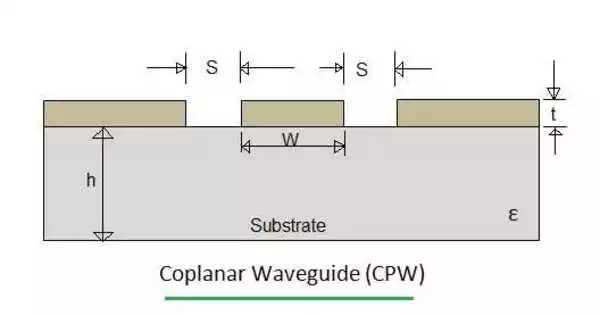
Coplanar waveguide (CPW) is a transmission line that is used in microwave and radio frequency (RF) integrated circuits. It is a type of electrical planar transmission line that can be made using printed circuit board technology and is used to transmit microwave signals. It is intended to transport electromagnetic waves between different circuit components or sections while maintaining controlled impedance and low signal loss. Coplanar waveguide transmission lines are also built into monolithic microwave integrated circuits on a smaller scale. All conductors, including the signal trace and ground plane, are located on the same plane or layer of a substrate in CPW.
A coplanar waveguide’s basic structure consists of a central signal trace flanked by two ground planes on either side. The signal trace is typically a metal strip, with ground planes being large conducting regions. To maintain symmetry, the gap or slot between the signal trace and the ground planes is typically equal on both sides.
A conventional coplanar waveguide (CPW) is made up of a single conducting track printed onto a dielectric substrate and two return conductors, one on each side of the track. All three conductors are coplanar because they are on the same side of the substrate. The return conductors are separated from the central track by a small gap that is the same width all the way down the line. Away from the central conductor, the return conductors usually extend to an indefinite but large distance, so that each is notionally a semi-infinite plane.
Here are some key features and advantages of coplanar waveguide:
- Broadband operation: CPW supports a wide range of frequencies, making it suitable for applications that require high-frequency operation.
- Low dispersion: CPW exhibits lower dispersion compared to other transmission line structures, which allows for improved signal integrity.
- Planar integration: Since all conductors are on the same plane, CPW can be easily integrated with other components on a substrate, enabling compact and efficient circuit designs.
- Low radiation loss: The ground planes on both sides of the signal trace help contain and confine the electromagnetic fields, reducing radiation loss and improving the overall efficiency of the transmission line.
- Easy impedance control: By adjusting the width of the signal trace and the spacing between the signal trace and the ground planes, the characteristic impedance of the CPW can be precisely controlled.
- Flexibility in design: CPW allows for various modifications and enhancements, such as adding ground vias, tapered transitions, or meandering structures, to meet specific circuit requirements.
Coplanar waveguide finds applications in microwave circuits, such as amplifiers, filters, mixers, antennas, and high-speed digital systems. It is commonly used in RF integrated circuits (ICs), wireless communication systems, radar systems, and high-speed digital interconnects.