Banks are exposed to five core risks through their operation, which are-credit risk, asset/liability risk, foreign exchange risk, internal control & compliance risk, and money laundering risk. Among these risks management of credit risk gets most attention. Credit risk arises due to the possibility that the borrower may fail to repay the loan. Following the recent global financial crisis, which originated from poor management of credit risk, credit risk is the most discussed topic in banking industry.
Prime bank limited is the emerging commercial bank in Bangladesh. Within a short period of time PBL has managed to establish itself as a strong performer in the financial market. It is rapidly expanding and enjoying a high growth rate. Its loan portfolio is increasing every year. For this reason efficient management of credit risk is crucial for continuous success of PBL. All commercial banks operating in Bangladesh are strictly regulated by Bangladesh Bank.
Bangladesh Bank has provided a guideline for credit risk management. All banks try to comply with that guideline. Prime bank is no exception of this practice. PBL has segregated the credit related activities. Marketing, preparation of credit proposal, other documentation, credit disbursement, credit monitoring etc are done at branch level. Credit
administration and credit risk management related works are done at head office.
Introduction
Risk is inherent in all aspects of a commercial operation. However, for Banks and financial institutions, credit risk is an essential factor that needs to be managed. Credit risk is the possibility that a borrower or counter party will fail to meet its obligations in accordance with agreed terms. Credit risk, therefore, arises from the bank’s dealings with or lending to corporate, individuals, and other banks or financial institutions. Credit risk management needs to be a
robust process that enables banks to proactively manage loan portfolios in order to minimize losses and earn an acceptable level of return for shareholders. It is essential for banks having robust credit risk management policies and procedures that are sensitive and responsive to these changes. Bangladesh Bank issued guidelines on the Credit risk management function and it emphasizes on – Policy guidelines, organizational structure and responsibility and procedural guidelines.
Background of the study
Bank is the most important financial institution in the economy. It plays vital role in the economy by providing means of payment and in mobilizing resources. The economic development of a country depends on the development of banking sector to a great extent. The dependence of banking sector in modern economy is increasing day by day because this sector ultimately contributes to run the wheel of development in a more dynamic way.
Today’s modern banks are not only provides traditional banking, rather banks are expanding the menu of financial
services, banks are making the untouchable service touchable for their customers. The changing and expanding role of banking has made the banking business more complex and competitive. For survival and growth of this business demands creativity, specialization and knowledge and adoption of new technology are used. But technology, creativity, specialization all these cannot support a bank to survive unless the services are marketed in the right track. For this banks need experts who will able to run the business even in against the wind.
Banks provide important capital in the form of loan and advances which are subject to nonrepayment which is termed as credit risk, the chance that a loan will not be repaid timely. Hence the main concern of the banks is credit risk and its management as credit or loans and advances are the main source of income for them.
Prime Bank Limited is one of the leading banks in this sector which arranges corporate and retail credit. This Bank is very much concerned with the credit risk and its management and has a credit risk management department. The success of the banks is hidden in the proper management of the all the sorts of risk related to the banking business.
Hence credit risk and its management has become a vital part of the bank. This report will give us an overall idea about the credit risk and its management as practiced by the Prime Bank Limited. Bangladesh Bank undertook a project to review the global best practices in the banking sector and examines the possibility of introducing these in the banking industry of Bangladesh. Four ‘Focus Groups’ were formed with participation from Nationalized Commercial Banks, Private Commercial Banks & Foreign Commercial Banks with representatives from Bangladesh Bank as team coordinators to look into the practices of the best performing banks both at home and abroad. These focus groups identified and selected six core risk areas and produced a document that would be a basic risk management model for each of the six ‘core’ risk areas of banking. The six core risk areas are as follows-
- Credit Risk;
- Asset-Liability Management/Balance Sheet Risk;
- Foreign Exchange Risk;
- Internal Control and Compliance Risk;
- Money Laundering Risk; and
- Information Technology risk.
Objective of the Report
The overall objective of this study is to acquire the practical knowledge about how a banking financial institution carries out its activities since we have gathered only the theoretical knowledge in BBA program. In light of this view, this report examines the credit management system of Prime Bank Limited.
Broad Objective:
Specific Objectives:
- To give a brief overview of Prime banks Ltd. and the day to day function and service offered by the bank.
- To have a close view as well as analyze the performance of the specific branch and the bank as a whole.
- Evaluation of credit risk management tools for effective measurement of customer satisfaction.
- To identify problems and challenges of Prime Bank Ltd.
- To get an overview of the banking system of Prime Bank Ltd.
- To analyze performance of the bank in terms of profitability over the entire bankingperformance.
- To have better orientation on “Credit Risk Management” activities of Prime Bank Limited, especially on various Credits and loan services offered by the bank.
- To find out the feasibility and practical market issues about new credit risk evaluation model and credit pricing model for the commercial banks in Bangladesh.
- To minimize the proportion of nonperforming assets to performing assets.
Finally, identify the major problem of PBL and provide subsequent recommendations.
Methodology of the Study:
Methodology is generally a guideline system for solving a problem with specific component such as phases, task, methods, techniques and tools. It is the systematic study of methods that are applied within a discipline. It also refers how to organize data from various sources to complete a successful study.
Methods of collecting Data:
The techniques of collecting primary data are not same as the techniques of collecting secondary data. The different methods and tools of collecting primary data and secondary data used in this report are described as follows:
Collection of Primary Data:
Various types of the data and information were collected from my practical experience and queries from the executives while doing my internship at The Prime bank Ltd.A questionnaire is made to collect Information and data regarding Overview of the Prime bank Ltd, evaluating criteria of Credit, credit disbursement, credit policy, credit limit, recovery system of defaulters, sound credit, necessary actions to the defaulters, controlling procedures over the credit etc. were collected from these sources. The questionnaire is added to the appendix.
Collection of Secondary Data:
Data regarding the credit risk management of Prime Bank Ltd. were collected from secondary sources like: Annual Reports, Brochures, Manuals and Publication of The Prime Bank Ltd., annual report of Bangladesh Bank, books, various business related articles and internet were the major sources of secondary data.
