Amazon River, the greatest river of South America and the largest drainage system in the world in terms of the volume of its flow and the area of its basin. The Amazon River is the second longest river in the world, and the largest in terms of the size of its watershed, the number of tributaries, and the volume of water discharged into the sea. No bridge crosses the river along its entire length.

The total length of the river—as measured from the headwaters of the Ucayali-Apurímac river system in southern Peru—is at least 4,000 miles (6,400 km), which makes it slightly shorter than the Nile River but still the equivalent of the distance from New York City to Rome. Its westernmost source is high in the Andes Mountains, within 100 miles (160 km) of the Pacific Ocean, and its mouth is in the Atlantic Ocean, on the northeastern coast of Brazil. However, both the lengths of the Amazon and its ultimate source have been subjects of debate since the mid-20th century, and there are those who claim that the Amazon is actually longer than the Nile.
- Length: 4,345 mi
- Discharge: 7.381 million cubic feet per second
- Basin: 7,050,000 km2 (2,722,000 sq mi)
- Source: Mantaro River
- Mouth: Atlantic Ocean
- Countries: Brazil, Peru, Colombia
Length
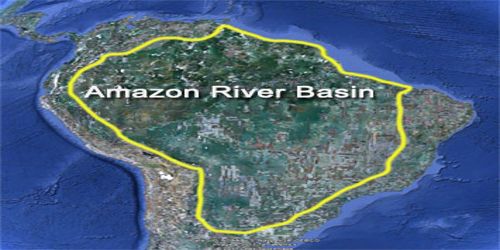
The vast Amazon basin (Amazonia), the largest lowland in Latin America, has an area of about 2.7 million square miles (7 million square km) and is nearly twice as large as that of the Congo River, the Earth’s other great equatorial drainage system. Stretching some 1,725 miles (2,780 km) from north to south at its widest point, the basin includes the greater part of Brazil and Peru, significant parts of Colombia, Ecuador, and Bolivia, and a small area of Venezuela; roughly two-thirds of the Amazon’s main stream and by far the largest portion of its basin are within Brazil.
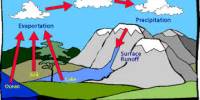
Rain Forest
The rainforest’s climate has heavy rainfalls and continuous high temperatures. These forests are so huge that scientists believe they actually help control the world’s climate in important ways. Destruction of the forests as settlers clear the land for farming and companies harvest trees for lumber is believed to be contributing to the problem of global warming.
People and Culture:
The Amazon is home to a variety of Indian cultures who have a great deal of knowledge about the rich and complex rainforest environment. As settlement brings changes to the forest, these cultural groups are also changing, and the lessons they have gained through thousands of years of living within the rainforest are in danger of being lost. Scientists are trying to learn from the Amazon’s native peoples about the amazing variety of rainforest plants and animals before they become extinct. Rainforest plants and animals may hold cures to diseases and provide information and materials valuable to people around the world.
Economic Importance of the Amazon River
The Amazon River is the second largest in the world. Found in South America, the river is 4,200 km long and holds a fifth of the whole world’s fresh water. Experts state that the Amazon flows at more than ten times the speed of the Mississippi river and every minute 12 billion liters of water flow in this river.
There are many benefits that the Amazon River offers the people who live around it. Amongst the key economic gains from this river include:
Fishing activities. The Amazon River has over 1,500 species of fish and some of these are harvested for trade purposes. These include the cat fish, turtles and other rare species of fish which are found in this fresh water river.
Trade channels. The governments of countries such as Brazil, Colombia, Peru, Ecuador and Bolivia have constructed transport systems especially roads around the Amazon River area to facilitate development projects and trade within these areas. The Amazon River has thousands of species of flora and fauna, most of which are exotic and rare. This has attracted several tourists to the area who come in search of adventure as well as research.
Mining and energy. Since the discovery of gold along the Amazon River in the 1980s, there have been several miners migrating into the area surrounding the river. Apart from gold, among the major minerals being mined includes bauxite. Additionally, the Amazon River is also known for hydro energy. Many companies are settling within the area in order to exploit the high potential of hydroelectric power supply.
The Amazon River is surrounded by tropical rainforests which have a huge variety of trees. The rubber trees in the rain forest are also very popular because of their high quality rubber products. There are also rose woods, Tonka bean woods and other scented trees that are used in making perfumes and other scented products.
A lot of land along the Amazon River has been turned to commercial farming purposes. This is because there are parts of the river basin which are highly fertile. Some of the crops that are grown on large scale are soybeans and corn.
Unfortunately, there have also been illegal economic activities within the Amazon River basin. For instance, illegal extraction of cocaine from the coca trees is one of the most lucrative economic activities that go on along the banks of river Amazon.
Amazon River Facts
- The Amazon River is located in South America. It runs through Guyana, Ecuador, Venezuela, Bolivia, Brazil, Colombia and Peru.
- There are no bridges that cross the Amazon, mostly because there is no need, the majority of the Amazon River runs through rainforests rather than roads or cities.
- The largest city along the Amazon River is Manaus. Located in Brazil it is home to over 1.7 million people.
- There are over 3000 known species of fish that live in the Amazon River, with more constantly being discovered.
- Anacondas lurk in the shallow waters of the Amazon Basin, they are one of the largest snakes in the world and occasionally attack larger animals such as goats that get to close the water.
- The Amazon River is also home to the piranha, a meat eating type of fish!
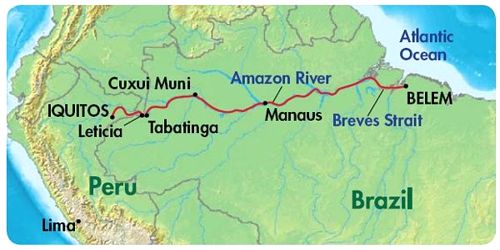
Conclusion: Due to the size of the Amazon River it is often called an Ocean River. The river is navigable by large cargo ships and ocean liners up stream for almost 2/3 of the length of the Amazon River from the Atlantic Ocean. Manaus, situated 1000 miles upstream is called on regularly by transatlantic sized ships. Iquitos Peru, at 2300 miles from the mouth of the Amazon River is the farthest inland port in the world that has ocean traffic.
Information Source: