Executive Summary
Banks are exposed to five core risks through their operation, which are-credit risk, asset/liability risk, foreign exchange risk, internal control & compliance risk, and money laundering risk. Among these risks management of credit risk gets most attention. Credit risk arises due to the possibility that the borrower may fail to repay the loan. Following the recent global financial crisis, which originated from poor management of credit risk, credit risk is the most discussed topic in banking industry.
Credit risk is one of the most vital risks for any commercial bank. Credit risk arises from non performance by a borrower. It may arise from either an inability or an unwillingness to perform in the pre-commitment contracted manner. The real risk from credit is the deviation of portfolio performance from its expected value. The credit risk of a bank is also effect the book value of a bank. The more credit of a particular is in risk, the more probability of a bank to be insolvent. Therefore, the status of depositor in the bank is at risk and probability of incurring loss from their deposited value.
In my whole report, I was working on the credit risk management practices of Prime Bank Limited. During the preparation of the report, I provide the last five years information of PBL from 2006-2010. In the whole report I also explained detailed credit policy and credit risk management of PBL.
If I make focus on the ratio analyses I found that, PBL was quite good in those selected ratios. The various ratios of PBL indicate that the credit risk in those years was in tolerable limit. In the comparison part, I make compare the credit risk of PBL with the industry average of the present time. In Capital Adequacy Ratio, PBL has shown great consistency and the ratio is more than the Bangladesh Bank requirement of 10%.
Finally, I like to conclude that PBL is one of the most promising and fast growing bank in our country. According to its operational excellence, it is now competing with some renowned foreign commercial banks which are operating in our country. Hopefully it may achieve its target to simplify the banking system in Bangladesh.
Introduction
Risk is inherent in all aspects of a commercial operation. However, for Banks and financial institutions, credit risk is an essential factor that needs to be managed. Credit risk is the possibility that a borrower or counter party will fail to meet its obligations in accordance with agreed terms. Credit risk, therefore, arises from the bank’s dealings with or lending to corporate, individuals, and other banks or financial institutions. Credit risk management needs to be a robust process that enables banks to proactively manage loan portfolios in order to minimize losses and earn an acceptable level of return for shareholders. It is essential for banks having robust credit risk management policies and procedures that are sensitive and responsive to these changes. Bangladesh Bank issued guidelines on the Credit risk management function and it emphasizes on – Policy guidelines, organizational structure and responsibility and procedural guidelines.
Background of the study
Bank is the most important financial institution in the economy. It plays vital role in the economy by providing means of payment and in mobilizing resources. The economic development of a country depends on the development of banking sector to a great extent. The dependence of banking sector in modern economy is increasing day by day because this sector ultimately contributes to run the wheel of development in a more dynamic way. Today’s modern banks are not only provides traditional banking, rather banks are expanding the menu of financial services, banks are making the untouchable service touchable for their customers. The changing and expanding role of banking has made the banking business more complex and competitive. For survival and growth of this business demands creativity, specialization and knowledge and adoption of new technology are used. But technology, creativity, specialization all these cannot support a bank to survive unless the services are marketed in the right track. For this banks need experts who will able to run the business even in against the wind.
Banks provide important capital in the form of loan and advances which are subject to non repayment which is termed as credit risk, the chance that a loan will not be repaid timely. Hence the main concern of the banks is credit risk and its management as credit or loans and advances are the main source of income for them.
Prime Bank Limited is one of the leading banks in this sector which arranges corporate and retail credit. This Bank is very much concerned with the credit risk and its management and has a credit risk management department. The success of the banks is hidden in the proper management of the all the sorts of risk related to the banking business. Hence credit risk and its management has become a vital part of the bank. This report will give us an overall idea about the credit risk and its management as practiced by the Prime Bank Limited
Objective of the Study
There had been some objectives set forward in doing this report so that it can be determined what task I have to perform in the bank. The objective of the report can be divided into two parts-
- Broad Objective:
- To identify the Credit Risk Management Practices of commercial Banks in Bangladesh.
- Specific Objective:
- To have better orientation on credit and credit risk management activities specially credit policy and practices, credit appraisal, credit-processing steps, credit management, financing in various sector and recovery, loan classification method and practices of Prime Bank Limited (PBL).
- To analyze the sector-wise credit and their contribution to GDP
- To analyze various Ratios of Prime Bank Limited.
- To analyze the sound lending policy of Prime Bank Limited.
- To get an overall idea about the performance of PBL.
- To identify and suggest scopes of improvement in credit risk management of PBL.
- To find out the feasibility and practical market issues about new credit risk evaluation model and credit pricing model for the commercial banks in Bangladesh.
Methodology of the Study
A) Sources of data:
There are two sources of data have been used and most of the data are collected from the secondary sources. The sources are-
- Primary Sources:
- Interviewing the bank officials of Credit Risk Management division and
- Official records and observing practical works.
- Secondary Sources:
- Annual reports of PBL Published Booklets/Manuals of the Bank,
- Website of the Bank, Bangladesh Bank, BIBM, CPD, Ministry of Finance etc.
- Various published documents like- Bangladesh Bank’s Monthly Economic Trend, Statistical Yearbook of BBS, Bangladesh Bank Annual Report etc.
B) Data analysis techniques:
This report is an analytical one. Different statistical tools are used in analysis and presentation of data throughout the report. The overall analysis techniques are-
- To find out the relationship among different variables with NPL, GDP, CPI Inflation and Exchange Rate Multiple Regression Analysis is conducted in case of credit risk analysis.
- Ratio calculation to analyze Credit risk scenario.
- Find significant relationship with the Probability of Book Value Insolvency with Risk Index and CAP through Multiple Regression Analysis.
- Microsoft Excel is used in calculating and constructing of graphs
- SPSS Statistical software is used to analyze correlation and multiple regression analysis.
- Tables and Line Graphs are used in presenting data.
This overall process of the study is as follows:
Rationale of the Study
Credit risk is one of the most vital risks for any commercial bank. Credit risk arises from non performance by a borrower. It may arise from either an inability or an unwillingness to perform in the pre-commitment contracted manner. The credit risk of a bank is also effect the book value of a bank. The more credit of a particular is in risk, the more probability of a bank to be insolvent. Therefore, the status of depositor in the bank is at risk and probability of incurring loss from their deposited value. That’s why; I am interested to prepare the report on the basis of Credit Risk Management Practices of the Commercial Banks in Bangladesh.
Scope of the Study
The study would focus on the following areas of Prime Bank Limited.
- Credit Risk Management process.
- The Credit operations
- Portfolio (loans & advances) management of Prime Bank Ltd.
- Preferred Organization structures and responsibilities of Credit Risk management.
- The analyses of some factors related to the credit risk.
Each of the above areas would be critically analyzed in order to determine the efficiency of PBL’s Credit appraisal and Management system.
Limitations of the Study
Though I tried my level best to produce a comprehensive and well-organized report on the Credit Risk Management practices of Prime Bank Ltd., some limitations were yet present there:
- A period of Three months was not sufficient to collect and understand the insights of the overall credit risk management practices of the bank.
- Recent data and information on different activities of PBL was unavailable.
Overview
The word credit comes from the Latin word “Credo” meaning “I believe”. It is a lender’s trust in a person’s/ firm’s/ or company’s ability or potential ability and intention to repay. In other words, credit is the ability to command goods or services of another in return for promise to pay such goods or services at some specified time in the future. Credit risk management is a dynamic field where a certain standard of long-range planning is needed to allocate the fund in diverse field and to minimize the risk and maximizing the return on the invested fund. Continuous supervision, monitoring and follow-up are highly required for ensuring the timely repayment and minimizing the probability of default. Actually the credit portfolio is not only constituted the bank’s asset structure but also a vital factor of the bank’s success. The overall success in credit risk and its management depends on the banks credit policy, portfolio of credit, monitoring, supervision and follow-up of the loan and advance. Therefore, while analyzing the credit risk management of PBL, it is required to analyze its credit policy, credit procedure and quality of credit portfolio.
