There has been much written about determining company strategy. However, there has been very little written about developing a sales strategy. A company strategy without a corresponding sales strategy is akin to an acquisition plan without a post-acquisition integration plan. One without the other is sure to disappoint.Emerging from our research is a framework that CEOs can use to develop and execute a sales strategy. The framework takes the classic idea of the three C’s (Costs, Competitors, Customers) to the implementation level with a focus on sales force execution.
Costs:Different companies making similar products may have a very different cost of sales. Businesses should expect their sales costs to decline systematically, at a rate that can be accurately predicted, as they gain selling experience. The amount of labor that goes into making a sale declines predictably as the number of sales are increased. Typically, the 4th widget sold should take only 80% of the labor required to sell the 2nd widget, so to speak.
Competitors: Understanding your company’s selling cost in comparison to your competitors’ selling cost builds the foundation for our second framework, the growth-share matrix. The idea can be summarized as follows: Some sales territories are growth businesses. These territories automatically compound because of repeat purchases. Some sales territories are stable businesses that throw off cash and maintain their value over time. Some sales territories are declining businesses and should be managed for cash flow. Still others are speculative – they either pay off or they do not. The key is how to manage each sales territory.
Customers:The needed sales strategy work just discussed has focused on understanding costs relative to the competition, and mostly reducing them. This framework also covers how to better reach customers where the focus is on value creation. The challenge with Sales Strategy is in implementation. Once you have designed the sales strategy and aligned the organization around it, the task of executing the strategy remains. At the heart of implementing sales strategyis the conception of a sales force as consisting of all the discrete activities it performs, “generating interest”, “developing needs”, “differentiating against the competition”, and “overcoming obstacles”.
The Call-To-Action message is this: How does your company’s performance of activity X measure up to your competitors’ in terms of value delivered? A framing device, such as the sales value chain analysis, can isolate every single component activity that goes into winning a deal. This breaks up the overall sales process up into units that can be benchmarked against other divisions, sales geographies, other companies, even other industries, that are performing the same activity.
What are the six Drivers of change in relationship selling and sales management?
What is relationship between management and change management?
change management is a crucial subset of management in the same way that making sure that your children are healthy is a vital component of parenting. Management refers here to a task or process. It.
¨ After six months of an Open yet monogamous relationship how do you change it to just a regular?
Both partners should seek a marriage counselor to find out why they wanted an open marriage in the first place. Generally couples that want open marriages do so because one or both become extremely.
¨ What is the role of sales promotion in sales management?
Sale promotion is an important component of a small marketing strategy along with advertising ,public relations, and personally selling.
¨ What is a change-request management tool?
¨ Can incarceration change your relationship for the better?
Not usually but that depends on the individuals involved.
¨ Sales are so rewarding
- With companies increasingly focusing on customer satisfaction and building long-term relationships with customers, they are tapping the sales and marketing ranks to fill CEO positions. Here are five steps you can take to place yourself in that swanky corner office: Autonomy, or the freedom of action and opportunities for personal initiative.
- Multifaceted and challenging activities as part of the job, sales activities that will be addressed later in this chapter.
- Financial rewards-salespeople hired right out of college, for example, tend to start at higher salaries the most other professions and also tend to keep up well during their careers with the compensation of their peers outside of sales (due to the nature of sales compensation being linked directly to performance).
- Favorable working conditions, often via telecommuting with a virtual office, and with less minute-to-minute direct supervision than most other careers.
¨ Sales jobs factors
As in any career, it makes sense to consider the pros and cons of a sales job before deciding if the employment path is right for you. Take a look at various factors involved and choose the employment in sales that is the best fit for your career goals and lifestyle.
When seeking employment in sales, it is common for a person to zero in on the compensation plan and consider little else about the company, position or even the product being sold. The problem with this line of thinking is that in a few weeks, the salesperson may find herself miserable in the position because she didn’t take the time to really analyze the job and company. To avoid this scenario, going about seeking employment in sales by weighing the pros and cons of any position in which you are interested.
Consider the following factors to make your employment in sales pleasant and profitable:
Employment in Sales Factor #1: Hours and Travel
You will want to find out right away how many hours the sales employment you are considering will to require. Will it be days, evening, weekdays, weekends, or all of the above? Will the schedule the employer sets forth be accommodating to you? Will you have flexibility?
