Main purpose of this report is to analysis Assessment of Motivation Process of National Bank Limited. Here discuss various theories to assessment motivation process. Report discuss on Maslow’s theory, Two factor theory, Alderfer’s ERG theory, Equity theory, Reinforcement theory, Acquired needs theory, Cognitive evaluation theory, Expectancy theory etc. these are followed by National Bank Limited in their HR policy for motivation process.
Business of NBL
At present, NBL has been carrying on business through its 85 branches spread all over the country. Besides, the Bank has drawing arrangement with 415 correspondents in 75 countries of the world as well as with 32 overseas Exchange Companies. NBL was the first domestic bank to establish agency arrangement with the world famous Western Union in order to facilitate quick and safe remittance of the valuable foreign exchanges earned by the expatriate Bangladeshi nationals. NBL was also the first among domestic bands to introduce international Master Card in Bangladesh. In the meantime, NBL has also introduced the Visa Card and Power Card. The Bank has in its use the latest information technology services of SWIFT and REUTERS. NBL has been continuing its small credit programme for disbursement of collateral free agricultural loans among the poor farmers of Barindra area in Rajshahi district for improving their lot. Alongside banking activities, NBL is actively involved in sports and games as well as in various Socio-Cultural activities. Upto September 2006, the total number of workforce of NBL stood at 2239, which include 1689 officers and executives and 550 staff.
Social obligation and commitment
Inspired by its social obligation and commitment and responsibility, NBL has been running a School and College upto Class XII solely on its own guardianship. From the very inception, this institution has been maintaining a good track record of results at the SSC and HSC Examinations. Conducted by an well-educated and trained team of teachers, reputation of this institution has been increasing bay-by-day as a result of their relentless and sincere endeavor.
Awards
Transparency and accountability of a financial institution is reflected in its Annual Report containing its Balance Sheet and Profit & Loss Account. In recognition of this, NBL awarded Crest in 1999 and 2000, and Certificate on Appreciation in 2001 by the Institute of Chartered Accountants of Bangladesh.
Services of NBL
Consumer Credit Scheme
National Bank’s Consumer Credit Scheme gives you a great opportunity to buy household and office items on easy installments. This scheme gives you the advantage of part payment to cope with the high price tags of many necessary home and office appliances.
Television, Refrigerator, VCR, Personal Computer, Photo-Copier, Washing Machine, Furniture, Microwave Oven, Car, and a number of other expensive items are now within your buying range. With this scheme NBL makes better living possible for people living on fixed income. Customers can buy those home and office equipment’s without over taxing their budget.
Special Deposit Scheme
For most of the people on fixed income the opportunity to supplement their monthly earning is a golden one. And NBL Special Deposit Scheme gives a customer just that.
Under this scheme, customers can deposit, money for a term of 5 years. The deposited money is fully refundable at the expiry of the term. At the same time, during the term period they can enjoy a monthly profit corresponding to their deposited amount. As for instance, under this scheme a deposit of Tk,55,000/- gives a monthly income of Tk.500/-.
Monthly Savings Scheme
This scheme is specially designed for the benefit of the limited income group members. This helps to accrue small monthly savings into a significant sum at the end of the term. So, after the expiry of the term period the depositor will have a sizeable amount to relish on.
A monthly deposit of Tk.500/- or Tk.1000/- for 5 or 10 years period earns in the end Tk.40,100/- or Tk.2,24,500/- respectively.
Credit Card
Through its Credit Card. National Bank Limited has not only initiated a new scheme but also brought a new life style concept in Bangladesh. Now the dangers and the worries of carrying cash money are memories of the past.
Credit Card comes in both local and international forms, giving the client power to buy all over the World. Now enjoy the conveniences and advantages of Credit Card as you step into the new millennium.
NBL ATM Service
National Bank Limited has introduced ATM service to its Customers. The card will enable to save our valued customers from any kind of predicament in emergency situation and time consuming formalities. NBL ATM Card will give our distinguished Clients the opportunity to withdraw cash at any time, even in holidays, 24 hours a day, 7 days a week.
NBL ATM card – your access to prompt cash.
