a device where the distribution people are to depend on “the natural demand” for Reckitt’s product at the retail level. That is if the retailers want a high volume of products then Reckitt can generate high-scaled revenue.
Here the key challenges they face are divided into two teams that is the distribution people and the brand team. The key challenges both the group faces are as follow:
- To create natural demand.
- To ensure visibility at point of sales (POS).
- To influence trade to be Brand Ambassador for RBBL products.
Forms of Distribution:
There are two forms of distribution in Reckitt Benckiser Bangladesh Limited
- Direct distribution.
- Indirect distribution.
Direct Distribution
In direct distribution process Reckitt Benckiser (Bangladesh) Limited has full control over the entire supply chain ranging from depot down to the point of sale. Here RBBL practice direct coverage policy. The benefit direct distribution is to retain ownership and control over supply chain.
Indirect Distribution
The control mechanism of indirect distribution passes to the wholesaler to ensure that the product is available at retail level. Indirect distribution is where RBBL don’t have full control of the entire supply chain. Indirect distribution is playing the role of passive distribution. In passive distribution one wholesaler is selected in a remote trade area and is given a certain profit margin. The percentage depends on the following factors such as:
- Distance of the market.
- Area coverage.
- Sales growth.
- Reputation in the market.
- Financial solvency.
The rationale to adopt the indirect distribution strategy is:
- To minimize the distribution cost.
- When the outlet universe is big and fragmented.
Defining market as the prerequisite of distribution planning:
Market can be defined based on:
- Administrative structure, whether the company has direct control over the market or out of it.
- Economic profile, the consumption pattern and the economy of that particular market area.
- Geographic nature, the geographic characteristic of the particular market. Such as Chittagong hill tracts, plain land markets are of Khulna.
Reckitt Benckiser (Bangladesh) Limited defines its market in following ways:
- Urban market: Urban market is based in metropolitan city and all the district head quarters.
- Sub-Urban market: Sub-Urban market is based on all the Thana head quarter.
- Rural market: market based in beyond Thana head quarter. For example, unions and bazaars.
Urban and Sub-Urban market:
Key features of urban and Sub urban markets are:
- Urban market accounts for more than 50% of the business for Reckitt Benckiser (Bangladesh) Limited.
- Disposal income is much higher than rural market.
- Density of population is much higher than rural area.
- Consumers are more critical as they are better informed.
- Consumers tend to follow the life style of capital city. Here capital sets the trend.
- Developed infrastructure.
- Easy access to electronic media.
Distribution Strategy for Urban and Sub-Urban Market:
1. Route planning is very critical. The responsible person who has expertise regarding the traffic routes of that area makes the route plan. Sometimes it is done with the negotiation of the responsible groups. But 3 factors should be kept in account always.
- Cost effectively.
- Traffic jam free routes.
- Highest area coverage.
Distributors sales representatives should not be over burdened.
Engage a mix of top and medium performers
2. Right service frequency for each route based on the 80-20 theory. It means high volume contributory routes should have higher service frequency. If required, additional service during the peak season or any occasion e.g. before Eid and shab-e-barat.
3. Close supervision on distribution services by launching Customer satisfaction measurement (CSM).
4. Ensuring distribution even in by-lines within the urban / semi-urban base market.
5. Outlet survey should be conducted in every November as the off pick season starts from the month of November.
Rural market:
Key Features of Rural Markets:
- Strong agro-based economy thereby disposable income is Limited.
- River, mountain and lots of small villages.
- Low density of population.
- Completely different life style than urban areas.
- Infrastructure is yet to be developed in many rural areas.
- Relatively less critical consumers.
- Access to electronic media is Limited. So point of sale is the key source of brand awareness.
- 62% of outlet universe belong to rural markets.
Distribution Strategy for Rural market:
Distribution channels are completely different in rural markets. Rural market is the future source of this business so companies should give extra emphasis.
Rural market penetration: Market prioritization is made through some approaches
Spot light approach:
Spot light approach is used through long-term analysis of some factors as
- Distribution network
- Performance of present distribution network.
- Manpower.
Now the grading colors of spotlights and their criteria are mentioned bellow:
Green: Good distribution network
Yellow: Where RBBL have distribution, but not up to the satisfactory level.
Red: Where RBBL have no distribution or have an extremely poor distribution. (Covers only highways with very low frequency).
Red and yellow markets are selected for RMP-distribution drive.