ORGANIZATION STRUCTURE
Highly skilled professionals having long experience in banking are managing Prime Bank Ltd. They constantly focus in understanding & anticipating customer needs & operate according to it to survive in the changing market condition. Now we would look in to each of the four basic management activities Planning, Organizing, Controlling and Leading that the bank practices, in order to stay on top of its competitors.
PLANNING:
The overall planning approach in Prime Bank is top-down. Management of Prime Bank Ltd. can be categorized in to two broader teams, one is the Top Management team and other one is the Mid Level Management team. The Top-Management team usually comprises of the Board of Director’s where the Bank’s Chairman heads the meetings. Long terms goals are usually been discussed in these high profile meetings, where the bank owners decides everything. For example, what should be the targeted profit for the next fiscal year. During their regular meeting
each month the directors tries to review the feedback from decisions given earlier. Changes are made if needed and new issues are also discussed.
The Mid Level Management team on the other hand deals with short term goals. They are here to see whether the short terms goals are in line with the long-term targets. Moreover, they also provide solutions to everyday challenges that can come up all the time. Most of the employees in the mid level are usually head of individual branches and is entitled to with responsibility to see the smooth operation of the branch.
ORGANIZING:
The term organizing for Bank indicates the way through which the day to day activities of the bank are carried out for smooth operation. Prime Banks follows two approaches for organizing its business, one the Branch Based Approach and the other is the Department Based Approach. In the Branched Based Approach, each individual branch is treated as the separate identity and is head by a branch manager. The branch manager is liable to the top management for the performance of that particular branch. Before the starting of a facial year and from than onward, it is the duty of the branch manager to see that targets are being met. Given below is an organ gram of an individual branch for better understanding.
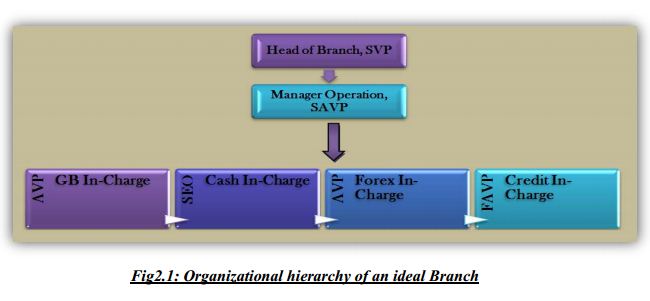
The Department Based Approach is similar to that of the branch based approach, where each department operates as a separate unit but sometimes collaborates in order operates more efficiently or to solve a common problem. Such departs are also treated as a separates entity but are much more specialized in on particular area of business unlike a branch, which has to be involve a multiple tasks. Examples of few other departments at Prime Bank Ltd are as given
below:
- Human resource Department.
- Financial and Administration Department.
- Monitoring and Inspection Department.
- Marketing.
- Personal and Relation Department.
- Merchant Banking.
- Investment Banking.
- Treasury Division.
- International Division.
- General service Division.
- Computer and Information Technology Division.
- Credit Administration Division.
- Corporate Affairs Division.
- Card Division.
Organizational Set-up at Credit Division:
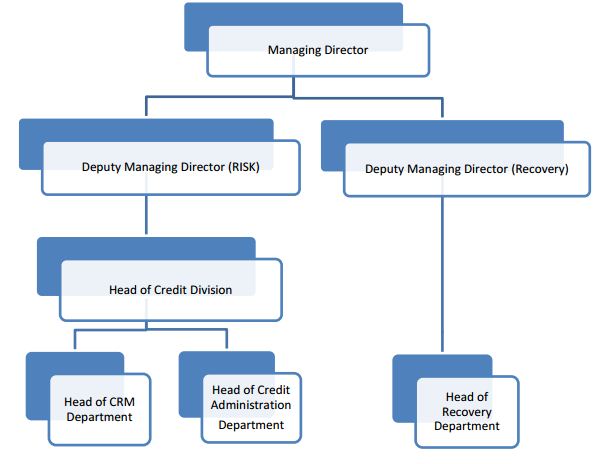
STAFFING:
Hiring the right people for the right position is one of the most important functions of any banks since it operates in the service industry. The Human Resource Department of Prime Bank Ltd performs this function. Staffing not only deals with recruitment but also involve in giving training to employees, performance appraisal and many other related activities.
Recruitment at Prime Bank is of two basic type, one is the hiring of fresh new employees and other is the recruitment of experienced employee. Every year new graduate students are recruited at the entry level of Management Trainee or Trainee officer, depending on individual qualification. For each of this entry level post, applicants have to sit for several written assessment test before moving on to a series of interview, from where the best are chosen. On the other hand, someone having previous banking experience might not have to sit for any written exam but it directly assessed by the top or mid level management through interviews.
LEADING AND CONTROLLING:
Prime Bank Ltd achieved its current success because of its expert team of management whether it be the Branch Manager or the Department Head, each has their equal shares in making this Bank a success.
The head of each branch belongs to the mid-level management unlike the department heads who usually belongs to the higher level in the corporate ladder. An employee form the top management level is likely to be responsible for several small departments of the bank, until and unless department requires very high skills. The executives from the mid and the top level management is also responsible for the well-being of all the employees working under them. He or She has to make sure that all the employees are working in accordance with the company policy is being fairly treated. For this appraisal function the manger of each branch has to fill out Annual Appraisal Report (AAR) each year to evaluate the performance of individual employee, based on which promotions, increment and bonuses are given out.