History of incorporation of The Organization
Prime Bank Limited is a fast growing private commercial bank of Bangladesh. The Bank has already at the top slot in terms of quality service to the customers and the value addition to the shareholders. Prime Bank Ltd. was incorporated under the Companies Act, 1994 on February 12, 1995 and on this day, filed a duly verified declaration in the prescribed form that the condition of section 150(1)(a) to (d) of the said Act, have been compiled with, is entitled to commence business as a public limited company.
Prime Bank Ltd. being a banking company has been registered under the Companies Act 1913 with its registered office at 5, Rajuk Avenue, Motijheel commercial area, Dhaka 1000. Later it was shifted to Adamjee Court Annex building, 119-120, Motijheel Commercial Area, Dhaka-1000. The bank operates as a scheduled bank under banking license issued by Bangladesh Bank, the central bank of the country on April 17, 1995 through opening of its Motijheel branch at Adamjee Court Annex Building, Motijheel commercial area, Dhaka-1000.
The Bank made satisfactory progress over the years after its starting. Despite difficult circumstances it became able to sustain with some achievements. The bank further expected and consolidated its customer base in both of its core business and retail banking. The bank retained its lead position with the capital adequacy ratio of 12.43% as on December end 2002, which is well above the stipulated requirement of 8%. The return on Asset (ROA) was 3.73% well above the industry average.
Commencement of Operation
Prime Bank Ltd. was established on 17th April 1995 with an authorized capital of Tk.1000 million and paid up capital of Tk.100 million (raised to Tk.200 million in 1997) by a group of highly successful entrepreneurs from various fields of economic activities such as shipping, oil, finance, garments, textiles and insurance etc. It is a full licensed scheduled Commercial bank set up in the private sector in pursuance of the policy of the Government to liberalize banking and financial services. The former governor of Bangladesh Bank Mr. Lutfar Rahman Sarkar was the first managing director of the bank. Highly professional people having wide experience in domestic and international banking are managing the bank. The network of branches increased to 120 including 15 SME center and licenses for few more branches are in hand which will be opened soon. Prime Bank Ltd. is the pioneer in providing consumer loans as well as financing to the industries and transport sectors through attractive leasing and hire purchase scheme. Prime is catering both conventional interest based banking and banking under Islamic Sharia Principles. The Islamic banking operations are completely separated from the conventional banking.
Vision Mission and Strategic Properties of Prime Bank Ltd.
“A Bank with a difference” is the motto of Prime Bank Limited. The Bank is prepared to meet the challenge of the 21st century well ahead of time. To cope up with the challenge of the new millennium it has hired experienced and well-reputed banker of the country from the inception. So the Bank defined:
Vision: To be the best Private Commercial Bank in Bangladesh in terms of efficiency, capital adequacy, asset quality, sound management and profitability having strong liquidity.
Mission: To build Prime bank limited into an efficient, market driven, customer focused institution with good corporate governance structure.
Continuous improvement in our business policies, procedure and efficiency through integration of technology at all levels.
Focus of Efforts: “on delivery of quality service in all areas of banking activities with the aim to add increased value to shareholders’ investment and offer highest possible benefits to our customers”
Strategic priorities of Prime Bank Limited: To have sustained growth, broaden and improve range of products and services in all areas of banking activities with the aim to add increased value to shareholders’ investment and offer highest possible benefits to our customers.
Objectives of the Bank
The objectives of the Prime Bank Limited are specific and targeted to its vision and to position itself in the mindset of the people as a bank with a difference.
- To mobilize the savings and channeling it out as loan or advance as the company approve.
- To establish, maintain, carry on, transact and undertake all kinds of investment and financial business including underwriting, managing and distributing the issue of stocks, debentures, and other securities.
- To carry on the Foreign Exchange Business, including buying and selling of foreign currency, traveler’s cheque issuing, international credit card issuance etc.
- To develop the standard of living of the limited income group by providing Consumer Credit.
- To encourage the new entrepreneurs for investment and thus to develop the country’s industry sector and contribute to the economic development.
Key financial indicators – At a Glance (Of last five years)
| Key Financial Data & Key Ratios | |||||
Particulars | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 |
| Interest income | 5199 | 7170 | 9096 | 10831 | 12,023 |
| Interest expenses | 3698 | 5267 | 7126 | 8426 | 7,790 |
| Net interest income | 1500 | 1903 | 1970 | 2405 | 4,234 |
| Non-interest income | 1732 | 2913 | 3808 | 5790 | 5,447 |
| Non-interest Expenses | 1101 | 1559 | 1931 | 2907 | 3,603 |
| Net Non-interest income | 631 | 1354 | 1877 | 2883 | 1,844 |
| Profit before provision and tax | 2131 | 3257 | 3847 | 5289 | 6,078 |
| Provision for loans and assets | 390 | 910 | 1384 | 700 | 540 |
| Profit after provision before tax | 1741 | 2347 | 2463 | 4589 | 5,538 |
| Tax including deferred tax | 689 | 946 | 1232 | 1805 | 2,535 |
| Profit after tax | 1052 | 1401 | 1232 | 2784 | 3,003 |
| Balance Sheet | |||||
| Authorized Capital | 4000 | 4000 | 10000 | 10000 | 10,000 |
| Paid-up Capital | 1750 | 2275 | 2844 | 3555 | 5,776 |
| Total Shareholder’s equity | 3860 | 5273 | 6697 | 11745 | 16,769 |
| Deposits | 54724 | 70512 | 88021 | 106956 | 124,519 |
| Long-term liabilities | 16877 | 15267 | 31044 | 38209 | 47,918 |
| Loans and advances | 45010 | 57683 | 75156 | 89252 | 111,167 |
| Investments | 7844 | 12698 | 23103 | 19934 | 20,484 |
| Property, Plant and Equipment | 412 | 660 | 1375 | 1573 | 1,692 |
| Earning Assets | 55458 | 72798 | 100261 | 109905 | 132,688 |
| Net current assets | 5286 | 1338 | 9962 | 3435 | 7,349 |
| Total assets | 60899 | 79588 | 110437 | 124806 | 152,797 |
| Current ratio | 0.88 | 0.97 | 0.88 | 0.96 | 1.09 |
| Equity Debt ratio | 7.00% | 7.10% | 6.45% | 10.39% | 12.33 |
| Other Business | |||||
| Import | 52639 | 70617 | 91424 | 96452 | 147,704 |
| Export | 41801 | 51316 | 68550 | 76097 | 106,943 |
| Remittance | 15050 | 15905 | 22669 | 26447 | 28,433 |
| Guarantee Business | 5386 | 7033 | 10010 | 13673 | 29,000 |
| Capital Measures | |||||
| Total risk weighted assets | 44324 | 55485 | 72253 | 82710 | 183,747 |
| Core capital (Tier-I) | 3860 | 5261 | 6265 | 9057 | 15,793 |
| Supplementary capital (Tier-II) | 549 | 1122 | 1594 | 3112 | 5,692 |
| Total Capital | 4409 | 6383 | 7859 | 12168 | 21,485 |
| Tier-I capital ratio | 8.71% | 9.50% | 8.67% | 10.95% | 8.60 |