Saving Insurance Scheme
This is an uncertain World and the threatening silhouettes of future catastrophes are always looming around. This NBL scheme gives your family protection against the insecurities of the world. This scheme is the first of its kind in Bangladesh. It combines the benefits of regular savings and insurance scheme, so, you get the usual rate of interest on the deposited amount while you enjoy the protection of a comprehensive insurance coverage. Under this scheme, the beneficiary(ies) get equal the deposit in case of natural death of the account holder whereas in the event of accidental death of the account holder the beneficiary(ies) will receive twice the deposit. As for example, if a customer picks up Easy Class (Tk.50,000/-) he/she will get Tk.50,000/- for natural death and Tk.1,00,000/- for accidental death apart from his/her deposited amount and interest.
Western Union Money Transfer
Joining with the world’s largest money transfer service “Western Union”, NBL has introduced Bangladesh to the faster track of money remittance. Now money transfer between Bangladesh and any other part of the globe is safer and faster than ever before.
This simple transfer system ,being on line eliminates the complex process and makes it easy and convenient for both the sender and the receiver. Through NBL – Western Union Money Transfer Service, your money will reach its destination within a few minutes.
Motivation
Motivation refers to the initiation, direction, intensity and persistence of behavior (Geen, 1995). Motivation is a temporal and dynamic state that should not be confused with personality or emotion. Motivation is having the desire and willingness to do something. A motivated person can be reaching for a long-term goal such as becoming a professional writer or a more short-term goal like learning how to spell a particular word. Personality invariably refers to more or less permanent characteristics of an individual’s state of being (e.g., shy, extrovert, conscientious). As opposed to motivation, emotion refers to temporal states that do not immediately link to behavior (e.g., anger, grief, happiness).
Theory of motivation
There is various theory of motivation. Various experts define motivation in various ways. Here we will discuss about the early and contemporary theory of motivation.
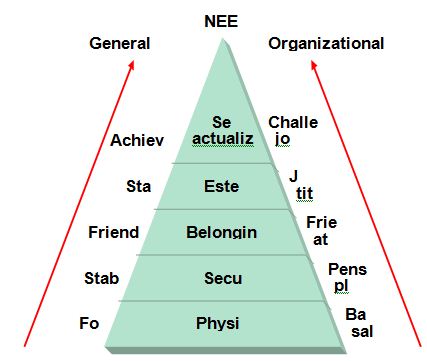
Maslow’s theory
Maslow’s Hierarchy of Needs is a theory in psychology that Abraham Maslow proposed in his 1943 paper A Theory of Human Motivation, which he subsequently extended to include his observations of man’s innate curiosity. His theory contends that as humans meet ‘basic needs’, they seek to satisfy successively ‘higher needs’ that occupy a set hierarchy. Maslow studied exemplary people such as Albert Einstein, Jane Addams, Eleanor Roosevelt, and Frederick Douglass rather than mentally ill or neurotic people, writing that “the study of crippled, stunted, immature, and unhealthy specimens can yield only a cripple psychology and a cripple philosophy.” Maslow also studied 1 percent of the healthiest college student population in order to obtain empirical research.
Maslow’s hierarchy of needs is often depicted as a pyramid consisting of five levels: the four lower levels are grouped together as deficiency needs associated with physiological needs, while the top level is termed growth needs associated with psychological needs. While deficiency needs must be met, growth needs are the need for personal growth. The basic concept is that the higher needs in this hierarchy only come into focus once all the needs that are lower down in the pyramid are mainly or entirely satisfied. Once an individual has moved past a level, those needs will no longer be prioritized. However, if a lower set of needs is continually unmet for an extended period of time, the individual will temporarily re-prioritize those needs – dropping down to that level until those lower needs are reasonably satisfied again. Innate growth forces constantly create upward movement in the hierarchy unless basic needs remain unmet indefinitely.
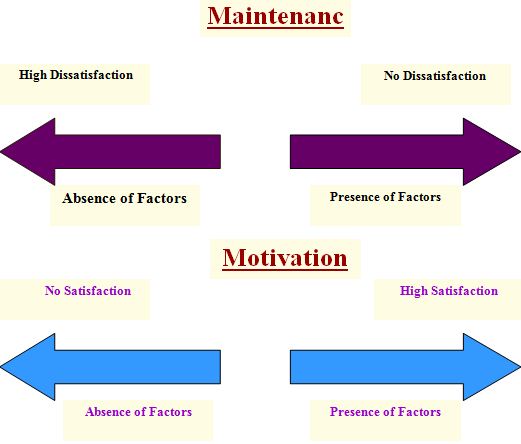
Two factor theory(Herzberg)
Frederick Herzberg, another well-known observer of management, developed a theory of motivation in his motivation-maintenance model.