TYPES OF CREDIT FACILITIES
i. Loan (General): Short, Medium & Long term loans allowed to individual/firm/industries for a specific purpose but for a definite period and generally repayable by installments fall under this type. These are mainly allowed to accommodate financing under the categories (a) Large & Medium Scale Industry & (b) Small & Cottage Industry.
ii. Housing Loan (Commercials): Loans allowed to individual/enterprises for construction of house for commercial purpose only fall under this type. The amount is repayable by monthly/quarterly installments within a specific period.
iii. Home Loan: Loan allowed to individuals for purchase of apartment or construction of house for residential purpose fall under this type. The amount is repayable by monthly installments within a specified period.
iv. House building Loan (Staff): Loans allowed to thee employees of PBL for purchase of apartment/construction of house shall be known as House Building Loan (Staff).
v. Lease Financing: Lease financing is one of the most convenient sources of acquiring capital machinery and equipment where by a customer is given the opportunity to have an exclusive right to use an asset usually for an agreed period of time against payment of rental.
vi. Customer Credit Scheme (CCS): It is a special credit scheme of the bank to finance purchase of consumer durable by the fixed income group to raise their standard of living. The loans are allowed on soft terms against personal guarantee and deposit of specified percentage of equity by the customers. The loan is repayable by monthly installments within a fixed period. Apart from the above loans there are some other loans which are:
- Household Durables
- Doctors Loan
- Any Purpose Loan
- Travel Loan
- CNG Conversion Loan
- Car Loan
- Advance against Salary
- Education Loan
- Marriage Loan
- Hospitalization Loan
SWOT ANALYSIS
SWOT Analysis is a strategic planning method used to evaluate the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats involved in a project or in a business venture. SWOT is an acronym for the internal strength and weakness of a firm and the environmental Opportunity and Threat facing that firm. It involves specifying the objective of the business venture or project and identifying the internal and external factors that are favorable and unfavorable to achieving that objective. The technique is credited by Albert Humphrey.

Here, the internal strength and weakness of Prime Bank Ltd. as well as the external opportunities and threats are discussed:
STRENGTH
i. Capital Adequacy: Prime Bank Ltd. is maintaining a strong capital base. By the end of year 2008, the capital adequacy ratio of the bank was 11.50% which was well above the stipulated requirement of 9%. The bank had a target to have Tk. 3000 million of capital fund by the year 2010, whereas it already reached capital fund of almost Tk. 2000 million by 2008, positioning the bank as one of the strong capital based bank of Bangladesh.
ii. Customer Service: Prime Bank Ltd. has a very good relationship with its customers. The bank believes in maintaining personal relationship with its clients. One of the major goals of the bank is to build long term relationship with the customer and to create value for them. To maintain this relationship, PBL sometimes waive high charge for those valued clients who are linked with the bank for a long period of time. As a result of such strong
customer service, the bank currently has more than 154000 customers, highest in the private sector commercial banks of our country.
iii. Liquidity Position: Liquidity position is a major criterion to measure a bank’s strength. By the end of 2008, PBL’s liquid assets ratio was 18.92%. So the liquidity risk of the bank is low and it makes its position stronger.
iv. Efficient Administration: Prime Bank Ltd. has a very efficient management. The work is done in a timely and systematic manner for which the efficient administration is responsible. This is close relationship between the employees and the management though the chain of command is maintained strictly. Overall, there is a good balance
between the administration and the employees.
v. Quality of asset: The asset of PBL is very high quality. The major portion of this asset is loan and advances. The default rate is less than 2% where as the average default rate in Bangladesh is 30%. This proves that the credit risk of PBL is very low.
WEAKNESS
i. Technology: One of the major weaknesses of Prime Bank Ltd. is the technology used by the bank. With the change of time, technological advancement is essential to survive in the competition. Hence, PBL is lagging far behind in this area. Most of the branches are not well equipped. There are not enough computers, telephones or fax machines in the branches which are often slower the pace of work. PBL was the pioneer in “Online Banking” but the online facility which the bank is providing currently is not up to the standard.
ii. Remuneration: The pay scale of employees in PBL is not competitive compared to other private banks of the country. The employees of PBL get compensation of around 60% of what other private banks, for example, Dhaka Bank, Bank Asia, Mercantile Bank, Southeast Bank etc. offer to their employees. This creates dissatisfaction among the employees which carries the risk of rise in employee turnover rate. Those who cannot switch bank are often discouraged to give their best effort in the job.
iii. Promotion: When an employee gets a promotion to the next level, he/she gets more compensation. PBL is regular in giving promotion, but the employees get late effect of this promotion. Often there is a long gap, for example a six month gap in getting the effect.
iv. Deposit Amount: Prime Bank Ltd. has acquired high amount of deposit till now. By the end of November 2008, the deposit amount was 2542 million. Most of this deposit amount remains idle in the bank. Not even half of this amount is used as loan and advance. The lending rate has been lowered by the government, so the interest rate from
loans cannot cover the interest given on deposit. The high amount deposit bears high cost. To reduce this cost, most of the deposit schemes have been discontinued. This has a negative effect on clients who expects a broad range of deposit services from the bank.
v. Training: Prime Bank Ltd. has its own training Institute PBTI (Prime Bank Training Institute) to strengthen the capabilities of human resources. However, it is not always possible to give thorough training. Especially, there is a lack of specific training for specific jobs. As a result, the employee has to learn things from the job by doing it
practically.
OPPORTUNITY
i. Branch Expansion: Prime Bank Ltd. is growing very quickly all over the country. Besides expanding in the urban areas, PBL has the prospect to open more branches in suburban areas which will eventually enhance the government’s effort at reviving the rural economy. It will also serve the people of those areas better.
ii. Training Facility: Prime Bank Training Institute (PBTI) is supporting the bank by offering in house training courses, workshop and seminar. As the bank has its own training institute to enhance the capability of their human resources, PBL can use this opportunity to train their employees in specific areas and create specialize and expert
people for the bank.
iii. Banking Software: Provide quality service is one of the major goals of PBL. The PBL is still lagging behind in upgrading their software system; the bank has the prospect to select high quality banking software which will make the banking operation fast and smooth.
