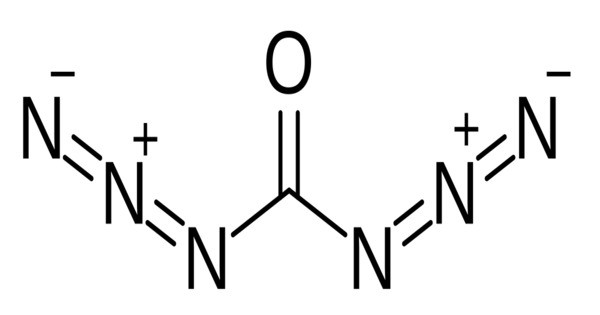
Carbonyl diazide is a chemical compound with the chemical formula CO(N3)2. It is a reactive and potentially hazardous compound, primarily used in organic chemistry as a diazidation reagent. In terms of its structure, it can be described as two azide groups −N3 covalently attached to the carbonyl group −C(=O)− by single bonds. It can be prepared by way of the reaction between triphosgene and tetra-n-butylammonium azide, in a dimethyl or diethyl solution.
The first synthesis of carbonyl diazide was reported in 1894, although there have been multiple alternative syntheses since then.
Properties
Carbonyl diazide is highly sensitive to shock, friction, and heat. It can decompose violently, which makes handling and storage challenging. It is a colorless, crystalline solid, though it is often prepared in the form of a solution due to its instability.
- Chemical formula: CO(N3)2
- Molar mass: 112.052 g·mol−1
- Solubility: It is soluble in organic solvents, but it can be unstable in the presence of moisture or under high-energy conditions.
- Reactivity: It is reactive due to the presence of azide groups, which can undergo rapid decomposition or reaction with other compounds, including metals or reducing agents.
- Decomposition: The decomposition reaction typically produces nitrogen gas and carbon monoxide, making it both dangerous and potentially hazardous to work with in confined spaces.
Occurrences
Synthetic Compound: Carbonyl diazide is typically synthesized in the laboratory rather than occurring naturally. It is used in research and as a precursor to other chemical compounds, particularly in the field of organic chemistry and materials science.
Explosives: Due to its sensitivity and explosive nature, carbonyl diazide has been investigated in the context of energetic materials and explosives.
Uses
Carbonyl diazide is mainly used in the synthesis of azides, which are valuable intermediates in organic chemistry. It can serve as a source of the azido group (N₃) for reactions like azidation (the addition of azide groups to other molecules). It is used in some specialized polymerization processes and can be involved in making more complex chemical compounds.
Safety Considerations
Due to its instability and explosive nature, carbonyl diazide must be handled with great care, typically in well-controlled laboratory environments. It can decompose explosively when exposed to heat, friction, or shock.