| Tier-II capital ratio | 1.24% | 2.00% | 2.21% | 3.76% | 3.09 |
| Total capital ratio | 9.95% | 11.50% | 10.88% | 14.71% | 11.69 |
| Credit Quality | |||||
| Non performing loans (NPLs) | 367 | 777 | 1323 | 1149 | 1,368 |
| NPLs to total loans and advances(%) | 0.82% | 1.35% | 1.76% | 1.29% | 1.23 |
| Provision for unclassified loans | 545 | 895 | 1040 | 1303 | 1,463 |
| Provision for classified loans | 309 | 478 | 734 | 631 | 642 |
| Share Information | |||||
| Market price per share (Taka) | 529 | 924 | 540 | 653 | 945 |
| No. of shares outstanding(Million) | 17.50 | 22.75 | 28.44 | 35.55 | 57.76 |
| No. of shareholders (actual) | 5262 | 7368 | 9180 | 10339 | 19,748 |
| Earnings per share (Taka) | 60.11 | 61.57 | 43.32 | 78.33 | 56.90 |
| Dividend | 30% | 35% | 25% | 40% | 40% |
| Cash | 0.00% | 10.00% | 0.00% | 10% | 5% |
| Bonus | 30% | 25% | 25% | 30% | 35% |
| Effective dividend ratio | 33.33% | 40.00% | 27.78% | 44.44% | 49.52 |
| Market capitalization | 9253 | 21021 | 15349 | 23212 | 54,572 |
| Net asset value per share (Taka) | 221 | 232 | 235 | 330 | 290 |
| Price earning ratio (times) | 8.80 | 15.01 | 12.46 | 8.34 | 16.60 |
| Key Financial Ratios | |||||
| Operating Performance Ratio | |||||
| Net interest margin on average earning assets | 3.23% | 2.97% | 2.28% | 2.31% | 3.49 |
| Net non-interest margin on average earning assets | 1.36% | 2.11% | 2.17% | 2.72% | 1.52 |
| Earning base in assets (average) | 90.71% | 91.29% | 91.07% | 89.34% | 87.39 |
| Cost income raito | 34.07% | 32.37% | 33.42% | 35.47% | 37.22 |
| Credit deposit raito | 82.25% | 81.81% | 85.38% | 83.45% | 89.28 |
| Cost of funds on average deposits | 8.15% | 8.41% | 8.55% | 8.41% | 6.39 |
| Yield on average advance | 13.52% | 13.96% | 13.69% | 13.18% | 11.92 |
| Return on average assets | 2.05% | 1.99% | 1.30% | 2.37% | 2.16 |
| Return on average equity | 31.55% | 30.68% | 20.58% | 30.19% | 21.06 |
| Other information | |||||
| No of Branches | 50 | 61 | 70 | 84 | 94 |
| No of SME | – | – | – | 5 | 14 |
| No of employees | 1172 | 1400 | 1551 | 1844 | 2,139 |
| No of foreign correspondents | 517 | 553 | 518 | 602 | 621 |
| Average earning assets | 46448 | 64128 | 86530 | 105083 | 121,296 |
| Average total assets | 51203 | 70244 | 95013 | 117622 | 138,802 |
| Average depostis | 45373 | 62618 | 79266 | 97488 | 115,737 |
| Average advance | 38463 | 51347 | 66420 | 82204 | 100,210 |
| Average equity | 3334 | 4566 | 5985 | 9221 | 14,257 |
Table 3.1: Key Financial Indicators of Prime Bank Limited
Corporate Profile
Core Business
PBL focuses on a wide range of financial products and services which include commercial banking through both conventional and Islamic mode, Merchant and Investment Banking, SME & Retail banking, Credit Card and Off-shore Banking. It plays Leading Role in Syndicated Financing. It has expertise in Corporate credit and Trade Finance and made extensive market penetration with continuous growth in Corporate, Commercial and Trade Finance sectors. It has fully owned exchange houses at Singapore and UK focusing on remittance inflow to Bangladesh.
Corporate Ranking
PBL ranked 8th in Dhaka Stock Exchange (DSE) by market capitalization and stood at Tk.54,572 million as at the end of 2010. It has been ranked as 3rd company by DSE-20 Index. Balance Sheet Size of around Tk 306 billion equivalent to USD 4.4 billion. With wide customer base PBL established itself as the Market Leader among the conventional private commercial banks for deposit and advances.
Credit Rating
CRISL upgraded long term rating to PBL to “AA+” from “AA” and reaffirmed short term rating to “ST-1” based on financials up to December 31, 2009 and other relevant quantitative and qualitative information.
LONG TERM | SHORT TERM | |
| Surveillance Rating 2009 | AA+ | ST-1 |
| Surveillance Rating 2008 | AA | ST-1 |
| Overlook | Stable | |
| Date of declaration | May 10, 2010 |
Prime Bank Limited Network
PBL has a large and well distributed network of branches in Bangladesh. It has 104 branches and 15 SME branches covering strategic financial centers. It has 3 Off-shore banking units at different EPZs in Bangladesh. It has fully owned exchange houses at Singapore and UK facilitating inward remittance to Bangladesh. It has active presence in Capital Market through Prime Bank Investment Limited.
Efficient Capital and Strong Asset Quality
PBL has a strong capital base and capital adequacy stands at 11.69 percent of the risk weighted assets against the regulatory requirement of 9 percent. The bank is also well positioned to maintain capital under BASEL-II as it has raised subordinated Bond and issued right shares to strengthen capital base. The bank has a good asset quality and maintaining an NPL ratio below 2 percent.
Focused Business Strategies
The bank is focused on few strategic issues encompassing change in management in the short to long period through the implementation of various policies, processes and activities to ensure continuous, sustainable and qualitative growth, with the sole objective of “InstitutionBuilding”. An effective cluster Management program was implemented. Branch management is now being continually exposed to mature thoughts and ideas through Mentors resulting in qualitative improvement of their business and operational activities. Organizational and structural changes were made in managing the bank’s operations more effectively. Business units like corporate/commercial, Retail, SME, Cards were restructured and established to provide sharper business focus to each of these revenue earning sources. Credit approvals, quality and recovery departments were strengthened and separated from business sales to facilitate faster growth and maintain quality simultaneously. Support services to ensure greater customer satisfaction with a wider range of products and services are implemented. New departments like Alternate Delivery Channels, cards back office, call centers, operational support were established
Overview
Credit planning implies efficient utilization of scarce (loanable fund) to generate earning for the bank. Constituents of credit planning are: forecasting of loanable fund likely to be available in a particular period of time and allocation of the same amongst alternative avenues in a prudent way. Credit planning has got a serious importance because –Loanable fund comes out of deposit mobilized from the people. So safety of people’s money should be ensured carefully. Unplanned lending may create harm in two ways; firstly, excess lending may create liquidity crisis for the bank. Secondly, too much conservative lending may make the loanable fund idle. Idle but cost bearing fund again incurs operating cost for the bank. Excess liquidity led by unplanned inadequate lending push the profitability to decline. Planned credit helps to maintain conformity with the national priority. Unplanned credit may upset the total economic stability from macro point of view either by making inflation or deflation.
Loan Products of PBL
Depending on the various nature of financing, all the credit facilities have been brought under two major groups: (a) Funded Credit and (b) Non-funded Credit. Under non-funded credit, there are basically two major products namely Letter of Credit and Letter of Guarantee.