THREAT
i. Level of Competition: Competition is always a major threat for any organization. In recent years, the number of private bank is increasing. These banks always pose a threat for others by coming up with new product line, innovative technology, quality services etc. Thus the level of competition raises and creates threat for Prime Bank Ltd.
ii. Technological Advancement: With time, technology is getting advanced. However, Prime Bank Ltd. is lagging behind. As the technology is getting advanced, most of the banks, especially private banks are upgrading their operating system to survive in the industry. PBL is still mostly dependent on manual work rather than technology. With time, the advancement of technology is posing a threat for the bank.
iii. Compensating Package: Compared to other private banks of Bangladesh, the compensation package of Prime Bank Ltd. is not attractive. Though the employees of PBL gets fair financial and other benefits, the base pay is not sufficient. This poses a threat of switching banks as other private banks are giving lucrative offer.
iv. Political Unrest: The political unrest as well as the law and order situation of Bangladesh is always a threat for banking industry. Especially, the events of recent years, the corruption level of our country, the poor infrastructure are affecting the national economy. The current economic situation is very likely to worse further. In this case, the
whole banking industry is facing a big threat.
“Credit Risk Management Guidelines Bangladesh Bank”
Guidelines of CRM by Bangladesh Bank
Overview:
Credit risk management in financial terms refers to the process of risk assessment that comes in an investment. Risk often comes in investing and in the allocation of capital. The risk must be assessed so as to derive a sound investment decision. Likewise the assessment of risk is also so crucial in coming up with the position to balance risks and returns.
The Importance of Credit Risk Management for Banking:
The importance of credit risk management for banking is tremendous. Banks and other financial institutions are often faced with risks that are mostly of financial nature. These institutions are often faced with risks that are mostly of financial nature. These institutions must balance risks as well as returns. For a bank to have a large consumer base, it must offer loan products that are reasonable enough. However, if the interest rates in loan products are too low, the bank will suffer from losses. In terms of equity, a bank must have substantial amount of capital on its reserve, but not too much that it misses the investment revenue, and not too little that it leads itself to financial instability and to the risk of regulatory non-compliance. Banks are constantly faced with risks. There are certain risks in the process of granting loans to certain clients. There can be more risks involved if the loan is extended t unworthy debtors. Certain risks may also come when banks offer securities and other forms of investments.
The risks of losses that result in the default of payments of the debtors is a kind of risks that must be expected. Because of the exposure of banks to many risks, it is only reasonable for bank to keep substantial amount of capital to protect its solvency and to maintain its economic stability. The second Basel Accords provides statements of its rules regarding the regulations of bank’s capital allocation in connection with the allocation in connection with the level of risks the bank is exposed to. The greater the bank exposed is risks, the greater the amount of capital must be
when it comes to its reserves, so as to maintain its solvency and stability. To determine the risks that come with lending and investment practices, banks must assess the risks. Credit risk management must play its role then to help banks be in compliance with Basel II Accord and other regulatory bodies.
To manage and assess the risks faced by banks, it is important to make certain estimates, conduct monitoring, and perform reviews of the performance of the bank. However banks are into lending and investing practices, it is relevant to make reviews on loans and to scrutinize and analyze portfolios. Loan reviews and portfolio analysis are crucial then determining the credit and investment risks.
The complexity and emergence of various securities and derivatives is a factor banks must be active in managing the risks. The credit risk management system used by many banks today has complexity; however it can help in the assessment of risks by analyzing the credits and determining the probability of defaults and risks of losses.
Credit risk management for banking is a very useful system, especially if the banks are in line with the survival of banks in the business world.
BANGLADESH BANK’S GUIDELINES FOR MANAGEMENT OF CREDIT RISKS
Bangladesh Bank has provided directional guidelines to the banking sector with a view to improve the Credit Risk Management culture, establish minimum standards for segregation of duties and responsibilities and assist in the ongoing improvement of the banking sector in Bangladesh. These guidelines were prepared and endorsed by the senior credit executives from private sector, foreign and nationalized commercial banks operating in Bangladesh.
Credit Risk
Management is of utmost importance to Banks, and as such, policies and procedures should be endorsed and strictly enforced by the MD/CEO and the Board of the Bank. The guidelines of Bangladesh Bank related with Management of Credit Risks have been organized into the following segments:
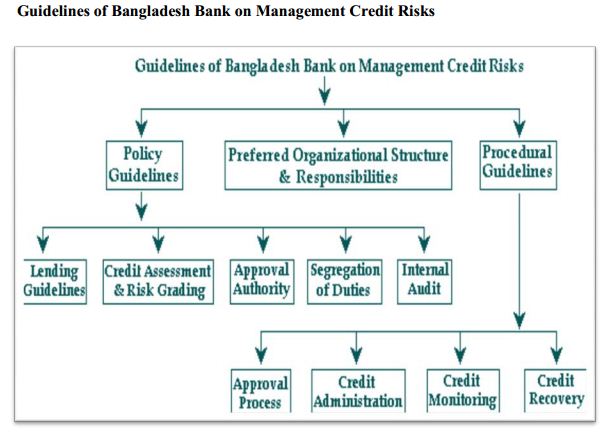
POLICY GUIDELINES:
Policy Guidelines focus on fundamental credit risk management policies that are recommended for adoption by all banks in Bangladesh. The guidelines outline general principles that are designed the implementation of more detailed lending procedures and risk grading systems within individual Banks.
DIFFERENT SEGMENTS OF POLICY GUIDELINES ARE DISCUSSED AS FOLLOWS:
All banks should establish Credit Policies (Lending Guidelines) that clearly outline the management’s view of business development priorities and the terms and conditions that should be adhered to in order for credits to be approved. The lending guidelines should be updated at least annually to reflect changes in the economic outlook and the evaluation of the bank’s credit portfolio. The lending guidelines should be approved by the MD/ CEO and the Board of Directors of the Bank based on the endorsement of the bank’s Head of Credit Risk Management and the Head of Corporate.
Any departure and deviation from the lending guidelines should be explicitly identified in credit applications and a justification for approval provided. Approval of credits that don’t comply with lending guidelines should be restricted to the bank’s Head of Credit or Managing Director/ CEO and the Board of Directors.
