Coeliac Disease
Definition
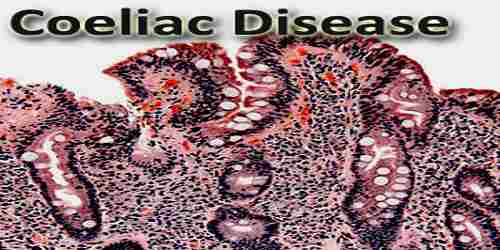
Coeliac disease is a lifelong autoimmune condition which is triggered by intolerance to gluten. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, rye and barley. It can cause a range of symptoms including diarrhoea, abdominal pain and bloating. Classic symptoms include gastrointestinal problems such as chronic diarrhoea, abdominal distention, malabsorption, loss of appetite, and among children failure to grow normally. This often begins between six months and two years of age.
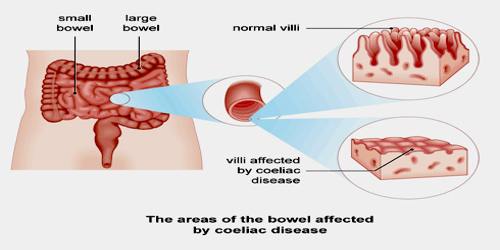
Coeliac disease is caused by an adverse reaction to gluten, a dietary protein found in three types of cereal:
- wheat
- barley
- rye
Gluten is found in any food that contains the above cereals, including:
- pasta
- cakes
- breakfast cereals
- most types of bread
- certain types of sauces
- some types of ready meals
In addition, most beers are made from barley.
Causes, Sign and Symptoms of Coeliac Disease
Coeliac disease is caused by a reaction to gluten, which are various proteins found in wheat and in other grains such as barley, and rye. Moderate quantities of oats, free of contamination with other gluten-containing grains, are usually tolerated. The occurrence of problems may depend on the variety of oat. Upon exposure to gluten, an abnormal immune response may lead to the production of several different autoantibodies that can affect a number of different organs. In the small-bowel this causes an inflammatory reaction and may produce shortening of the villi lining the small intestine (villous atrophy). This affects the absorption of nutrients, frequently leading to anaemia. Coeliac disease isn’t an allergy or an intolerance to gluten.
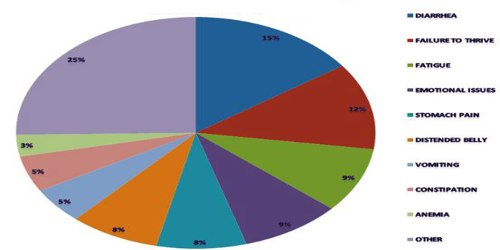
Diarrhoea is the most common symptom of coeliac disease. It’s caused by the body not being able to fully absorb nutrients.
Malabsorption can also lead to stools containing abnormally high levels of fat (steatorrhoea). This can make them foul smelling, greasy and frothy. Other common gut-related symptoms include:
- abdominal pain
- bloating and flatulence (passing wind)
- indigestion
- constipation
- vomiting (usually only affects children)
And more general symptoms may include:
- fatigue (extreme tiredness), which may be a sign of iron deficiency anaemia or vitamin B12 folate deficiency anaemia
- unexpected weight loss
- an itchy rash (see below)
- difficulty getting pregnant
- tingling and numbness in your hands and feet (peripheral neuropathy)
- disorders that affect co-ordination, balance and speech (ataxia)
- swelling of the hands, feet, arms and legs caused by a build-up of fluid (oedema)
Diagnosis and Treatment of Coeliac Disease
Diagnosis is often very difficult so that most cases are diagnosed with great delay. There are several tests that can be used. Testing is usually only recommended for people at an increased risk of developing coeliac disease, such as those with a family history of the condition.

There’s no cure for coeliac disease, but switching to a gluten-free diet should help control symptoms and prevent the long-term consequences of the condition.
At present, the only effective treatment is a lifelong gluten-free diet. No medication exists that will prevent damage or prevent the body from attacking the gut when gluten is present. Strict adherence to the diet allows the intestines to heal, leading to resolution of all symptoms in most cases and, depending on how soon the diet is begun, can also eliminate the heightened risk of osteoporosis and intestinal cancer and in some cases sterility. The diet can be cumbersome; failure to comply with the diet may cause relapse.
Reference: