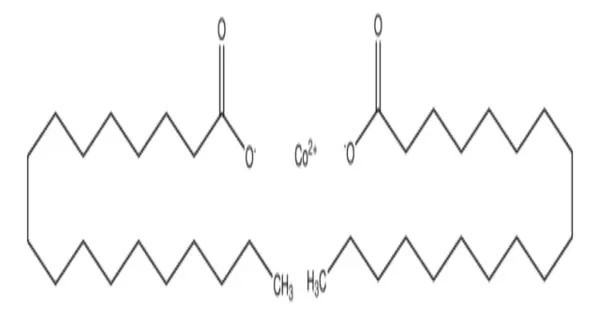
Cobalt(II) stearate is an organometallic compound formed by the reaction of cobalt salts with stearic acid, a long-chain fatty acid. It is a metal-organic compound, a salt of cobalt and stearic acid with the chemical formula C36H70CoO4. The compound is classified as a metallic soap, i.e. a metal derivative of a fatty acid. This compound appears as a violet to reddish powder or waxy solid, insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar organic solvents and oils due to its hydrophobic stearate chains.
Cobalt(II) stearate is typically produced by neutralizing stearic acid with cobalt(II) hydroxide or cobalt(II) carbonate. Although useful, it should be handled with care, as cobalt compounds can cause skin sensitization and have potential toxicological effects if inhaled or ingested. Its stability is good under normal conditions, but it may decompose at high temperatures, releasing irritating fumes. Proper ventilation and protective equipment are recommended during handling.
Properties
It is typically a violet to pinkish powder, insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents like toluene or mineral oils. It has hydrophobic properties and is stable under normal conditions but can decompose upon strong heating. As a metallic soap, it functions as a lubricant, heat stabilizer, and catalyst. It has a relatively high melting point (often above 200 °C) and can act as a drier in paints, promoting oxidation and polymerization of oils.
- Cobalt(II) stearate forms a violet substance, occurring in several crystal structures.
- Chemical formula: C36H70CoO4
- Molar mass: 625.46
- Appearance: violet substance
- Density: 1.7 g/cm3
- Melting point: 109 °C (228 °F; 382 K)
- Boiling point: 359.4 °C (678.9 °F; 632.5 K)
- Solubility in water: insoluble It is insoluble in water.
Occurrences
Cobalt(II) stearate does not occur naturally and is produced industrially by reacting cobalt salts (such as cobalt chloride or sulfate) with sodium or potassium stearate. It is commonly used in the plastics, rubber, and coatings industries—especially in PVC stabilization, as a pigment dispersant, and as a curing agent in unsaturated polyester resins. Its presence is largely confined to manufactured products rather than natural environments.
Uses
Cobalt(II) stearate is a high-performance bonding agent for rubber. The compound is suitable for applications in natural rubber, cisdene, styrene-butadiene rubber, and their compounds to bond easily with brass- or zinc-plated steel cord or metal plates as well as various bare steel, especially for bonding with brass plating of various thicknesses.
It is widely used as a drier (curing agent) in paints, varnishes, and inks, where cobalt ions catalyze the oxidative cross-linking of drying oils, accelerating the hardening process. In plastics and rubber industries, cobalt(II) stearate functions as a heat stabilizer, lubricant, and mold-release agent. It can also serve as a catalyst in certain polymerization reactions and as an adhesion promoter for coatings.