The lending guidelines should provide the key foundations for account officers/ relationship managers to formulate their recommendations for approval and should include the following ones:
Industry and Business Segment Focus – The lending guidelines should clearly identify the business/ industry sectors that should constitute the majority of the bank’s credit portfolio. For each sector, a clear indication of the bank’s appetite for growth should be indicated for example Textiles: Grow; Cement: Maintain; Construction: Shrink.
Types of Credit facilities – The type of credits that are permitted should be clearly indicated, such as Working Capital, Trade Finance, Term Loan, etc.
Single Borrower/ Group Limits – Details of the Bank’s single Borrower/ Group limits should be included as per Bangladesh Bank guidelines. Banks may wish to establish more conservative criteria in this regard.
Lending Caps – Bank should establish a specific industry sector exposure cap to avoid over concentration in any one industry sector.
Discouraged Business Types – Banks should outline industries or lending activities that are discouraged. As a minimum the following should be discouraged:
- Military Equipment/ Weapons finance.
- Highly leveraged Transactions.
- Finance of Speculative Investments.
- Logging, Mineral Extraction/ Mining, or other activity that is ethically or environmentally sensitive.
- Lending to companies listed on CIB black list or known defaulters.
- Counterparties in countries subject to UN sanctions.
- Share Lending.
- Taking an Equity Stake in Borrowers.
- Lending to Holding Companies.
- Bridge Loans relying on equity/ debt issuance as a source of repayment.
Credit Facility Parameters – Facility parameters e.g. maximum size, maximum tenor, covenant and security requirements, etc. should be clearly stated. As a minimum the following parameters should be adopted:
- Banks should not grant facilities where the Bank’s security position is inferior to that of any other financial institution.
- Assets pledged as security should be properly insured.
- Valuations of property taken as security should be performed prior to credits being granted. A recognized 3rd part professional valuation firm should be appointed to conduct the valuations.
Cross Border Risk – Risk associated with cross border lending. Borrowers of a particular country may be unable or unwilling to fulfill principle and/ or interest obligations. Distinguished from ordinary credit risk because the difficulty arises from a political event, such as suspension of external payments:
- Synonymous with political and sovereign risk.
- Third world debt crisis. For example, export documents negotiated for countries like Nigeria.
Credit Assessment & Risk Grading:
Credit Assessment – A thorough credit and risk assessment should be conducted prior to the granting of credits and at least annually thereafter for all facilities. The results of this assessment should be presented in a credit application that originates from the Account Officer/ Relationship Manager (RM), and is approved by Credit Risk Management (CRM). The RM should be the owner of the customer relationship, and must be held responsible to ensure the accuracy of the entire credit proposal submitted for approval. RM(s) must be familiar with the bank’s Lending Guidelines and should conduct due diligence on new borrowers, principals and guarantors.
All Banks should have established KYC (Know Your Customer) and Money Laundering guidelines which should be adhered to at all times. Credit Applications should summaries the results of the risk assessment and include, as a
minimum, the following details:
- Amount and Type of Credit(s) proposed.
- Purpose of Credit(s) applied for.
- Credit Structure (Tenor, Covenants, Repayment Schedule, Interest)
- Security Arrangements.
In addition the following risk areas should be addressed:
Borrower Analysis: The majority shareholders, management team, and group or affiliate companies should be assessed. Any issues regarding lack of management depth, complicated ownership structures or inter–group transactions should be addressed and risks mitigated.
Industry Analysis: The key risk factors of the borrower’s industry should be assessed. Any issues regarding the borrower’s position in the industry, overall industry concerns or competitive forces should be addressed and the strengths and weaknesses of the borrower relative to its competition should be identified.
Supplier/ Buyer Analysis: Any customer or supplier concentration should be addressed, as these could have a significant impact on the future viability of the borrower.
Historical Financial Analysis: An analysis of a minimum of 03(three) years historical financial statements of the borrower should be presented. Where reliance is placed on a corporate guarantor, guarantor financial statements should also be analyzed. The analysis should address the quality and sustainability of earnings, cash flow, leverage and profitability.
Projected Financial Performance: Where term facilities are being proposed, a projection of the borrower’s future financial performance should be provided, indicating an analysis of the sufficiency of cash flow to service debt repayments. Credit should not be granted if projected cash flow in insufficient to repay debts.
Account Conduct: For existing borrowers, the historic performance in meeting repayment obligations (trade payments, cheques, interest and principal payments, etc.) should be assessed. Adherence to Lending Guidelines: Credit applications should clearly state whether or not the proposed application is in compliance with the bank’s Lending Guidelines.
Mitigating Factors: Mitigating factors for risks identified in the credit assessment should be identified. Possible risks include, but are not limited to: margin sustainability and /or volatility, high debt load (leverage/ gearing), overstocking or debtor issues; rapid growth, acquisition or expansion; new business line/ product expansion; management changes or succession issues; customer or supplier concentration; and lack of transparency or industry issues.
Credit Structure: The amount(s) and tenor(s) of financing proposed should be justified based on the projected repayment ability and credit purpose. Excessive tenor or amount relative to business needs increases the risk of fund diversion and may adversely impact the borrower’s repayment ability.
Security: A current valuation of collateral should be obtained and the quality and priority of security being proposed should be assessed. Credit should not be sanctioned based solely on security. Adequacy and the extent of the insurance coverage should be assessed.
Name Lending: Credit proposals should not be unduly influenced by an over reliance on the sponsoring principal’s reputation, reported independent means, or their perceived willingness to inject funds into various business enterprises in case of need. Rather, credit proposals and the granting of credits should be based on sound fundamentals, supported by a thorough financial and risk analysis.
Risk Grading – All banks should adopt a credit risk grading system. The system should define the risk profile of borrower’s to ensure that account management, structure and pricing are commensurate with the risk involved. Risk grading is a key measurement of a Bank’s asset quality and as such, it is essential that grading is a robust process. All facilities should be assigned a risk grade. Where deterioration in risk is noted, the Risk Grade assigned to a borrower and its facilities should be immediately changed. Borrower Risk Grades should be clearly stated on Credit proposal.
