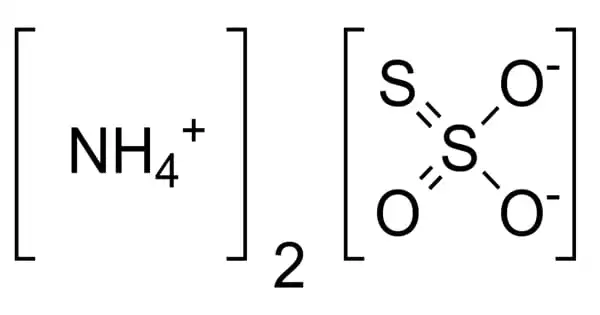The inorganic compound ammonium thiosulfate has the formula (NH4)2S2O3. It has an ammonia odor and is a white crystalline solid that is easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in acetone, and insoluble in ethanol and diethyl ether.
Ammonium thiosulfate is a crystalline white substance. It dissolves easily in water. The primary risk is the threat to the environment. Immediate action should be done to limit its environmental spread. It is utilized in photography, chemical analysis, and a variety of other applications.
Properties
Ammonium thiosulfate crystals are colorless, monoclinic, or white, with an ammonia-like odor. It is highly soluble in cold water, mildly soluble in acetone, and completely insoluble in alcohol and ether. It has an ammonia odor and is a white crystalline solid that is easily soluble in water, slightly soluble in acetone, and insoluble in ethanol and diethyl ether.
- Chemical formula: (NH4)2S2O3
- Molar mass: 148.20 g·mol−1
- Appearance: colorless or white, hygroscopic solid
- Density: 1.679 g/cm3
- Melting point: decomposes at 100 °C
- Solubility in water: 173 g/100 mL (20 °C)
- Solubility: slightly soluble in acetone; insoluble in alcohol

Production
It is produced by treating ammonium sulfite with sulfur at temperatures between 85 and 110 °C:
(NH4)2SO3 + S → (NH4)2S2O3
Preparation Method
Ammonium sulfite is generated by the reaction of ammonium bicarbonate with sulfur dioxide and water, and then reacts with sulfur, whereas ammonium thiosulfate is formed by filtration, evaporation, cooling crystallization, and separation. Alternatively, ammonium pentasulfide and excess aqueous ammonia are added to an aqueous solution of ammonium sulfate, and after the reaction, the sulfur is extracted by filtering and then evaporated under vacuum at a low temperature to get ammonium thiosulfate.
Applications
Ammonium thiosulfate is used in photographic fixer. It is a so-called rapid fixer, acting more quickly than sodium thiosulfate fixers. Fixation involves these chemical reactions (illustrated for silver bromide):
AgBr + 2 (NH4)2S2O3 → (NH4)3[Ag(S2O3)2] + NH4Br
AgBr + 3 (NH4)2S2O3 → (NH4)5[Ag(S2O3)3] + NH4Br
Ammonium thiosulfate is also employed in the leaching of gold and silver. It works because copper is present as a catalyst here. This method of gold cyanidation is harmless. The advantage of ammonium thiosulfate is that the pyrolysis of its silver complexes leaves just silver sulfide residue, as opposed to complexes formed from sodium thiosulfate.
Ammonium thiosulfate can also be used as a fertilizer. According to certain research investigations, it can also be utilized as an addition to coal-waste combinations to prevent the generation of dioxins and furans during combustion.