Herzberg’s research indicates that two sets of factors affect how people behave in organizations. These two sets of factors are Maintenance and Motivation Factors.
Maintenance factors are those factors that prevent dissatisfaction but do not generate satisfaction or motivate workers to greater effort.
Motivation factors are those factors that provide satisfaction and therefore motivation, but whose absence causes no satisfaction.
Alderfer’s ERG theory
Alderfer classifies needs into three categories:
Growth need
- Relatedness needs
- Existence needs
Alderfer’s theory suggest that:
- Not every one is motivated by same thing.
- The needs hierarchy probably mirrors the organizational hierarchy to a certain extent.
Equity theory
Equity theory said that it is not the actual reward that motivate, but the perception, and the perception is based not on the reward in isolation, but in comparison with the efforts that went into getting it, and the reward and effort of others.
Reinforcement theory
It describes the effects of the consequence of a particular behavior on the future occurrence of the behavior. There are four types of Operant conditioning.
- Positive reinforcement.
- Negative reinforcement
- Extinction
- Punishment
Acquired needs theory
Some needs are acquired as a result of life experiences
- Needs for achievement, accomplish something difficult
- Needs for affiliation, from close personal relationship.
- Needs for power, control others.
Cognitive evaluation theory
This theory suggests that there are actually two motivation systems: intrinsic and extrinsic that corresponds to two kinds of motivators, Intrinsic motivators and extrinsic motivators.
Expectancy theory (Vroom):
Basically this theory comes down to this equation
Motivation= Expectancy*Instrumentality* Valence
Motivation methods
- Empowerment
- Creativity and innovation
- Learning
- Quality of life
- Monetary incentive
- Enhance persona fulfillment
- Giving respect
Scoring Key
Assessment
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 5 |
| 11 | 4 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 2 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 4 |
| 13 | 2 | |
| 20 | 5 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 5 |
| 14 | 5 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 3 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 3 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 4 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 3 |
| 18 | 5 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 4 |
| 10 | 5 | |
| 19 | 6 | |
| Total Score | 87 |
The score is little dissatisfactory for motivation process because the highest level of the score is 120
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 3 | 8 | Regular | 5 |
| 2 | Reverse | 2 | 9 | Regular | 3 |
| 3 | Reverse | 2 | 10 | Regular | 4 |
| 4 | Reverse | 1 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 3 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 0 | 13 | Regular | 4 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 3 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 3 | 8: | 5 | 8 | ||
| Training | 2: | 2 | 9: | 3 | 5 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 2 | 10: | 4 | 6 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 1 | 11: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 3 | 12: | 1 | 4 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 0 | 13: | 4 | 4 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 3 | 4 | ||
| Total | 38 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. so the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 2.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 5 |
| 11 | 6 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 5 |
| 12 | 6 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 4 |
| 13 | 3 | |
| 20 | 6 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 5 |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 5 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 4 | |
| 8 | 6 | |
| 17 | 4 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 4 |
| 18 | 3 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 6 | |
| 19 | 5 | |
| Total Score | 100 |
the score is standard.
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 2 | 8 | Regular | 1 |
| 2 | Reverse | 1 | 9 | Regular | 1 |
| 3 | Reverse | 2 | 10 | Regular | 2 |
| 4 | Reverse | 3 | 11 | Regular | 4 |
| 5 | Reverse | 1 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 2 | 13 | Regular | 3 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 2 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 2 | 8: | 1 | 3 | ||
| Training | 2: | 1 | 9: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 2 | 10: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 3 | 11: | 4 | 7 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 1 | 12: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 2 | 13: | 3 | 5 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Total | 26 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 3.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 5 |
| 11 | 5 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 6 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 6 |
| 13 | 5 | |
| 20 | 4 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 6 |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 6 | 4 | |
| 15 | 6 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 5 | |
| 8 | 6 | |
| 17 | 5 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 5 |
| 18 | 5 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 3 | |
| 19 | 4 | |
| Total Score | 103 |
The score is almost standard.