Approval Authority: The authority to sanction/ approve credits must be clearly delegated to senior credit executives by the Managing Director/ CEO and the Board based on the executive’s knowledge and experiences. Approval authority should be delegated to individual executives and not to committees to ensure accountability in the approval process.
The following guidelines should apply in the approval/ sanctioning of credits:
- Credit approval authority must be delegated in writing from the MD/CEO and Board (as appropriate), acknowledged by recipients and records of all delegation retained in CRM.
- Delegation approval authorities must be reviewed annually by MD/ CEO/ Board.
- The credit approval function should be separate from the marketing/ relationship management (RM) function.
- The role of Credit Committee may be restricted to only review of proposals i.e. recommendations or review of bank’s credit portfolios.
- Approvals must be evidenced in writing, or by electronic signature. Approval records must be kept on file with the Credit applications.
- All credit risks must be authorized by executives within the authority limit delegated to them by the MD/ CEO/ Board. The “pooling” or combining of authority limits should not be permitted.
- Credit approval should be centralized within CRM function. Regional Credit Centers may be established.
Internal Audit: Banks should have a segregated internal audit/ control department charged with conducting audits of all departments. Audits should be carried out annually and should ensure compliance with regulatory guidelines, internal procedures, Lending Guidelines and Bangladesh Bank requirements.
PREFERRED ORGANIZATIONAL STRUCTURE & RESPONSIBILITIES:
The appropriate organizational structure must be in place to support the adoption of the policies. The key feature is the segregation of the Marketing/ Relationship Management/ Administration functions.
Credit approval should be centralized within the CRM function. Regional Credit Centers may be established; however, all applications must be approved by the Head of Credit and Risk Management or MD/ CEO/ Boards or delegated Head Office Credit executives.
Key Responsibilities: The key responsibilities of the above functions are as follows Credit Risk Management (CRM):
- Oversight of the bank’s credit policies, procedures and controls relating to all credit risks arising from corporate/ commercial/ institutional banking, personal banking and treasury operations.
- Oversight of the bank’s asset quality.
- Directly manage all Substandard (SS), Doubtful (DF) and Bad & Loss (BL) accounts to maximize recovery and ensure that appropriate and timely Loan Loss Provisions (LLP) have been made.
- To approve (or decline) within the delegated authority, Credit Applications recommended by RM. Where aggregate borrower exposure is in excess of approval limits, to provide recommendation to MD/CEO for approval.
- To provide advice/assistance regarding all credit matters to line management/RM(s).
- To ensure that lending executives have adequate experience and/or training in order to carry out job duties effectively.
Credit Administration:
- To ensure that all security documentation complies with the terms of approval and is enforceable.
- To monitor insurance coverage to ensure appropriate coverage is in place over assets pledged as collateral, and is properly assigned to the bank.
- To control credit disbursements only after all terms and conditions of approval have been met and all security documentation is in place.
- To maintain control over all security documentations.
- To monitor borrower’s compliance with covenants and agreed terms and conditions and general monitoring of account conduct/ performance.
Relationship Management/ Marketing (RM):
- To act as the primary bank contact with the borrowers.
- To maintain thorough knowledge of borrower’s business and industry through regular contact, factory/ warehouse inspections, etc. RMs should proactively monitor the financial performance and account conduct of borrowers.
- To be responsible for the timely and accurate submission of Credit Applications for new proposals and annual reviews, taking into account the credit assessment requirements.
- To highlight any deterioration in borrower’s financial standing and amend the borrower’s Risk Grade in a timely manner. Changes in Risk Grades should be advised to and approved by CRM.
- To seek assistance/ advice at the earliest from CRM regarding the structuring of facilities, potential deterioration in account or for any credit related issues.
Internal Audit/ Control:
Conducts independent inspections annually to ensure compliance with Lending Guidelines, operating procedures, bank policies and Bangladesh Bank directives. Reports directly to MD/ CEO or Audit Committee of the Board.
Credit Monitoring: To minimize credit losses, monitoring procedures and systems should be in place that provides an early indication of the deteriorating financial health of a borrower. At a minimum, systems should be in place to report the following exceptions to relevant executives in CRM and RM team:
- Past due principal or interest payments, past due trade bills, account excesses and breach of credit covenants.
- Credit terms and conditions are mentioned, financial statements are received on a regular basis and any covenant breaches or exceptions are referred to CRM and the RM team for timely follow–up.
- Timely corrective action is taken to address findings of any internal, external or regulator inspection/ audit.
- All borrower relationships/ credit facilities are reviewed and approved through the submission of credit application at least annually.
- Computer systems must be able to produce the above information for central/ Head Office as well as local review. Where automated systems are not available, a manual process should have the capability to produce accurate exception reports.
Credit Recovery: The Recovery Unit (RU) of CRM should directly manage accounts with sustained deterioration (a Risk Rating of Sub Standard i.e. 6 or worse). Banks may wish to transfer EXIT accounts graded 4–5 to the RU for efficient exit based on recommendation of CRM and Corporate banking. Whenever an account is handed over from Relationship Management to Recovery Unit, a Handover/ Downgrade Checklist should be completed.
The RU’s primary functions are:
- Determine Account Action Plan/ Recovery Strategy.
- Pursue all options to maximize recovery, including placing customers into receivership or
- liquidation as appropriate.
- Ensure adequate and timely loan loss provisions are made based on actual and expected losses.
Credit Risk Management Process of Prime Bank Limited
Overview
Risk is inherent in all types of business. However, for Banks and financial institutions credit risk is considered to be the toughest one. Though Banks and Financial Institutions have been facing difficulties over the years for a multitude of reasons, the major cause of serious banking problems continues to be directly related to lax credit standards for borrowers and counterparties, poor portfolio management or lack of attention to changes in economic or other circumstances that can lead to a deterioration in the credit standing of a bank’s counterparty.
