Advanced maternal age (AMA) refers to a woman who becomes pregnant at age 35 or older. This term is used because the risk of certain complications during pregnancy and childbirth increases as a woman gets older.
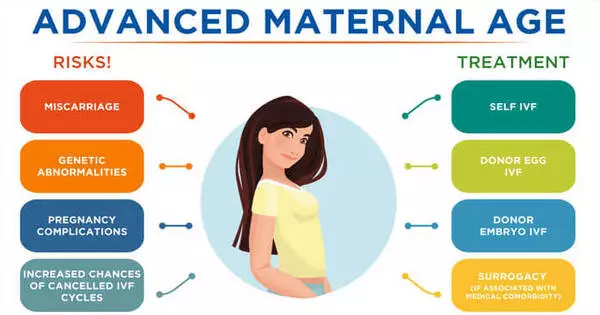
AMA is a medical term for women over the age of 35 who are pregnant. When the birth parent is 35 or older, there is an increased risk of certain complications. Some of these complications include increased miscarriage rates, genetic disorders, and pregnancy complications such as high blood pressure or gestational diabetes.
In a broad sense, advanced maternal age refers to a woman being of an older age at a stage of reproduction, though specific age and stage of reproduction are defined differently. The variability in definitions can be explained in part by the fact that the effects of increasing age occur as a continuum rather than as a threshold effect.
The average age of first childbirth has been increasing, particularly in OECD countries, with South Korea having the highest average age of 32.6, followed by 32.1. (Ireland and Spain). In a number of European countries (including Spain), the average age of women at first childbirth has surpassed 30 years. This is not a European-only phenomenon. Asia, Japan, and the United States are all seeing an increase in the average age at first birth, and the trend is spreading to developing countries such as China, Turkey, and Iran. In 2018, the average age of first childbirth in the United States was 26.9.
Advanced maternal age is linked to negative reproductive outcomes such as an increased risk of infertility and children with chromosomal abnormalities. The corresponding paternal age effect is weaker.
Some of the risks associated with advanced maternal age include:
- Increased risk of miscarriage
- Increased risk of chromosomal abnormalities, such as Down syndrome
- Increased risk of gestational diabetes
- Increased risk of high blood pressure and preeclampsia
- Increased risk of preterm birth
- Increased risk of stillbirth
- Increased risk of having a baby with a low birth weight
- Increased risk of having a baby with birth defects
It is important for women who are considering pregnancy at an advanced age to discuss the potential risks with their healthcare provider and receive appropriate prenatal care to monitor and manage any potential complications.