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 1 | 8 | Regular | 4 |
| 2 | Reverse | 0 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 1 | 10 | Regular | 5 |
| 4 | Reverse | 1 | 11 | Regular | 3 |
| 5 | Reverse | 2 | 12 | Regular | 2 |
| 6 | Reverse | 0 | 13 | Regular | 4 |
| 7 | Reverse | 3 | 14 | Regular | 5 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 1 | 8: | 4 | 5 | ||
| Training | 2: | 0 | 9: | 6 | 6 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 1 | 10: | 5 | 6 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 1 | 11: | 3 | 4 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 2 | 12: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 0 | 13: | 4 | 4 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 3 | 14: | 5 | 8 | ||
| Total | 37 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 4.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 6 |
| 11 | 6 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 6 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 5 |
| 13 | 3 | |
| 20 | 6 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 6 |
| 14 | 4 | |
| 6 | 3 | |
| 15 | 2 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 4 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 5 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 6 |
| 18 | 5 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 2 |
| 10 | 6 | |
| 19 | 6 | |
| Total Score | 97 |
The score is almost standard
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 0 | 8 | Regular | 1 |
| 2 | Reverse | 1 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 0 | 10 | Regular | 2 |
| 4 | Reverse | 0 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 1 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 1 | 13 | Regular | 2 |
| 7 | Reverse | 0 | 14 | Regular | 1 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 0 | 8: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Training | 2: | 1 | 9: | 6 | 7 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 0 | 10: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 0 | 11: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 1 | 12: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 1 | 13: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 0 | 14: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Total | 18 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 5.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 6 |
| 11 | 6 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 6 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 2 |
| 13 | 3 | |
| 20 | 6 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 3 |
| 14 | 5 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 2 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 6 |
| 16 | 5 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 6 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 6 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 6 | |
| 19 | 6 | |
| Total Score | 103 |
The score is satifactory
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 0 | 8 | Regular | 1 |
| 2 | Reverse | 1 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 0 | 10 | Regular | 1 |
| 4 | Reverse | 0 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 0 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 1 | 13 | Regular | 1 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 1 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 0 | 8: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Training | 2: | 1 | 9: | 6 | 7 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 0 | 10: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 0 | 11: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 0 | 12: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 1 | 13: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Total | 16 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 6.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 4 |
| 11 | 5 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 5 |
| 12 | 5 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 5 |
| 13 | 6 | |
| 20 | 4 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 2 |
| 14 | 2 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 2 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 5 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 6 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 6 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 4 | |
| 19 | 6 | |
| Total Score | 94 |
the score is satisfactory
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 2 | 8 | Regular | 6 |
| 2 | Reverse | 4 | 9 | Regular | 5 |
| 3 | Reverse | 4 | 10 | Regular | 6 |
| 4 | Reverse | 1 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 3 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 1 | 13 | Regular | 4 |
| 7 | Reverse | 3 | 14 | Regular | 3 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 2 | 8: | 6 | 8 | ||
| Training | 2: | 4 | 9: | 5 | 9 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 4 | 10: | 6 | 10 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 1 | 11: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 3 | 12: | 1 | 4 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 1 | 13: | 4 | 5 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 3 | 14: | 3 | 6 | ||
| Total | 45 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 7.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 5 |
| 11 | 6 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 5 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 6 |
| 13 | 5 | |
| 20 | 6 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 3 |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 2 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 5 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 6 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 6 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 4 | |
| 19 | 6 | |
| Total Score | 105 |
The score is almost standard
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 2 | 8 | Regular | 6 |
| 2 | Reverse | 3 | 9 | Regular | 5 |
| 3 | Reverse | 3 | 10 | Regular | 6 |
| 4 | Reverse | 1 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 3 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 1 | 13 | Regular | 4 |
| 7 | Reverse | 3 | 14 | Regular | 3 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 2 | 8: | 6 | 8 | ||
| Training | 2: | 3 | 9: | 5 | 8 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 3 | 10: | 6 | 9 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 1 | 11: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 3 | 12: | 1 | 4 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 1 | 13: | 4 | 5 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 3 | 14: | 3 | 6 | ||
| Total | 43 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 8.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 4 |
| 11 | 5 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 5 |
| 12 | 2 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 2 |
| 13 | 6 | |
| 20 | 5 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 3 |
| 14 | 1 | |
| 6 | 5 | |
| 15 | 1 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 6 | |
| 8 | 6 | |
| 17 | 6 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 4 |
| 18 | 5 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 4 | |
| 19 | 5 | |
| Total Score | 86 |
The score is little dissatisfactory.