Credit risk is most simply defined as the potential that a borrower or counterparty will fail to meet its obligations in accordance with the agreed terms and conditions. In other words, it is the loss associated with degradation in the credit quality of the borrowers or counterparties. In a Bank’s portfolio, losses stem from outright default due to the inability or unwillingness of the customer or counterparty to meet commitments in relation to lending, trading, settlement and other financial transactions. Alternatively, losses result from reduction in portfolio value arising from actual or perceived deterioration in credit quality. Credit risk emanates from a bank’s on and off balance sheet dealings with an individual, corporate, bank, financial institution or a sovereign. Credit risk may take the following formsIn the case of direct lending: principal and/or interest may not be repaid; In the case of guarantees or letters of credit: funds may not be forthcoming from the constituents upon crystallization of the liability;
In the case of treasury operations: the payment or series of payments due from the counter parties under the respective contracts may not be forthcoming or ceases; In the case of security trading business: funds/securities settlement may not be effected; In the case of cross border exposure: the availability and free transfer of foreign currency funds may either cease or restrictions may be imposed by the sovereign.
Credit Risk Management (CRM) Department
The Credit Risk Management Department shall perform the following duties:
a) Assess risks inherent in the credit proposal sent by Corporate Division and also evaluate proposed facility pricing based on risks, security, structuring and terms and conditions to suit the business condition and to protect Bank’s interest.
b) Compliance to the existing rules and regulations of the Bank and all regulatory authorities and laws of the country and to advise the Corporate Division for rectification, if required.
c) Advise the Corporate Division about changes, if required, in the structure and terms and conditions of the proposed facility.
d) Process credit proposal for approval of the competent authority.
e) Issue sanctions advice for credit facilities or decline.
f) Maintain Limit Sanction Register.
g) Review the performance of the customer on Off-site Basis and prescribe appropriate remedial measures, if required until the loan account becomes a “Special Mention” one.
h) Review/revise risk grading of the customer from time to time based on the “Early Alert Report” and Downgrade Proposal submitted by Corporate Division.
i) Handover loan to the Recovery Department as and when it is degraded to Special Mention or below.
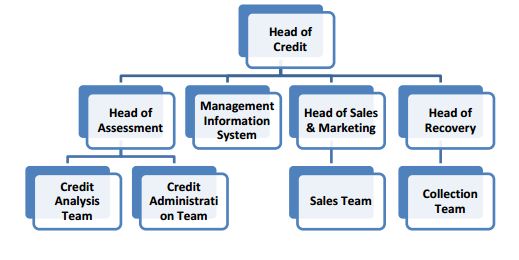
Major Functions of CRM
a) To update Bank’s Credit Policy/Lending Guideline, procedures and control mechanisms related with all credit risks arising from corporate/commercial banking and retail banking etc.
b) To approve/decline credit proposal received from Corporate Division (presently from Branches) within delegated authority and to recommend to the higher authority if it is beyond delegation.
c) To provide advice/assistance regarding all credit matters to Corporate Division/Branches.
d) Periodical review of different types of credits, maintain effective follow-up and supervision and take all possible measures in time to save from classification.
Duties and Responsibilities of CRM:
a) Examine/review credit proposals (new/renewal) sent by corporate division/branches to: Process for approval
Placing credit proposals in the Head Office Credit Committee. Decline credit proposals if they do not meet criteria.
Recommendation credit proposal to Additional Managing Director/Managing Director/EC/ Board for their approval
Prepare facility sanction letter and send copies to:
- Corporate division/Branches
- Credit Administration Division
b) Review on a periodical basis in the light of: Structuring Adequacy of security Pricing and profitability Financial analysis & Form and content Performance Turnover Repayment
c) Review delegated credit approval authorities on an annual basis
d) Review approval procedures of Retail Credit from time to time
e) Review and update bank’s credit manual and credit operating procedures on an annual basis.
f) Conduct industry analysis and detect risk involved with each industry.
Credit Risk Grading
While providing credit facility to a customer, Bank undertakes many risks among which credit risk is considered to be the most important one. As such, an in-depth study should be conducted on the borrower’s creditworthiness which will help the bank to identify all possible risks underlying in a particular credit transaction. A formal evaluation of borrower’s financial health and ability to repay debt obligation is called credit rating which helps the Bank to grade the concerned customer. As such, it is also called credit risk grading. And, risk identified through
credit rating/risk grading is quantified for better understanding and taking appropriate mitigating technique. Besides, it helps the Bank to charge commensurate risk premium on a particular credit facility. Therefore, it is important to accurately measure the risks in a transaction and rate/grade the facility accordingly.
Basic Framework
As per recommendation of the Financial Sector Reform Project (FSRP), Bangladesh Bank made it mandatory for the Banks to conduct a “Lending Risk Analysis (LRA)” in the prescribed format before sanction of a loan which is still in force. Later, Bangladesh Bank instructed all commercial Banks to develop its own credit risk grading system vide its Guidelines on Credit Risk Management. In the said Guideline, Bangladesh Bank provided a sample Risk Grading Model and advised Banks to design their own model in line with that one.
Prime Bank’s Risk Grading Framework
All credit proposals must be supported by a comprehensive risk analysis. It will encompass the following three things: (a) Lending Risk Analysis (LRA), (b) Risk Grading Scorecard and (c) Risk Grading. No proposal can be put up for approval unless there has been a complete written analysis subject to the condition that LRA will be conducted where it is applicable as per Bangladesh Bank Guideline. It is the absolute responsibility of the proposal originating officer to conduct comprehensive risk analysis and affix its result e.g Risk Grading Score, Risk Grade etc in the proposal. He/she will also ensure that all necessary documents/papers/information in support of the proposed risk grading are annexed with the proposal before the facility request is sent to the competent approval authority.
Asset Migration
Risk Grading Model will be used for assessing / measuring risk in the credit exposure taken on a particular customer. It is the key measurement of Bank’s asset quality. Therefore, all facilities will be assigned a risk grade. And, asset portfolio of the Bank will be reviewed quarterly. At each quarter end, Credit Risk Management Unit, Credit Division will report summarizing the migration of the assets with respect to risk grade and place before the management for review. The Management will ensure non-concentration of assets in lower grades.
