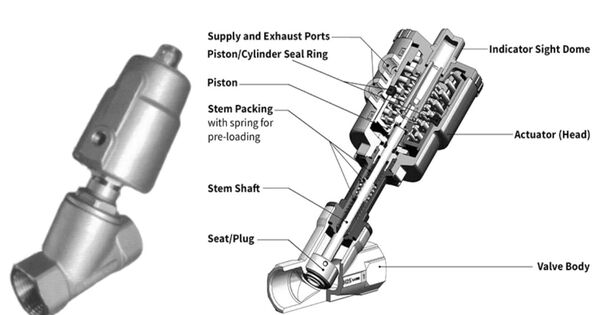
An angle seat piston valve is a pneumatically operated valve with a piston actuator that provides linear actuation to lift a seal from its seat. It is a pneumatic valve that controls the flow of fluids in a system. When unseated, the seat is tilted to allow for the most flow feasible. It is made out of a piston that moves linearly within a seat at an angle, therefore the name “angle seat.” This design ensures that the valve is sealed efficiently.
Angle seat piston valves are well suited to applications requiring high temperatures and high flow rates, such as steam or water. When used in reverse, several versions of angle seat piston valves eliminate water hammer.
Here’s how it typically works –
- Inlet and Outlet Ports: The valve has at least two ports, one for fluid inlet and one for fluid outlet. In some designs, there may be additional ports for auxiliary functions.
- Piston: Inside the valve, there’s a piston that moves up and down in response to changes in pressure. This piston is typically actuated by compressed air or another pneumatic actuator.
- Sealing Mechanism: The piston has a sealing element that forms a tight seal against the valve seat when the valve is closed. This prevents fluid from flowing through the valve.
- Flow Control: When the valve is actuated, the piston lifts off the seat, allowing fluid to flow through the valve. The flow rate can be controlled by adjusting the position of the piston.
- Reliability and Versatility: These are known for their reliability and versatility. They can handle a wide range of fluids and are suitable for applications where precise control of flow is required.
Common applications
These valves are commonly used in industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, water treatment, and HVAC (heating, ventilation, and air conditioning) systems. Their robust construction and efficient sealing make them suitable for various demanding environments.
- Steam Control: These are often used in steam control applications, where they regulate the flow of steam in heating systems, industrial processes, and steam-powered equipment.
- Liquid Control: They are employed in various liquid control applications such as water treatment plants, irrigation systems, beverage processing, and pharmaceutical manufacturing for precise control of liquid flow.
- Air and Gas Control: These valves are used in controlling air and gas flow in pneumatic systems, HVAC systems, gas boilers, and industrial gas processing plants.
- Cleaning Systems: They are utilized in cleaning systems such as car wash systems, industrial cleaning equipment, and automated cleaning processes for controlling the flow of cleaning agents and water.
- Textile Industry: In the textile industry, these valves are used in dyeing machines, fabric treatment processes, and textile manufacturing equipment for controlling the flow of chemicals and dyes.
- Agricultural Equipment: In agriculture, these are used in irrigation systems, fertilization equipment, and crop spraying systems for controlling the flow of water, fertilizers, and pesticides.
- Automotive Industry: They find applications in automotive manufacturing processes for controlling the flow of fluids in hydraulic systems, coolant systems, and lubrication systems.