Another factor to consider is how much travel the position will require. Some sales jobs are local and do not require significant travel while others necessitate weeks or even months out on the road. High travel employment in sales may seem like no big deal or even fun for a single person, but it can be a hardship for an individual with a family or a dislike of being on the road.
Employment in Sales Factor #2: Training
No matter how good you may be at sales, training and continuing education is essential for growth for employment in sales. You may even find it is necessary for you to obtain certain training for the type of sales employment you are considering. Find out what training if any is necessary and determine who pays for such training.
Employment in Sales Factor #3: Cold Calling
Few things cause more stress in the sales business than cold calling. Some salespeople have a real talent for this and others shake in their boots if they simply hear the words. Which describes you? If you do not like to cold call then you should be sure that a job you are considering does not count cold calling as one of the job duties. .
Employment in Sales Factor #4: Perks and Benefits
This is a big one especially if you are thinking about employment in sales that involves travel. Will you get a company car or at least compensated for the miles you rack up on your personal vehicle? Will you get an expense account while out on the road in order to pay for food and other essentials? Also, determine whether you will receive other benefits, including health or life insurance coverage. If these are not part of your benefits package, you will have to pay for these out of pocket.
Employment in Sales Factor #5: Compensation
While not always the first thing to consider it should not be overlooked either. Find out up front how you will be compensated. This is more than how much you will make an hour. Will you get any kind of commissions? Will you receive bonuses? Also, how often will you get paid? Many people assume that payroll is weekly or bi-weekly, but some sales employment opportunities will be with companies that only pay out once a month.
Employment opportunities will come and go, but you should be sure to take the job opportunity that will give you the best shot at meeting your professional and personal goals. Many people find that employment fields other than sales is not what they want at all, and they prefer a sales environment in which they can set their own hours and create their own success. If you have exceptional sales skills and a definite drive to succeed, you may be a great candidate to go into sales for your own business.
¨ Sales selected associate activities
Pre-Sales Activities
The Pre-Sales Activities can be broken into two areas, planning and preparing for the call. Planning, by definition, is action based and is a scheme or method, developed in advance, for doing, proceeding or making something. Planning, in the Pre-Sales Activities, can include Prospect/Customer identification, Product/research/customer analysis review, competitor/industry research, creating a call strategy, evaluation of your products and services relative to the competition. This not an inclusive list but a good start in planning for the call. How many of us do that much research? Come on, be honest, we don’t spend that much time. Some of us may engage in the research but we do not do so thinking ahead how we will use this data in our sales calls; we should.
To prepare is to put together or make by combining various elements or ingredients. So how do you prepare for the sales call? It’s time to transfer your plan to a written document. How do you use the information gathered in the planning phase? You will use that information when you write a clear objective for each sales call. Write an objective, determine the processes you will use to achieve those objectives, set quantifiable goals for each objective and practice for the call.
Pre-Sales Activities around preparation will look like creation of meeting presentation material, proposal/pricing creation, contract generation, determining use of marketing material, identifying customer objections, and planning to address those in the presentation or meeting, and defining the quantifiable return you expect to see after the meeting. After you have set the objective and determined how to meet the objective, you must practice for the call; that practice is integral in preparing for the sell.
Wow, seems like we are spending a significant amount of time in Pre-Sales Activities. Well, we are. Analysis indicates most sales reps do not spend enough time in pre-sales. The reps that do more planning and preparing see a higher return on the time investment and tend to be less frustrated after sales calls.
Sales Activities
We all know what Sales Activities look like right? Probably but let’s make sure we are all on the same page. Sales Activities are the execution of all your hard work planning and preparing. These activities may include the sales call/meeting, negotiation or follow-up, closing the deal/order taking, and relationship building and networking. Easy? Easier when you are prepared and carry out your plan. In another article we will dive deeper into how to execute.
Post Sales Activities
How many sales reps live for, or even like, Post Sales Activities? Be honest, not many of us. That’s because Post Sales Activities such as product/service implementation, customer service and support, gathering customer feedback, continued customer relationship building, future sales forecasting, and evaluation of the sales call are not what we want to do. None of these activities are highlights of the sales reps day but they are all integral. I would point out that of all Post Sales Activities, the one that should be of most interest to the sales rep is evaluation after a call. Given open and honest diagnosis of your sales call, this activity will set you up better for your next call and will, in and of itself, lend to more productive sales in the future. Why you ask? If you truly evaluate and determine what went well/what could have gone better on the last call and make changes based on this data, future calls will go more smoothly.
