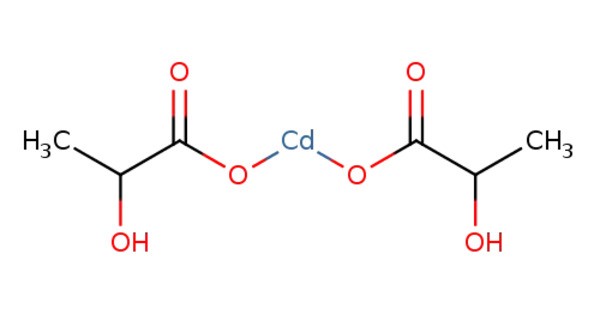
Cadmium lactate is an organic chemical compound, a salt of cadmium and lactic acid with the formula Cd(C3H5O3)2. It usually appears as a white crystalline powder. It is generally soluble in water. Like other cadmium compounds, cadmium lactate is highly toxic and poses significant health risks, particularly through ingestion, inhalation, or prolonged exposure. Cadmium is known to accumulate in the kidneys and liver and can lead to kidney damage, lung disease, and cancer.
It is primarily used in specialized chemical research and is not naturally occurring. It has some potential applications in industries that use cadmium-based materials but is handled with caution due to the toxicity of cadmium.
Properties
Cadmium lactate forms colorless (white) crystals. It is soluble in water but insoluble in ethanol. It is a carcinogen and poison.
- Chemical formula: C6H10CdO6
- Molar mass: 290.55
- Appearance: Colorless crystalls
- Solubility in water: Very soluble
Synthesis
Cadmium lactate can be obtained by dissolving cadmium carbonate in lactic acid. It can also be obtained by mixing boiling solutions of lactate of lime and cadmium sulfate.
Occurrences
Cadmium lactate is a synthetic compound and does not occur naturally in large quantities. It is typically produced by combining cadmium salts with lactic acid under controlled conditions in a laboratory or industrial setting. Cadmium is a relatively rare metal, and its compounds, like cadmium lactate, are generally of interest in specialized chemical applications.
Production
Cadmium lactate can be produced by reacting cadmium salts (often cadmium sulfate or cadmium chloride) with lactic acid in a controlled solution. The resulting product is purified and crystallized.
Uses
- Industrial Applications: Cadmium salts, including cadmium lactate, may be used in various industrial processes, such as in electroplating, pigments, and batteries.
- Chemical Research: Cadmium compounds like cadmium lactate are sometimes used in laboratory research, particularly in studies involving heavy metals, their effects, and their chemistry.
Health and Safety Concerns
Cadmium is classified as a carcinogen (cancer-causing agent) by the International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Prolonged exposure to cadmium, even in small amounts, can lead to severe health issues, so handling cadmium compounds requires extreme care, including proper ventilation, personal protective equipment, and compliance with safety regulations.