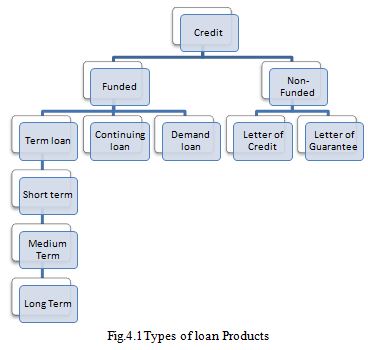
Funded Credit Products
Under Funded Credit, there are the following products:
Loan (General): Short, Medium & Long term loans allowed to individual/firm/industries for a specific purpose but for a definite period and generally repayable by installments fall under this type. These are mainly allowed to accommodate financing under the categories (I) Large & Medium Scale Industry and (ii) Small & Cottage Industry. Very often term loans for (I) Agriculture & (ii) Others are also included here.
Housing Loan (Commercial): Loans allowed to individual/enterprises for construction of house for commercial purpose only fall under this type. The amount is repayable by monthly/quarterly installments within a specified period.
Home Loan: Loans allowed to individuals for purchase of apartment or construction of house for residential purpose fall under this type. The amount is repayable by monthly installments within a specified period.
House Building Loan (Staff): Loans allowed to our Bank employees for purchase of apartment/construction of house shall be known as House Building Loan (Staff) or HBL (Staff).
Other Loans to Staff: Loans allowed to employees other than House Building Loan are grouped under Staff Loan (Gen).
Cash Credit (Hypo): Advances allowed to individual/firm for trading as well as wholesale purpose or to industries to meet up the working capital requirements against hypothecation of goods as primary security fall under this type of lending. It is a continuous credit. It is allowed under the categories (I) “Commercial Lending” when the customer is other than an industry and (ii) “Working Capital” when the customer is an industry.
Cash Credit (Pledge): Financial accommodations to individual/firms for trading as well as for whole-sale or to industries as working capital against pledge of goods as primary security fall under this type of advance. It is a continuous credit and like Cash Credit (Hypo) allowed under the categories (i) “Commercial Lending” and (ii) Working Capital”.
Hire Purchase: Hire Purchase is a type of installment credit under which the customer agrees to take the goods on hire at a stated rental, which is inclusive of the repayment of Principal as well as interest for adjustment of the loan within a specified period.
Lease Financing: Lease Financing is one of the most convenient sources of acquiring capital machinery and equipment whereby a customer is given the opportunity to have an exclusive right to use an asset usually for an agreed period of time against payment of rental. It is a term financing repayable by lease rental.
Consumer Credit Scheme (CCS): It is a special credit scheme of the Bank to finance purchase of consumer durable by the fixed income group to raise their standard of living. The loans are allowed on soft terms against personal guarantee and deposit of specified percentage of equity by the customers. The loan is repayable by monthly installments within a fixed period.
Secured Overdraft (Financial Obligation): SOD (Financial Obligation) is allowed to individuals/firms against financial obligations (FDR, MBDR, Scheme Deposits of our Bank or similar products of other banks). This is a continuous loan having usual maturity period of 1 (one) year and renewable for further periods at maturity.
Secured Overdraft (General): SOD (General) is allowed to individuals/firms for miscellaneous purpose. This is a continuous loan having usual maturity period of 1 (one) year and renewable for further periods at maturity
Secured Overdraft (Work Order): Advances allowed against assignment of work order for execution of contractual works falls under this type. This advance is generally allowed for a definite period and specific purpose. It falls under the category “Others”.
Secured Overdraft (Export): Advance allowed for purchasing foreign currency for payment of Back to Back L/C liability where the exports do not materialize before due the date of import payment. This is categorized as “Export Finance”.
Payment against Documents: Payment made by the Bank against lodgment of shipping documents of goods imported through L/C falls under this type. It is an interim advance connected with import and is generally liquidated against payments usually made by the customer for retirement of the documents towards release of imported consignment from the customs authority. It may fall under anyone of the category “Agriculture/Export Finance/Commercial Lending/Others”.
Loan Against Import: This is funded credit facility allowed for retirement of shipping documents and release of goods imported through L/C taking effective control over the goods by pledge in godowns under Bank’s lock & key. This is a temporary advance connected with import which is known as post-import finance and falls under the category “Commercial Lending”.
Loan Against Trust Receipt: Advance allowed for retirement of shipping documents and release of goods imported through LC falls under this type. The goods are handed over to the importer on trust with the arrangement that sale proceeds will be deposited to liquidate the loan account within the stipulated time.
Inland Bills Purchased: Payment made through purchase of inland bills/cheques denominated in local currency to meet urgent requirement of the customer of other than Export Sector falls under this type. This temporary advance is adjustable from the proceeds of bills/cheques purchased and sent for collection. It may fall under any of the categories.
Export Cash Credit (ECC): Funded credit facility allowed to a customer for export of goods falls under this type and is categorized as “Export Cash Credit”. The advances must be liquidated out of export proceeds within 180 days.
Packing Credit (P.C.): Advance allowed to a customer against bills under BTB L/C and/or firm contract for processing/packing of goods to be exported falls under this type and is categorized as “Packing Credit”. Packing Credit must be adjusted from proceeds of the relevant exports within 180 days. It falls under the category “Export Credit”.
Foreign Documentary Bills Purchased: Payment made to a customer through purchase/negotiation of a Foreign Documentary bill falls under this type. This temporary advance is adjusted from the proceeds of the shipping/export documents. It falls under the category “Export Credit”.
Inland Documentary Bills Purchased: Payment made against documents representing sell of goods to Local export oriented industries which are deemed as exports and denominated in Foreign Currency falls under this type. This temporary liability is adjustable from proceeds of the Bill.
Foreign Bills Purchased: Payment made to a customer through Purchase or Foreign Currency Cheques/Drafts falls under this type. This temporary advance is adjustable from the proceeds of the cheque/draft.
Non-funded credit products
Under non-funded credit products there are-
Letter of Credit
- Letter of Credit-Sight
- Letter of Credit-Deferred
- Back to Back L/C
Letter of Guarantee
- Advanced Payment Guarantee
- Bid Bond
- Performance Bond
- Payment Bond
- Custom Guarantee
- Retention Money Guarantee
- Shipping Guarantee
- Guarantee-Others
Islamic Banking investment products
- Bai-Murabaha
- Bai-Salam
- Quard-e-Hasana
- Bai-Muajjal
- Izarah
- HPSM (Hire Purchase Under Shirkatul Melk)
- Musharaka
Term Investment-Retail:
- Doctors Investment Scheme
- Travel Investment
- Car Investment
Investment Against Salary
- CNG Conversion Investment
- Education Investment
- Hospitalization Investment
- Swapna Neer (Home Investment)
- Any Purpose Investment
- Household Durable Investment
Product Parameters
There are some parameters of the loan products which can be termed as characteristics. They are as follows:
Maximum Size: Maximum size of any funded credit facility to a single customer shall at best be 15% of the total capital of the Bank. And maximum size of any non-funded credit facility shall at best be 35% of total capital and 50% of the total capital of the Bank for the non-export sector customers and export sector customers respectively.
Maximum Tenor: Maximum tenor for any continuous loan shall be 1 (one) year which is renewable at maturity or within the validity period upon satisfactory performance of the customer. And period of any term loan shall be fixed on case to case basis considering repayment capacity, projected cash flow etc.
