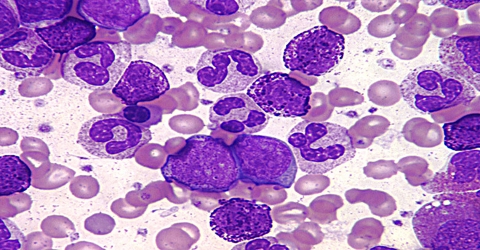
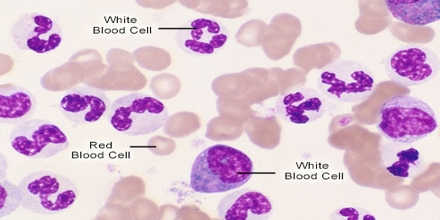
Chronic myelogenous leukemia is a disease in which the bone marrow makes too much white blood cells. It is a kind of cancer that affects the white blood cells and tends to growth slowly over many years. It can arise at any age, but is mainly common in older adults around 60-65 years of age. Usually this disease occurs during or after middle age, and rarely occurs in children. In general, their treatment is the same as for adults.
Symptoms of Chronic myelogenous leukemia
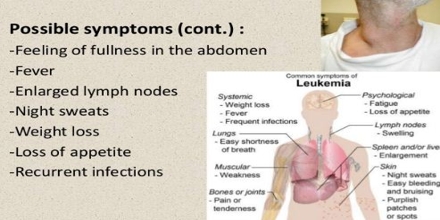
CML doesn’t typically have any symptoms in its early stages and may only be picked up during tests carried out for another reason.
As the situation develops, symptoms can include:
- Tiredness
- Have a fever
- Have night sweats
- Be short of breath
- Lose some weight
- Feel less hungry
- Get swelling or pain on your left side (which could be a sign of an enlarged spleen)
- Feel pain in your bones
Causes of Chronic myelogenous leukemia
Chronic myelogenous leukemia occurs when something goes wrong in the genes of your blood cells. It’s not apparent what originally sets off this procedure, but doctors have discovered how it progresses into chronic myelogenous leukemia. It is caused by a genetic change (mutation) in the stem cells produced by the bone marrow.
The mutation causes the stem cells to produce too many underdeveloped white blood cells. It also leads to a reduction in the number of other blood cells, such as red blood cells.
The change involves bundles of DNA called chromosomes. Within each stem cell, a section of DNA from one chromosome swaps with a section from another. This change is known as the “Philadelphia chromosome”. Read more about genes and chromosomes.
It’s not known what causes this to happen, but it’s not something you’re born with and you can’t pass it on to your children.
Treatment
The goal of treatment is to demolish the leukemia blood cells in your body and reinstate healthy ones to a standard level. It’s generally not doable to get rid of all the bad cells. The main goal of chronic myelogenous leukemia treatment is to eliminate the blood cells that hold the abnormal BCR-ABL gene that causes the overabundance of diseased blood cells.
Targeted drugs that block the action of tyrosine kinase include:
- Imatinib (Gleevec)
- Dasatinib (Sprycel)
- Nilotinib (Tasigna)
- Bosutinib (Bosulif)
- Ponatinib (Iclusig)
Targeted drugs are the early treatment for most people diagnosed with chronic myelogenous leukemia. If the disease doesn’t respond or becomes resistant to the first targeted drug, doctors may consider other targeted drugs, such as omacetaxine (Synribo), or other treatments. Side effects of these targeted drugs include swelling or puffiness of the skin, nausea, muscle cramps, rash, fatigue, diarrhea, and skin rashes.
Conclusion
Chronic myelogenous leukemia is a fairly sluggish growing leukemia, but it can also change into a fast-growing acute leukemia that is hard to treat.
CML regularly happens when you’re middle-aged or older. The symptoms tend to come on steadily. Many of them can also be signs of other illnesses. For instance, you might feel tired, lose weight when you’re not trying to, or sometimes get a fever.