So, no matter what you call the Sales Execution Model it should consist of three phases, Pre-Sales Activities, Sales Activities and Post Sales Activities. Remember to spend more time, do your due diligence, in the Pre-Sales Activities phase. This will garner you better results.
¨ B2B AND B2C
Business-to-business (B2B) describes commerce transactions between businesses, such as between a manufacturer and a wholesaler, or between a wholesaler and a retailer. Contrasting terms are business-to-consumer (B2C) and business-to-government (B2G).
The volume of B2B (Business-to-Business) transactions is much higher than the volume of B2C transactions. The primary reason for this is that in a typical supply chain there will be many B2B transactions involving sub components or raw materials, and only one B2C transaction, specifically sale of the finished product to the end customer. For example, an automobile manufacturer makes several B2B transactions such as buying tires, glass for windscreens, and rubber hoses for its vehicles. The final transaction, a finished vehicle sold to the consumer, is a single (B2C) transaction.
B2B is also used in the context of communication and collaboration. Many businesses are now using social media to connect with their consumers (B2C); however, they are now using similar tools within the business so employees can connect with one another. When communication is taking place amongst employees, this can be referred to as “B2B” communication.
Differences between B2B AND B2C
The major difference between B2B (Business to Business) and B2C (Business to Customer) in internet terms is the role of the B2B website. B2B concerns itself primarily with supply chain management. These are portals that allow businesses to deal directly with their suppliers and distributors online. Allowing electronic transfer of orders, invoicing and even payments. Wholesalers, distributors and manufacturers fall in this category.
B2C websites are intermediary portals to link customers to suppliers. Some of the major ones are ebay, an auction site. Yell, an internet version of yellow pages and ZDNet a technology market place. All of these businesses exist primarily on the internet. They are what is known as e-businesses (electronic businesses). All of them can be classified under one general heading, market places.
B2C concerns itself with selling to the end user. Typically these are sites like Amazon, online book retailers, lastminute.com, a “good times” portal. These sites are more interested in passing the goods to the end user. There is likely a slight difference between them and your business. They are actually internet based. That is to say they exist primarily on the internet. Offices and warehousing are borne from necessity of their internet success.
A B2B site deals primarily with other businesses, not the general public, a B2C site sells directly to the end user. B2B sites normally handle a lot more than just sales of products, they are a portal to conduct business transactions.
Whether your business is going to be an e-business or an e-commerce centre is down to the nature of your business. If you require some assistance, simply contact us and we will help as best we can. It is free of charge of course.
¨ Stage of selling process
A sales process, also known as a sales tunnel or a sales funnel, is a systematic approach to selling a product or service. A growing body of published literature approaches the sales process from the point of view of an engineering discipline (see sales process engineering). Reasons for having a well thought-out sales process include seller and buyer risk management, standardized customer interaction in sales, and scalable revenue generation. A major advantage of approaching the subject of sales from a “process point of view” is that it offers a host of well-tested design and improvement tools from other successful disciplines and process-oriented industries.] In turn, this offers potential for quicker progress. Quality expert Joseph Juran observed, “There should be no reason our familiar principles of quality and process engineering would not work in the sales process”. A sales team’s fundamental job is to move a greater number of larger deals through the sales process in less time. Specific steps or stages in a sales process vary from company to company but generally include the following elements:
- Initial contact
- Application of Initial Fit Criteria
- Sales lead
- Need identification
- Qualified prospect
- Proposal
- Negotiation
- Closing
- Deal Transaction
An alternate but similar series of steps is as follows:
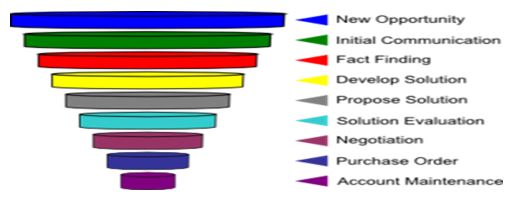
Sales tunnel layers
- Prospecting/Initial contact
- Preapproach- planning the sale
- Approach
- Need assessment
- Presentation
- Meeting objections
- Gaining commitment
- Follow-up
These eight steps of the sales process is more current/accurate compared to traditional sales. These are the typical steps taken, which are usually obtained in the same order, however can vary depending on the current situation. These steps of the sales process are given and explained in one of the most influential sales textbooks written by Gregory A. Rich, Rosann L. Spiro, and William J Stanton, entitled “Management of a Sales Force” Twelfth Edition.