Security: Bank will try to have as much security coverage as possible against each and every credit facility sanctioned to the customers. Security requirement will be determined on case to case basis based on customer’s business strength, level of risk bank is undertaking. However, Bank will always prefer to have security equivalent to 1.25 times of the total funded limit except for the following products: SOD (FO), SOD (WO), SOD (EM), SOD (EDF), SOD (CI), FDBP, IDBP, Bid Bond. Security may be in the following forms:
i) Bank deposit
ii) Gold / gold ornaments
iii) Government Bond / Sanchayapatra
iv) Guarantee given by Government or Bangladesh Bank
v) Bank Guarantee
vi) Pledgeable goods
vii) Land and Building
viii) Share
ix) Stock
x) Machinery and Equipment
xi) Charge on the fixed and floating asset
xii) Paripassu Charge on fixed and floating assets
xiii) Corporate Guarantee of another company backed by Board Resolution.
xiv) Personal Guarantee
xv) Bill or Receivables
xvi) Ownership of vehicles / assets
xvii) Life Insurance Policy.
xviii) Post Dated Cheque
xix) Trust Receipt
xx) Others as deemed acceptable by the approving authority
Pricing Loan Products
The process followed by the PBL as guided by the BB regarding the pricing of the loan products are discussed below:
Loan Pricing
Credit facilities to the customer are the prime source of the Bank’s income. More specifically, interest from loans accounts the lion share of the total revenue of the Bank. On the other hand, financial market of our country is apparently very competitive due to participation of 49 (forty nine) banks in our small financial market. As such, pricing is very crucial for business growth of the Bank. Prime Bank Limited has been fixing/re-fixing price of different credit facilities from time to time considering changes in the market condition.
Basis of Pricing
Price of all credit facilities will be fixed based on the level of risk and type of security offered. Rate of interest will be the reflection of risk inherent in a particular transaction i.e. the higher the risk, the higher the rate of interest. Therefore, loan pricing will be directly correlated with the risk grade of the customer.
Types of Rate
Usually, Bank will charge fixed interest rate which will be subject to changes by the Management. In this respect, all loan contracts will contain a provision to the effect that rate of interest is subject to changes by the Management. And, interest rate will be revised as and when a significant fluctuation occurs in the cost of fund of the Bank due to volatility of interest rate in the market. The Bank will charge floating interest only in SOD (EDF). In all other cases, fixed interest rate will be applied.
For fixed interest rate, the Board of Directors will fix a Band for a particular Sector/Industry/Product. Customers will be allowed a fixed rate within that band. Any deviation from the approved interest rate band will be mentioned in the Credit Assessment Form with proper justification. The Managing Director may sanction a credit facility at a rate within the Band. However, other executives will exercise their delegated authority to sanction credit facility at the highest rate of the approved Band.
Revision of Rates
The Management of the Bank will continuously monitor interest rate situation in the market and discuss the same in the Asset Liability Management Committee (ALCO) meeting at least once in a month. As per decision of the Asset Liability Management Committee (ALCO), the Management of the Bank may approach the Board of Directors to revise rate of interest, commission, charges etc.
Loan Approval Process
Like every other banks the PBL follows the loan approval process. This process is consists of some steps which describes the ways in which the loan or credit asked from the bank is approved. The process is discussed in the following paragraphs.
Step-1: A potential customer collects prescribed Credit Application Form from the Relationship Officer of Branch/Regional Corporate Banking Department/Corporate Banking Division, Head Office/Web address of the Bank. Later, he/she submits the filled in Credit Application Form along with necessary papers and documents.
Step-2: The Relationship Officer scrutinizes the Credit Application Form and other documents submitted by the customer and make a preliminary assessment on creditworthiness of the potential borrower. He/she collects further information from the customer if it is felt necessary. And, if he/she finds the proposal not bankable, he/she sends a refusal letter to the customer immediately. On the other hand, if he/she finds it acceptable, he/she forwards the application to the concerned Relationship Manager.
Step-3: The Relationship Manager, singly or jointly with Relationship Officer, visit the customer’s business premise and try to acquire proper understanding about the business position, actual credit requirement, repayment capacity etc. Besides, he/she negotiates with the customer about the structure of the proposed credit facility. Apart from this he/she assesses the value of the security to be offered and prepares Valuation Report. Finally, the Relationship Manager summarizes all these information in the Pre-sanction Inspection Report/Call Report/Visit Report in the Bank’s prescribed format in which he/she recommends for some specific credit facility for the customer.
Step-4: The Relationship Manager sends the Pre-sanction Inspection Report to the Corporate Banking Division, Head Office or to the Regional Corporate Banking Department, if any. The Head of Corporate Banking Division/Regional Corporate Banking Department assesses the credit proposal. He/she might contact with the Relationship Manager or directly to the customer for any query. Finally, if he/she decides to refuse the proposal or to proceed further with the proposal and communicates his /her decision to the Relationship Manager.
Step-5: If the Head of Corporate Banking Division/Regional Corporate Banking Department refuses, the Relationship Manager sends a refusal letter to the customer. If he/she is positive, the Relationship Officer collects duly filled in CIB Inquiry Form from the customer and submits it to the Credit Information Bureau of Bangladesh Bank for latest CIB Report through Credit Administration Department, Head Office. Everything may stop here if CIB report shows that the customer has classified liability in its name and/or in the name of its sister concern(s). In that case, the customer is regretted accordingly.
Step-6: Meanwhile, the Relationship Officer rates the customer as per Risk Grading System of the Bank. Finally, the Relationship Manager originates a formal Credit Proposal in which the Head of Corporate Banking Division affixes his/her recommendation regarding the proposal.
Step-7: The Head of Corporate Banking Division, Head Office then forwards the proposal to the Credit Risk Management Department, Credit Division along with necessary papers. The concerned Credit Officer conducts in-depth Credit Analysis (Due Diligence) and affixes his/her comments/observations/findings.
Step-8: The Credit Officer places the proposal along with his/her comments/observations/findings before the Head of Credit/Head Office Credit Committee. The Head of Credit may contact with the Head of Corporate Banking for his/her queries. He/she may also express his/her reservation on a particular issue/risk and ask the Head of Corporate Banking to clarify his/her position and/or risk minimization technique(s). Finally, he might decline the proposal. And, if he/she is fully satisfied he/she may approve the facility if it is within his/her delegated authority. If it is beyond his/her delegated authority, he /she would recommend the proposal to the Managing Director.
Step-9: The Managing Director may decline the proposal if he/she is not satisfied about the proposal. If he/she is satisfied and if it is within his/her delegated power, he/she approves the proposal. If the proposal exceeds his/her delegated authority, he/she recommends it to the Executive Committee of the Board of Directors, which has the supreme authority to sanction any loan.
Step-10: If the facility is approved (whoever is the approval authority), the Credit Risk Management Department of Credit Division issues sanction letter to the Corporate Banking Division/Branch along with a Documentation Check List which clearly spells out what are the documentation formalities required to be completed before disbursement. A copy is sent to Credit Administration Department, Credit Division.
Step-11: The Corporate Banking Division/Branch then issues sanction letter to the customer in line with the letter of Credit Risk Management Department and requests the customer to complete documentation formalities.
Credit Approval Authority
Each and every bank, as per the requirements of BB, must delegate authority of approving loans of certain limit. The authority clearly indicates who can approve the loan and up to what amount and who will be responsible for the approval of the loan. The detail of the practices of the PBL is discussed here.
Delegation of Approval Authority:
Credit approval authority to the proper body and/or executive is a precondition for ensuring smooth and transparent credit operation in the Bank. Since inception, credit approval authority has been delegated to different tiers of both the Board of Directors and the Management. Authorities who enjoy delegation of business power i.e credit approval authority are as follows:
- The Board of Directors
- The Executive Committee of the Board
- The Managing Director
- Executives working as head of Branches.
Credit Approval Authority
Credit approval authority may be delegated to the following body/Executive:
- The Board of Directors
- The Executive Committee of the Board
- Different tier of the Management
The Board of Directors: The Board of Directors will have the authority to sanction any loan for the amount not exceeding the regulatory limit the Bank can provide to a single customer. Besides, all proposals for waiver of interest, commission, charges etc and principal must be approved by the Board of Directors. Any proposal for reduction of rate of interest by more than one percent from minimum level of approved interest rate band must be approved by the Board.
