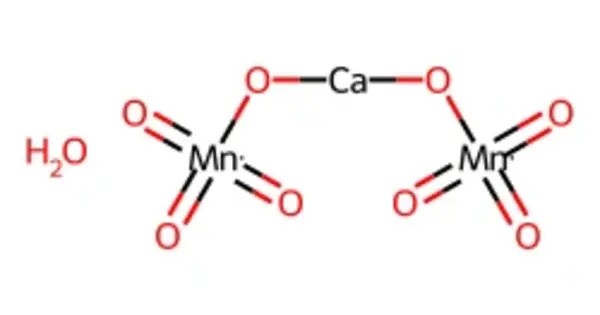
Calcium permanganate is an oxidizing agent and chemical compound with the chemical formula Ca(MnO4)2. It consists of calcium cations (Ca²⁺) and permanganate anions (MnO₄⁻). It is the calcium salt of permanganic acid, containing the permanganate anion (MnO₄⁻), known for its strong oxidizing properties. Known for its strong oxidizing properties, it is less common than potassium or sodium permanganate. This salt consists of the metal calcium and two permanganate ions.
It is soluble in water, forming a purple solution. Calcium permanganate is used in water treatment, disinfectants, and occasionally in organic synthesis. It must be stored carefully, as it can react violently with organic materials or reducing agents. Exposure to heat or light can cause it to decompose, releasing oxygen and manganese oxides. Its oxidizing strength makes it useful but hazardous if mishandled.
Properties
- Chemical formula: Ca(MnO4)2
- Molar mass: 277.9493 g/mol
- Appearance: purple crystals
- Density: 2.49 g/cm3
- Melting point: 140 °C (284 °F; 413 K) (decomposes, tetrahydrate)
- Solubility in water: tetrahydrate: 331 g/100 mL (14 °C), 338 g/100 mL (25 °C)
- Solubility: soluble in ammonium hydroxide, decomposes in alcohol
Preparation
The salt is prepared from the reaction of potassium permanganate with calcium chloride or from the reaction of aluminium permanganate with calcium oxide. It can also be prepared by reacting manganese dioxide with a solution of calcium hypochlorite and a little bit of calcium hydroxide to increase the pH level.
Reacting potassium permanganate (KMnO₄) with calcium salts in solution:
2KMnO4+CaCl2→Ca(MnO4)2+2KCl
Double displacement methods using soluble permanganates and calcium chloride/nitrate.
Reactivity and Behavior
- Decomposition: Upon heating or contact with reducing agents, calcium permanganate can decompose, producing manganese dioxide (MnO₂), oxygen (O₂), and calcium oxide (CaO).
- Reaction with acids: Forms permanganic acid (HMnO₄), which is unstable.
- Reaction with organic substances: Can cause combustion or explosions due to its strong oxidizing ability.
Occurrence
Does not occur naturally; it is a synthetic compound.
Permanganates in nature (e.g., pyrolusite – MnO₂) are not found as calcium salts.
Safety
- Oxidizer: Can intensify fires or cause combustion when mixed with combustible materials.
- Toxic if ingested, inhaled, or in contact with skin in significant amounts.
- Should be handled with protective equipment and stored away from organic materials, acids, and heat.
Uses
Calcium permanganate is used in the textile industry, for sterilization of water, and as a deodorizer. It is believed to help whiten teeth. It was formerly used as a component of rocket fuel by the Luftwaffe.
- Water treatment: Can be used for disinfection and removal of iron/manganese from water.
- Oxidizing agent in organic synthesis.
- Occasionally used in analytical chemistry for redox titrations.