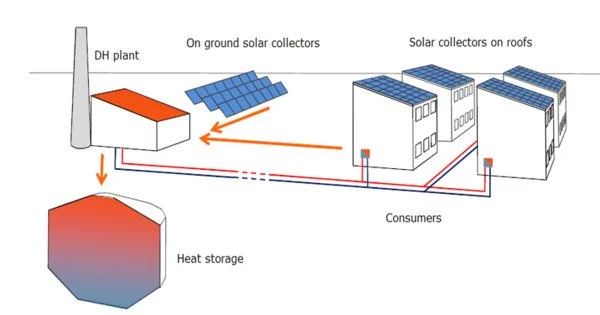
Central solar heating is the use of solar energy to provide central heating and hot water via a system in which the water is heated centrally by arrays of solar thermal collectors (central solar heating plants – CSHPs) and distributed via district heating pipe networks (or ‘block heating’ systems in the case of smaller installations).
Solar collectors for block systems are typically mounted on building rooftops. Collectors for district heating systems can instead be installed on the ground. Solar collectors, a heat transfer fluid, a heat storage system, and a distribution network are typical components of a central solar heating system. Solar collectors, which are typically mounted on rooftops or in open areas, capture sunlight and convert it into thermal energy. This energy is then transferred to a heat transfer fluid, such as water or glycol, which circulates through the collectors and absorbs the solar heat.
The collected heat is then carried by the heat transfer fluid to a central storage system, where it is stored for later use. Large tanks or underground thermal reservoirs capable of storing thermal energy for use when sunlight is unavailable, such as at night or on cloudy days, can be included in the storage system. The stored heat can be used to provide space heating and hot water throughout the community as needed.
Central solar heating can involve large-scale thermal storage, ranging from diurnal to seasonal thermal energy storage (STES). Thermal storage increases the solar fraction – the ratio of solar energy gain to total energy demand in the system – for solar thermal systems. The goal of using seasonal storage is to transfer solar energy collected during the summer to the winter months.
The stored heat from the central storage system is distributed to the community’s buildings via an insulated pipe distribution network. Each building has its own heat exchanger, which extracts heat from the circulating fluid and transfers it to the heating and hot water systems. This way, each building can benefit from the central system’s solar heat.
Central solar heating systems have a number of advantages. They use renewable solar energy, which reduces reliance on fossil fuels and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. They can also save money in the long run because solar energy is free once the infrastructure is in place. Moreover, these systems can provide heating and hot water to a large number of buildings, making them suitable for residential neighborhoods, commercial areas, or even entire cities.
Application
Central solar systems can also be used for solar cooling in the form of district cooling. Because of the strong correlation between energy demand and solar radiation, overall efficiency is high in this case.
Central solar heating systems, on the other hand, necessitate careful planning, design, and investment. Consideration must be given to factors such as the availability of suitable locations for solar collectors, the size of the storage system, and the design of the distribution network. Furthermore, installation and maintenance costs can be relatively high, though long-term energy savings can offset these costs.