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 1 | 8 | Regular | 2 |
| 2 | Reverse | 2 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 2 | 10 | Regular | 1 |
| 4 | Reverse | 2 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 0 | 12 | Regular | 2 |
| 6 | Reverse | 2 | 13 | Regular | 2 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 2 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 1 | 8: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Training | 2: | 2 | 9: | 6 | 8 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 2 | 10: | 1 | 3 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 2 | 11: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 0 | 12: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 2 | 13: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Total | 27 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 9.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 4 |
| 11 | 4 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 5 |
| 12 | 5 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 2 |
| 13 | 2 | |
| 20 | 5 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 3 |
| 14 | 1 | |
| 6 | 5 | |
| 15 | 1 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 6 | |
| 8 | 6 | |
| 17 | 6 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 4 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 4 | |
| 19 | 5 | |
| Total Score | 85 |
the score is little dissatisfactory
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 1 | 8 | Regular | 2 |
| 2 | Reverse | 2 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 2 | 10 | Regular | 1 |
| 4 | Reverse | 2 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 0 | 12 | Regular | 2 |
| 6 | Reverse | 2 | 13 | Regular | 2 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 2 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 1 | 8: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Training | 2: | 2 | 9: | 6 | 8 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 2 | 10: | 1 | 3 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 2 | 11: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 0 | 12: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 2 | 13: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Total | 27 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 10.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 6 |
| 11 | 6 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 5 |
| 12 | 6 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 2 |
| 13 | 5 | |
| 20 | 6 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 3 |
| 14 | 5 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 2 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 6 |
| 16 | 5 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 6 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 6 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 6 | |
| 19 | 6 | |
| Total Score | 104 |
the score is standard
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 0 | 8 | Regular | 1 |
| 2 | Reverse | 1 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 0 | 10 | Regular | 1 |
| 4 | Reverse | 0 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 0 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 1 | 13 | Regular | 1 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 1 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 0 | 8: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Training | 2: | 1 | 9: | 6 | 7 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 0 | 10: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 0 | 11: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 0 | 12: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 1 | 13: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Total | 16 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 11.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 6 |
| 11 | 6 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 6 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 2 |
| 13 | 6 | |
| 20 | 5 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 3 |
| 14 | 3 | |
| 6 | 5 | |
| 15 | 3 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 5 | |
| 8 | 6 | |
| 17 | 6 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 6 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 5 |
| 10 | 5 | |
| 19 | 5 | |
| Total Score | 100 |
the score is standard
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 0 | 8 | Regular | 1 |
| 2 | Reverse | 0 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 0 | 10 | Regular | 1 |
| 4 | Reverse | 1 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 1 | 12 | Regular | 2 |
| 6 | Reverse | 1 | 13 | Regular | 2 |
| 7 | Reverse | 0 | 14 | Regular | 2 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 0 | 8: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Training | 2: | 0 | 9: | 6 | 6 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 0 | 10: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 1 | 11: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 1 | 12: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 1 | 13: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 0 | 14: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Total | 19 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 12.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 5 |
| 11 | 6 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 6 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 5 |
| 13 | 5 | |
| 20 | 6 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 4 |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 6 | 4 | |
| 15 | 4 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 6 |
| 16 | 6 | |
| 8 | 4 | |
| 17 | 5 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 6 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 6 |