The Executive Committee of the Board: The Executive Committee of the Board of Directors may sanction any loan for the amount not exceeding the regulatory limit the Bank can provide to a single customer. However, it will not have the authority to approve any proposal for waiver of interest, commission; charges etc and principal must be approved by the Board of Directors. Any proposal for reduction of rate of interest by one percent or less from the minimum level of approved interest rate band may be approved by the Executive Committee of the Board. Any proposal beyond the delegated authority of the Managing Director will be placed before the Executive Committee of the Board for approval.
The Management: Different tier of the Management may be delegated credit approval authority to ensure timely disposal of the credit proposals at root level. In the Management, the following executives may be delegated credit approval authority:
- The Managing Director
- The Deputy Managing Director supervising Credit Division
- Executives working at Credit Risk Management Unit, Credit Division
- Executives working as Head of Branches
Composite Limit
Credit Limit to a single customer comprising of more than one facility/product will be treated as a Composite Limit. Different tier of the Management may be delegated authority to sanction a composite credit limit to a customer which the respective executive will exercise after complying with all preconditions set in different chapters of this policy document and in the relevant circulars in force. Specially, any executive having delegated authority to sanction a composite limit will exercise this provided that the subject composite limit is covered by collateral security having forced sale value which is at least 1.25 times of the total funded limit. However, the executives having approval authority may sanction following facilities without taking collateral security within their authority: SOD (FO), SOD (WO), SOD (EM), SOD (EDF), SOD (CI), FDBP, IDBP, Bid Bond and the Managing Director may sanction following facilities without taking collateral security within his authority: SOD (FO), SOD (WO), SOD (EM), SOD (EDF), SOD (CI), FDBP, IDBP, LIM, LTR and all non-funded facilities. Different tiers of the Management may be delegated the following authority for approving composite credit limit:
Fig. in Lac Tk
| Sl. No | Designation | Authority to be delegated | Maximum Total | |
Funded | Non-funded | |||
| 1. | Managing Director | 250.00 | 300.00 | 300.00 |
| 2. | Deputy Managing Director | 200.00 | 250.00 | 250.00 |
| 3. | Senior Executive Vice President | 150.00 | 200.00 | 200.00 |
| 4. | Executive Vice President | 100.00 | 150.00 | 150.00 |
| 5. | Senior Vice President | 75.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| 6. | Vice President | 50.00 | 80.00 | 80.00 |
| 7. | Senior Assistant Vice President | 40.00 | 60.00 | 60.00 |
| 8. | Assistant Vice President | 25.00 | 50.00 | 50.00 |
Credit Risk Management (CRM) Department
The Credit Risk Management Department shall perform the following duties:
a) Assess risks inherent in the credit proposal sent by Corporate Division and also evaluate proposed facility pricing based on risks, security, structuring and terms and conditions to suit the business condition and to protect Bank’s interest.
b) Compliance to the existing rules and regulations of the Bank and all regulatory authorities and laws of the country and to advise the Corporate Division for rectification, if required.
c) Advise the Corporate Division about changes, if required, in the structure and terms and conditions of the proposed facility.
d) Process credit proposal for approval of the competent authority.
e) Issue sanctions advice for credit facilities or decline.
f) Maintain Limit Sanction Register.
g) Review the performance of the customer on Off-site Basis and prescribe appropriate remedial measures, if required until the loan account becomes a “Special Mention” one.
h) Review/revise risk grading of the customer from time to time based on the “Early Alert Report” and Downgrade Proposal submitted by Corporate Division.
i) Handover loan to the Recovery Department as and when it is degraded to Special Mention or below.
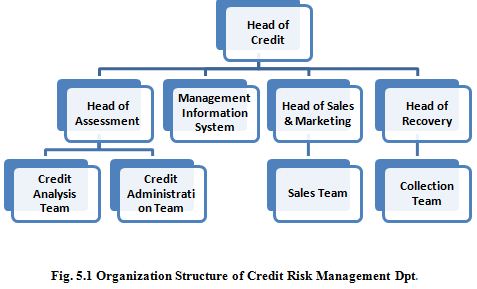
Major Functions of CRM
a) To update Bank’s Credit Policy/Lending Guideline, procedures and control mechanisms related with all credit risks arising from corporate/commercial banking and retail banking etc.
b) To approve/decline credit proposal received from Corporate Division (presently from Branches) within delegated authority and to recommend to the higher authority if it is beyond delegation.
c) To provide advice/assistance regarding all credit matters to Corporate Division/Branches.
d) Periodical review of different types of credits, maintain effective follow-up and supervision and take all possible measures in time to save from classification.
Credit Risk Review and Monitoring Process
The credit review and monitoring process of PBL mainly based on the risk grading and its review. The overall process is discussed here.
Credit Risk Grading
While providing credit facility to a customer, Bank undertakes many risks among which credit risk is considered to be the most important one. As such, an in-depth study should be conducted on the borrower’s creditworthiness which will help the bank to identify all possible risks underlying in a particular credit transaction. A formal evaluation of borrower’s financial health and ability to repay debt obligation is called credit rating which helps the Bank to grade the concerned customer. As such, it is also called credit risk grading. And, risk identified through credit rating/risk grading is quantified for better understanding and taking appropriate mitigating technique. Besides, it helps the Bank to charge commensurate risk premium on a particular credit facility. Therefore, it is important to accurately measure the risks in a transaction and rate/grade the facility accordingly.
Credit Risk Grading
To assess the borrower’s creditworthiness, an in-depth study should be conducted that will help the bank to identify all possible risks underlying in a particular credit transaction.
Basic Frame Work:
Bangladesh Bank made it mandatory for the Banks to conduct a “Credit Risk Grading (CRG)” in the prescribed format before sanction of a loan. In the said Guideline, Bangladesh Bank provided a sample Risk Grading Model and advised Banks to design their own model in line with that one.
Credit Administration
Objectives:
- To separate documentation and disbursement activity from credit approval process.
- To ensure discipline in Credit Management.
Duties and Responsibilities:
- Documentation: To ensure that security documents are prepared in accordance with approval terms and are legally enforceable.
- Disbursement: To allow disbursements under loan facilities only after completion of all documentation formalities. The branches shall send a copy of Certificate of Documentation (Check list) to Credit Administration Department, Head Office seeking approval for disbursement. In respect of business credit facilities allowed by the Head of branch under the business power delegated to him, Certificate of documentation (check list) alongwith a copy of sanction advice to be also sent to the Credit Administration Department for disbursement authority. They shall send it by fax followed by mail. The Credit Administration Department shall promptly response for advising about disbursement preferably on the same day. If disbursement authority is given to the Branch with some exception i.e. incomplete documentation with the undertaking of the Head of Branch to get it completed within a given time frame having approval from the competent authority, the Credit Administration Department shall continuously follow-up with the concerned Branch to ensure completion of the documentation within the given time frame. In the cases of Large Loan the representative of Credit Administration Department may visit the Branch to verify the status of documentation.
- Custodial Duty: To ensure safekeeping of all security documents. Presently, the document files shall be preserved by the branches under joint custody. Credit Administration, HO shall supervise, control and monitor the custodial matter.
- CIB Related Function: To collect CIB report of the borrower as and when asked by the Corporate Division/branches. They shall submit CIB statement to Bangladesh Bank and perform all CIB related activities.
- Compliance: To prepare and submit all required Bangladesh Bank returns in the correct format in a timely manner. To ensure that all Bangladesh Bank circulars/regulations are maintained centrally, and advised to all relevant departments to ensure compliance.
