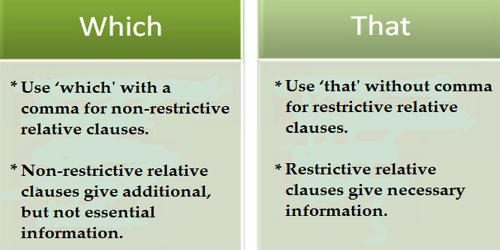
To understand when to use that or which, it’s important to understand clauses. Clause implies a set of words that is a part of a sentence, but it contains its own subject and predicate. A defining clause gives information essential to the meaning of the sentence. A relative clause is a type of clause that expresses the person or thing, the speaker is referring to. We use ‘that’ to refer to people or things, whereas we use ‘which’ to refer to things only.
Basically, we use who, whose, whom, that and which, in relative clauses. By identifying your clauses as defining or non-defining, you can easily remember when to use which and when to use that. Many people suffer dilemma in using that and which in the sentences. While that is used to talk about things and sometimes about people, which is used to discuss things only.
Difference between That and Which –
THAT
- That is normally used to point out a person or an object, distant to the speaker, or add a clause that enhances the meaning of the subject.
- That’ is a pronoun, which is mainly used to point out something or someone, not in direct contact with the speaker. It may also be used to add a clause to the main clause, so as to enhance its meaning.
- ‘That’ is a relative pronoun which identifies a particular person or thing, referred by the speaker. It is commonly used with singular nouns.
- When it comes to usage, ‘that’ is used to institute an essential/restrictive clause. An essential clause is one that adds some information that is important with respect to the subject of the sentence.
- When writing sentences with relative clauses, we use ‘that’ to provide further information, which elucidates the antecedent in the main clause.
- Example: Paul called me on the number that was out of service. The man who is standing at the door that’s my father.
WHICH
- ‘Which’ is a wh-word, which is used to ask questions or add some information to the preceding noun, which is not pertinent to the subject.
- ‘That’ can be used as a pronoun, determiner, conjunction, and adverb, which can be used only as a pronoun and determiner.
- ‘Which’ is an interrogative pronoun, i.e. a wh-word that is used for asking the question, or seeking information concerning one or more people or objects from a given set.
- Further, ‘which’ is also used to refer to something which is already specified to institute a clause for providing additional information incidental to the main clause.
- When it comes to usage, a non-essential/non-restrictive clause is introduced by ‘which’, i.e. it only adds supplementary or incidental information.
- Example: The train runs to Nagpur, which is its last destination. She went to the village, which is situated near the river.



![Internship report on National credit and commerce bank Ltd [part-1]](https://assignmentpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/03/ncc-bank-110x55.jpg)