| 10 | 6 | |
| 19 | 4 | |
| Total Score | 106 |
the score is standard
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 0 | 8 | Regular | 1 |
| 2 | Reverse | 1 | 9 | Regular | 5 |
| 3 | Reverse | 1 | 10 | Regular | 1 |
| 4 | Reverse | 0 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 0 | 12 | Regular | 1 |
| 6 | Reverse | 0 | 13 | Regular | 1 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 1 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 0 | 8: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Training | 2: | 1 | 9: | 5 | 6 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 1 | 10: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 0 | 11: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 0 | 12: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 0 | 13: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 1 | 2 | ||
| Total | 15 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 13.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 4 |
| 11 | 4 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 5 |
| 12 | 1 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 6 |
| 13 | 6 | |
| 20 | 5 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 2 |
| 14 | 3 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 2 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 6 |
| 16 | 6 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 5 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 4 |
| 18 | 6 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 4 |
| 10 | 4 | |
| 19 | 3 | |
| Total Score | 88 |
the score is little dissatisfactory
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 1 | 8 | Regular | 2 |
| 2 | Reverse | 2 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 2 | 10 | Regular | 1 |
| 4 | Reverse | 2 | 11 | Regular | 2 |
| 5 | Reverse | 0 | 12 | Regular | 2 |
| 6 | Reverse | 2 | 13 | Regular | 2 |
| 7 | Reverse | 1 | 14 | Regular | 2 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 1 | 8: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Training | 2: | 2 | 9: | 6 | 8 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 2 | 10: | 1 | 3 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 2 | 11: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 0 | 12: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 2 | 13: | 2 | 4 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 1 | 14: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Total | 27 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 14.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 5 |
| 11 | 5 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 6 |
| 12 | 5 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 6 |
| 13 | 2 | |
| 20 | 5 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 4 |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 6 | 6 | |
| 15 | 3 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 4 | |
| 8 | 5 | |
| 17 | 5 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 4 |
| 18 | 4 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 4 |
| 10 | 5 | |
| 19 | 6 | |
| Total Score | 95 |
The score is standard
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 2 | 8 | Regular | 6 |
| 2 | Reverse | 3 | 9 | Regular | 6 |
| 3 | Reverse | 1 | 10 | Regular | 2 |
| 4 | Reverse | 3 | 11 | Regular | 5 |
| 5 | Reverse | 1 | 12 | Regular | 2 |
| 6 | Reverse | 3 | 13 | Regular | 4 |
| 7 | Reverse | 0 | 14 | Regular | 3 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 2 | 8: | 6 | 8 | ||
| Training | 2: | 3 | 9: | 6 | 9 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 1 | 10: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 3 | 11: | 5 | 8 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 1 | 12: | 2 | 3 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 3 | 13: | 4 | 7 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 0 | 14: | 3 | 3 | ||
| Total | 41 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Scoring Key
Assessment 15.
| Skill area | Item | Score |
| Diagnosing performance problem | 1 | 6 |
| 11 | 4 | |
| Establishing expectation and setting goals | 2 | 5 |
| 12 | 4 | |
| Facilitating performance (Enhancing ability) | 3 | 3 |
| 13 | 1 | |
| 20 | 4 | |
| Linking performance to rewards and discipline | 5 | 2 |
| 14 | 6 | |
| 6 | 5 | |
| 15 | 3 | |
| Using salient internal and external incentives | 7 | 5 |
| 16 | 6 | |
| 8 | 6 | |
| 17 | 4 | |
| Distributing rewards equitably | 9 | 4 |
| 18 | 4 | |
| Providing timely and straightforward performance feedback | 4 | 4 |
| 10 | 4 | |
| 19 | 4 | |
| Total Score | 84 |
the score is standard
Step-1
| Items | Score | Items | Score | ||
| 1 | Reverse | 1 | 8 | Regular | 3 |
| 2 | Reverse | 0 | 9 | Regular | 5 |
| 3 | Reverse | 0 | 10 | Regular | 2 |
| 4 | Reverse | 0 | 11 | Regular | 1 |
| 5 | Reverse | 0 | 12 | Regular | 3 |
| 6 | Reverse | 2 | 13 | Regular | 3 |
| 7 | Reverse | 0 | 14 | Regular | 3 |
Step-2
| Type of performance problem | Score on items | Total of two items | |||||
| Perception | 1: | 1 | 8: | 3 | 3 | ||
| Training | 2: | 0 | 9: | 5 | 5 | ||
| Aptitude | 3: | 0 | 10: | 2 | 2 | ||
| Resources | 4: | 0 | 11: | 1 | 1 | ||
| Expectations | 5: | 0 | 12: | 3 | 3 | ||
| Incentives | 6: | 2 | 13: | 3 | 5 | ||
| Reward salience | 7: | 0 | 14: | 3 | 3 | ||
| Total | 22 | ||||||
Below 50 is not standard. So the score is below standard.
Conclusion
Firm can motivate employee in various way. But rewarding employees financially improves level of employees work.. Renowned organization of the world gets success by using this motivating tool. But use of other tools re also very important. Because need of money is not important I all level of employee. Higher-level employee want something more than money.