- Enlistment: To enlist and manage all third party service providers (Surveyors/valuers, lawyers, insurers, CPAs etc.) and review their performance on an annual basis.
- Others: To prepare all monthly statements as required by the Management.
Recovery Process
The recovery department is responsible for the recovery of the loan. The Recovery Department of Credit Division manages accounts with sustained deterioration (a Risk Grade of Sub-Standard (6) or worse). Sometimes, as per recommendation of the Credit Risk Management Department and Corporate Banking Division the Management decides to transfer some EXIT accounts graded 4-5 to the RU for efficient exit. Whenever an account is handed over from Corporate Banking Division/Relationship Management to RU, a Handover/Downgrade Checklist is prepared. Down grading process is done immediately and is not postponed until the annual review process.
The RU’s primary functions are to:
- Determine Account Action Plan/Recovery Strategy
- Pursue all options to maximize recovery, including placing customers into receivership or liquidation as appropriate.
- Ensure adequate and timely loan loss provisions are made based on actual and expected losses.
- Regular review of grade 6 or worse accounts.
- Management of classified loans and special mention accounts.
- Waiting off B/L loan accounts and related works with the approval of the Board.
The recovery of problem loans is a dynamic process, and the associated strategy together with the adequacy of provisions is regularly reviewed.
NPL Account Management
All NPLs is assigned to Account Manager(s) within the Recovery Department, who is responsible for coordinating and administering the action plan/recovery of the account, and serves as the primary customer contact after the account is downgraded to substandard. The Recovery Department sought assistance from Corporate Banking/Relationship Management if required to ensure that appropriate recovery strategies are in force.
Account Transfer Procedure
Within 7 days of an account being downgraded to substandard (grade 6), a Request for Action (RFA) and a handover/Downgrade Checklist is prepared by the RM and forwarded to Recovery Department for acknowledgment. The account is assigned to an account manager within the Recovery Department, who will review all documentation, meet the customer, and prepare a Classified Loan Review Report (CLR) within 15 days of the transfer. The CLR is approved by the Head of Credit, and copied to the Head of Corporate Banking and to the Branch/office where the loan proposal was originated. This initial CLR highlights any documentation issues, loan structuring weaknesses, proposed workout strategy, and should seek approval for any loan loss provisions that are necessary.
Recovery Departments ensures that the following is carried out when an account is classified as Sub Standard or worse:
- Facilities are withdrawn or repayment is demanded as appropriate. Any drawings or advances should be restricted, and only approved after careful scrutiny and approval from appropriate executives within CRM.
- CL report is updated according to Bangladesh Bank guidelines and the borrower’s Risk Grade is changed as appropriate.
- Loan loss provisions are taken based on Forced Sale Value (FSV) of the underlying collaterals.
- Loans are rescheduled in conjunction with the Loan Rescheduling Guidelines of Bangladesh Bank which are in force. Any rescheduling should be based on projected cash flow and should be strictly monitored.
- Prompt legal action is taken if the borrower is non-cooperative.
Non-Performing Loan (NPL) Monitoring
On a quarterly basis, a Classified Loan Review (CLR) is prepared by the Recovery Department Account Manager to update the status of the action/recovery plan, review and assess the adequacy of provisions, and modify the bank’s strategy as appropriate. The Head of Credit approves the CLR for NPLs up to 15% of the banks capital, while MD’s approval is required for NPLs in excess of 15%. The CLR’s for NPLs above 25% of capital is approved by the MD/CEO, with a copy presented before the Board of Directors.
Strengths of Prime Bank Limited:
- A powerful strategy supported by good corporate governance to increase shareholders value by being efficient, professional transparent and accountable to society and environment.
- PBL has strong brand image as it has won the prestigious ICAB award for being the best bank in Bangladesh and “A” graded bank according to the CAMEL rating.
- Products and services are as diversified as the market segment demands and the customer group range from individuals, big corporate clients, NGOs to Non residents.
- PBL has strong capital position.
- The asset and liability committee (ALCO) of the bank maintains a satisfactory trade-off between liquidity and profitability.
- The bank is able to achieve higher growth of loans and deposit than the industry rate.
- Prime bank limited has strong balance sheet with favorable ROE and ROA.
- Low non-performing assets or classified loans of the bank signify strengths in credit customer selection.
- The bank has covered all the global locations of homebound remittance.
- The bank has now a network of 89 branches throughout the country.
- The quality of asset is one of the strong areas of operation of PBL.
- Many of the branches of PBL are under CBS T24. This is helping to minimize the errors.
- PBL has well diversified asset portfolio to retail, SME and capital market.
- PBL has a good credit rating of AA which is rated by Credit Rating and Information Services Limited (CRISL).
Weaknesses of Prime Bank Limited:
- All of the branches of PBL are still not under the CBS T24. This lacking is creating operating inefficiency such as human error, fraud and forgeries.
- The junior level management of PBL is not as efficient as the mid and top level management. This may be because of the lack of proper training to the junior and training officer.
- Risk management of lending portfolio often require stress testing which are based on sophisticated mathematics tools and cannot solely be dependent on existing MIS. The level of technology in banking industry is yet acquiring that sophistication.
- the employees of the branches which are under T24 are facing some sort of problem to cope up with the new software that is why it is taking more time to serve a customer.
- The ATM booths owned by the PBL are not sufficient in comparison to the other banks.
- PBL has lack of manpower to serve the growing customer demand.
Opportunities of Prime Bank Limited:
PBL took a strategic shift towards developing and expanding the SME financing which has received considerable attention of policy makers.
Implementation of world class CBS T24 in number of branches will reduce fraud and forgeries and other operating risks arising from human error.
this bank has establish remittance arrangement with 24 leading exchange companies and banks including the global money transfer agency Western Union in 2007.
The bank introduced direct selling service recruiting highly trained and customer focused professionals.
Finance Act of 2007-08 has withdrawn the withholding tax on purchases by credit card and it is expected that credit card business will expand rapidly in near future.
Threats of Prime Bank Limited:
- Changes in general economic condition resulting from calamities and political disturbance.
- The bank is now facing increasing interest sensitive customer who are demanding higher rate of return.
- Changes in government policy –
- Increase in tax, VAT on banking services,
- increase in corporate tax rate,
- Increase in CRR and SLR of the banks,
- Withdrawal of incentives given to some thrust sectors which may make the project slow moving,
- Directive to reduce the lending rates to finance essential items,
- Increase in provisioning requirement would reduce the ROA and ROE,
- Reducing the margin ratio for investment accounts.
- Volatility in interest rate.
- Introduction of compliance issues raised by the international forums which is likely to affect the export growth.
- The rising price of oil and other importable items have exerted pressure on dollar which has squeezed the exchange and fee earning of the bank.
Comparison of PBL with Industry Norm
Here in this section I have tried to provide a brief idea at a glance on how PBL is performing in terms of some selected ratio compare to the other banks in the industry. Here I have taken the averages of Private Commercial Banks ratios which are available.
Capital Adequacy Ratio
The capital adequacy ratio is measured by the ratio of banks capital to risk weighted asset. This ratio indicates the bank’s safety position to meet up the depositor demand in case any emergency
year | PBL | PCBs |
2006 | 9.95% | 9.80% |
2007 | 11.50% | 10.60% |
2008 | 10.88% | 11.40% |
2009 | 14.71% | 12.10% |
2010 | 11.69% | 11.30% |
From the above table we can see that PBL is performing well compare to the Industry average in terms of Capital Adequacy Ratio. Particularly in the year 2009 when industry average was 12.1% the PBL had maintained a CAR of 14.71%, the reason might be the global financial crisis going on that period.