Mapping a process provides a starting point for further careful analysis and continuous improvement. Diagramming a process flow is considered to be one of the seven basic quality improvement tools. ]Elements in the list above (among many others) have been described and/or flow-charted in the published literature. Some examples have primarily focused on functions performed by a sales “department”.At least one cross-functional approach depicts and integrates a variety of interdependent areas, such as sales, marketing, customer service, and information systems.
From a seller’s point of view, a sales process mitigates risk by stage-gating deals based on collection of information or execution of procedures that gate movement to the next step – Of the large number of initially interested persons on the narrow end of orders only a fraction of the initially interested people remain and actually place an order. This controls seller resource expenditure on non-performing deals. Ideally this also prevents buyers from purchasing products they don’t need though such a benefit requires ethical intentions by the seller. Because of the uncertainty of this assurance, buyers often have a buying or purchasing process. The interface between the selling and buying process has also been diagrammed.
A formalized sales process is generally more common for companies that either have complex sales cycles, large revenue risks that require systematic assurance of revenue generation, and/or those that choose to use a more consultative sales approach (e.g. Saturn, IBM, Hewlett-Packard).
An effective sales process can be described through steps that walk a salesperson from meeting the prospect all the way through closing the sale. Often a bad sales experience can be analyzed and shown to have skipped key steps. This is where a good sales process mitigates risk for both buyer and seller. A solid sales process also has the dramatic impact of forecasting accuracy and predictability in revenue results.
Many companies develop their own sales process; however, off the shelf versions are available from a number of companies in the sales performance improvement industry. A large number of these methods have been described by their promoters in books available to the public, primarily addressing tactics employed by an individual sales representative. These provide a customizable process and a set of electronic tools that can be freestanding or can be integrated if required with the company’s SFA, CRM, or other opportunity management system.
Seven Stages of selling process:
The process of selling has seven stages, namely, research, objectives, problem identification, objections, benefits, close and follow-up. Of these seven stages, research and objectives constitute the primary stages called preparation, whereas problem identification, objections and benefits make up the middle stages called negotiation. The final stages called relationship include close and follow-up.
It is believed that all the stages of selling process do not fall under the responsibility of a single person. Organizations, however, would prefer all these stages to be included under the responsibility of a single individual.
The research stage necessitates clear understanding of the product on the part of the sales person. He should study the relationship between the organization and the customer very well indeed. It would be advantageous for him to have a good idea about the products of the competitors too. Objectives have to be well set in terms of carrying out sales of the products to customers through negotiation since selling is about negotiation. Problem identification lies in allowing the customers to respond to questions that would strengthen a sales contact. These questions should center on the pros and the cons of the product as: In what way this product fails to meet your expectations?, What are the primary reasons for your interest in our product? and the like.
Any sales process would have objections as a natural part in the sense that they can prop up any time starting from the very beginning of a sales contact and ending when the sales person is about to close the sale. It is quite natural that objections have to be raised somewhere down the line. If objections are not raised, then any sales person that has a good standing in the field of product sales would sense something seriously wrong with the product or service. A good sales person should not view objections as mere excuses. Instead he should consider them genuine assertions that trigger further discussions pertaining to the quality of the product or the service. Hence it is an accepted fact that objections are viewed as assertions that bear great importance to a buyer.
Benefits lie in their presentation to the customers by the experienced sales person with a view to make them understand the advantages of the product better. Hence benefits can be conveyed in two phases, namely, when they are accrued by the possession of a particular product and when they are accrued by the association with the organization that manufactures the product or offers the service. Closing lies in closing the sale of a product. Sales negotiation gets to the last stage by the realization of the objectives of sales contact through close. Follow-up would simply mean after-sales service that results in more sales and improved business for the organization. Any sales person for that matter is expected to successfully carry out all these stages of selling process to nicety so that he becomes instrumental in boosting the sales of products and increasing the business of an organization too thereby.