Credit Monitoring Process
Credit monitoring process starts immediately after disbursement of the facility. Steps involved in monitoring process are as follows:

Step-1: The customer starts repayment of the loan. Simultaneously, Branch relationship officer starts monitoring the loan on on-site basis. If he/she finds any deviation to the terms and conditions of the sanction or borrowers financial health, he/she prepares an Early Alert Report and sends it to the Corporate Banking Division, Head Office. Customer starts repayment of the loan Branch relationship officer starts monitoring the loan on-site basis. Credit Administration Dept. monitors the loan on an off-site basis & reports the findings to the CRM dept. Branch relationship officer regularly reminds the customer as per the of the CRM dept about the irregular repayment, if any.
Step-2: Simultaneously, Credit Administration Department monitors the loan on an off-site basis and reports its findings to the Credit Risk Management Department. On the other hand, Corporate Banking Division informs the Credit Risk Management Department about the customer’s position on the basis of Early Alert Report received from Relationship Officer. It may propose revising the customer’s risk grading. Credit Risk Management Department ultimately decides on the customer and directs Corporate Banking Division to take necessary action.
Step-3: The Relationship Officer regularly reminds the customer as per decision of the Credit Risk Management Department about the irregular repayment, if any and/or breach of contract through letter and/or phone call and/or visit in person.
Findings:
During my internship period I have some findings related with Credit appraisal & credit management system of Prime Bank Limited. The findings are shown in parts of credit appraisal, credit recovery and credit default.
Findings of Credit Appraisal:
- PBL uses credit appraisal technique comprising technical, market, financial, economic, and management & organization analysis.
- Credit appraisal technique is good enough itself, but the problems lie with personnel involves in appraisal process
- Physical verification is not rigorously done for every project that is why the project appraisal techniques do to bring any outstanding results. Sometimes, the amount of loan sanction is more than that is required by the
project because of over invoicing from the part of sponsors.
Findings about the Credit Recovery:
Usually PBL inform the borrowers before 7 days of the scheduled date of payment about his/her next upcoming installment due. Visiting to the borrowers premises is hardly done before the loan is defaulted. The recovery department cannot coerce or make bound to repay the loan because of pressure from political and other higher management. Sometimes sponsors do like to linger the repayment time to have the replacement facilities.
The recovery amount has been increasing for last 5 years, and the variance between recovery targets.
Recommendation:
A banker cannot sleep well with bad debts in his portfolio. The failure of commercial banks occurs mainly due to bad loans, which occurs due to inefficient management of the loans and advances portfolio. Therefore any banks must be extremely cautious about its lending portfolio and credit policy. So far Prime Bank Limited has been able to manage its credit portfolio skillfully and kept the classified loan at a very lower rate —thanks go to the standard and
stringent credit appraisal policy and practices of the bank.
But all things around us are changing at an accelerating rate. Today is not like yesterday and tomorrow will be different from today. Given the fast changing, dynamic global economy and the increasing pressure of globalization, liberalization, consolidation and disintermediation, it is essential that Prime bank limited has a robust credit risk management policies and procedures that are sensitive to these changes.
Prime bank Limited has an efficient & excellent credit management team and performing with great expertise and care. There are some limitations that can be overcome by some measures to make the performance outstanding. There are some suggestions for prime banks credit management team from my observation.
In credit management, it is conventional that proposals of credit facilities must be supported by a complete analysis of the proposed credit. More importance should be given on refund of loans out of funds generated by the borrower from their business activities (cash flow) instead of realization of money by disposing of the securities held against the advance, which is very much uncertain in present context of Bangladesh, where a number of creditors are willful defaulters.
For commercial lending, most of the time clients are unable to submit audited financial statements. The reason is no legal bounding to prepare audited financial statements for all commercial organization. So the credit officer has to face difficulties about the reliability of financial statements submitted. So there should be some flexibility for
proprietorship concerns.
On the basis of that Return on Equity (ROE) model, risk and return of the bank is analyzed. Prime Bank has a good return in the following years from its operation. But Bank should be careful in its riskiness. It should improve its liquid assets to reduce the liquidity risk. It should also try to increase its reserve. Prime Bank’s approving credit is sometimes very conservative. Through it classified loans can be minimized but the credit committee should be more liberal to faster the growth of its credit operation.
In Bangladesh there is no risk measuring Model. Bangladesh Bank should take immediate steps to introduce a risk measuring model by which all Banks can measure the credit risk. Besides Bangladesh bank must enforce all the banks to introduce risk based credit pricing. There should be detailed guidelines in this regard. Bangladesh Bank should create a data storage cell for industry/business data so that while credit risk grading bankers can access those data.
CONCLUSION
Researchers support the fact that economic and financial development of a country are highly correlated to the development of its banking and financial system. The more developed and efficient the banking sector of a country is, the more developed is the business industry sectors will be.
With a view to improving the quality and soundness of loan portfolio, credit risk management methods were updated in 2005. The Bank is now applying a new system of credit risk assessment and lending procedures by striker separation of responsibilities between risk assessments and lending decisions and monitoring functions. The Bank monitors its exposure to particular sectors of economy on an ongoing basis. The Bank has undertaken the changes in
policy of credit risk management, credit risk administration and credit monitoring and recovery in line with the guidelines of Bangladesh Bank, formulated in the last year.
Credit Appraisal system of this bank is pretty efficient. From the beginning of the process of credit appraisal system the credit committee is sufficiently committed and caring. After received loan application from the client, in-depth study of various related documents & gathering of information from different banks and other sources are performed. The loan proposal that is prepared by the credit officer and submitted to the higher authority for approval is the most important part of credit appraisal system because based on this proposal the granting of credit
decision is made. Credit collection process of PBL is also strict and satisfactory.
We hope that PBL will lead by example by continuing its efficient lending policy in keeping the bank’s financial performance indicators at above industrial average and contribute to country’s economic development-thus attaining a middle income status in the world.