The return on asset
The return on asset measures an enterprise’s overall profitability of assets. The more the ROA the greater the Profitability.
| year | PBL | PCBs |
2006 | 2.05 | 1.1 |
2007 | 1.99 | 1.3 |
2008 | 1.3 | 1.4 |
2009 | 2.37 | 1.6 |
2010 | 2.16 | 1.8 |
From the above table wee can see that fro year 2006 to 2010 PBL has earned greater ROA than the industry average. In year 2007 and 2008 PBL was not earning well but was very close to the industry averages.
NPL to Loan Ratio
Non Performing loan means the loans that are going to be or about to be uncollectable because of several reasons. The larger amount of NPL will show the bank’s inability to select right customers to disburse the credit facility. Generally a banks credit risk will be measured in the form of calculating the amount of classified loan. The large portion in the classified loan will indicate the greater risk a bank has.
year | PBL | PCBs |
2006 | 0.008 | 1.8 |
2007 | 0.013 | 1.4 |
2008 | 0.018 | 0.9 |
2009 | 0.013 | 0.5 |
2010 | 0.012 | 0.6 |
From the above table we can see that PBL has a very low NPL ratio and pretty much good than the industry average.
Findings
During my internship period I have some findings related with Credit appraisal & credit management system of Prime Bank Limited. The findings are shown in parts of credit appraisal, credit recovery and credit default.
Findings on Credit appraisal
- PBL uses credit appraisal technique comprising technical, market, financial, economic, and management & organization analysis.
- Credit appraisal technique is good enough itself, but the problems lie with personnel involves in appraisal process
- The main problems can be summarized in the following way:
- One of the problems with credit appraisal is inadequate and inaccurate data.
- Sponsors always tend to overstate their future cash flow, revenue and income and understate the risk with capturing market and expenses.
- Market don’t remain same over the years especially over the time gap between loan sanction and loan recovery.
- Lengthy procedure and long time involved in the appraisal of project
- Sometimes, there is pressure groups’ involvement in sanctioning loan.
- Many viable projects do not get sanctioned loan due to absence of bribe and pressure from political and other pressure group.
- The personnel involve in project appraisal are either not quite expert in their respective field or corrupt.
- Physical verification is not rigorously done for every project that is why the project appraisal techniques do to bring any outstanding results.
- Sometimes, the amount of loan sanction is more than that is required by the project because of over invoicing from the part of sponsors.
Findings about the Credit Recovery
- Usually PBL inform the borrowers before 7 days of the scheduled date of payment about his/her next upcoming installment due.
- Visiting to the borrowers premises is hardly done before the loan is defaulted.
- The recovery department cannot coerce or make bound to repay the loan because of pressure from political and other higher management.
- Sometimes sponsors do like to linger the repayment time to have the replacement facilities.
- The recovery amount has been increasing for last 5 years, and the variance between recovery targets.
Findings about Credit Defaults
- The causes of the loan defaults are:
- Willing defaults
- Government policy, sometimes, causes a firm to stop business operation or due to changes in the government policy a firm may incur loss.
- Due to market changes firms may not get buyers to sell production resulting in a no sale, no cash, and no repayment.
- Technological change may also lead a firm to incur losses because of obsolete technology cannot compete with modern technology resulting in less cash generation.
- Sometimes, project is not implemented because the shortages of fund from the part of borrower.
- Lack of financial commitment from the part of borrower the result is the failure of mobilization of equity. They divert their equity in other purposes after getting the loan amount
- Default amount shows a down-ward trend during 5 years
- Law department functions very slowly and follow a difficult bureaucratic process.
- After enactment of the, the legal action has got speed and the number law suits have increased.
- Most of the cases settled outside the court.
- There are some problems of taking over the company, like maintenance of the property and selling the property.
- It takes time to settle a suit, because the borrower has right to writ against the verdict.
Analytical Findings
- Throughout credit analysis of Prime Bank Limited some mentionable results are found-
- Bank is doing well in its credit operation. The amount of interest earning shows the success.
- The bank’s Net Interest Margin is in the decreasing trend.
- ROI is very as compared with NBL, though Prime bank limited invested more amount than NBL.
- PBL has good credit ratings. That is a plus point for it.
- Strong financial condition helps the bank to be a market leader.
- From regression analysis it has shown that loan amount of the bank is inversely related with Interest rate.
- PBL is mainly focusing on Industrial credit beside other type of credit.
Recommendations
A banker cannot sleep well with bad debts in his portfolio. The failure of commercial banks occurs mainly due to bad loans, which occurs due to inefficient management of the loans and advances portfolio. Therefore any banks must be extremely cautious about its lending portfolio and credit policy. So far Prime Bank Limited has been able to manage its credit portfolio skillfully and kept the classified loan at a very lower rate —thanks go to the standard and stringent credit appraisal policy and practices of the bank.
But all things around us are changing at an accelerating rate. Today is not like yesterday and tomorrow will be different from today. Given the fast changing, dynamic global economy and the increasing pressure of globalization, liberalization, consolidation and disintermediation, it is essential that Prime bank limited has a robust credit risk management policies and procedures that are sensitive to these changes.
Prime bank Limited has an efficient & excellent credit management team and performing with great expertise and care. There are some limitations that can be overcome by some measures to make the performance outstanding. There are some suggestions for prime banks credit management team from my observation.
- In credit management, it is conventional that proposals of credit facilities must be supported by a complete analysis of the proposed credit. More importance should be given on refund of loans out of funds generated by the borrower from their business activities (cash flow) instead of realization of money by disposing of the securities held against the advance, which is very much uncertain in present context of Bangladesh, where a number of creditors are willful defaulters.
- For commercial lending, most of the time clients are unable to submit audited financial statements. The reason is no legal bounding to prepare audited financial statements for all commercial organization. So the credit officer has to face difficulties about the reliability of financial statements submitted. So there should be some flexibility for proprietorship concerns.
- Credit officer measures the risk associated with the credit facility. He should not be liberal in this respect; he should strictly follow the credit evaluation principle setup by the bank. It should improve in file management system to faster the dealings with the client’s proposal.
- On the basis of that Return on Equity (ROE) model, risk and return of the bank is analyzed. Prime Bank has a good return in the following years from its operation. But Bank should be careful in its riskiness. It should improve its liquid assets to reduce the liquidity risk. It should also try to increase its reserve.
Conclusion
Researchers support the fact that economic and financial development of a country are highly correlated to the development of its banking and financial system. The more developed and efficient the banking sector of a country is, the more developed is the business industry sectors will be.
With a view to improving the quality and soundness of loan portfolio, credit risk management methods were updated in 2005. The Bank is now applying a new system of credit risk assessment and lending procedures by striker separation of responsibilities between risk assessments and lending decisions and monitoring functions. The Bank monitors its exposure to particular sectors of economy on an ongoing basis. The Bank has undertaken the changes in policy of credit risk management, credit risk administration and credit monitoring and recovery in line with the guidelines of Bangladesh Bank, formulated in the last year.
Credit Appraisal system of this bank is pretty efficient. From the beginning of the process of credit appraisal system the credit committee is sufficiently committed and caring. After received loan application from the client, in-depth study of various related documents & gathering of information from different banks and other sources are performed. The loan proposal that is prepared by the credit officer and submitted to the higher authority for approval is the most important part of credit appraisal system because based on this proposal the granting of credit decision is made. Credit collection process of PBL is also strict and satisfactory.
We hope that PBL will lead by example by continuing its efficient lending policy in keeping the bank’s financial performance indicators at above industrial average and contribute to country’s economic development-thus attaining a middle income status in the world.
















