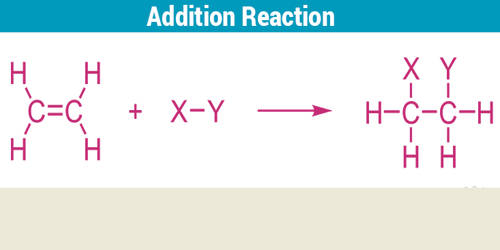Addition Reaction is a chemical reaction in which one molecule is added to another. An addition reaction, in organic chemistry, is in its simplest terms an organic reaction where two or more molecules combine to form a larger one (the adduct). It is a reaction in which one molecule combines with another to form a larger molecule with no other products. It occurs when atoms are added to a compound containing a double or triple bond.
An addition reaction is essentially a reverse decomposition reaction wherein a decomposition reaction is a reaction where one compounds one or more elements or compounds. They are limited to chemical compounds that have multiple bonds, such as molecules with carbon-carbon double bonds (alkenes), or with triple bonds (alkynes). It is a reaction in which radicals are added to both sides of a double or triple bond. Atoms can only be added to molecules when forming a product; nothing is eliminated or taken away. Molecules containing carbon—hetero double bonds like carbonyl (C=O) groups, or imine (C=An addition reaction is essentially a reverse decomposition reaction wherein a decomposition reaction is a reaction where one compounds one or more elements or compounds. N) groups, can undergo addition, as they too have double-bond character.
An addition reaction is the reverse of an elimination reaction. For instance, the hydration of an alkene to alcohol is reversed by dehydration. It may be visualized as a process by which the double or triple bonds are fully or partially broken in order to accommodate additional atoms or groups of atoms in the molecule. They are very useful for the modification of polymers and practically, many are identical to their small-molecule counterparts.
There are two main types of polar addition reactions: electrophilic addition and nucleophilic addition. Two non-polar addition reactions exist as well, called free-radical addition and cycloadditions. Addition reactions are also encountered in polymerizations and called addition polymerization.
Electrophilic Addition reactions – It can be described as an addition reaction in which a reactant with multiple bonds as in a double or triple bond undergoes has its π bond broken and two new σ bonds are formed.
Nucleophilic Addition reactions – It is an additional reaction where a chemical compound with an electron-deficient or electrophilic double or triple bond, a π bond, reacts with a nucleophile which is an electron-rich reactant with the disappearance of the double bond and creation of two new single, or σ, bonds.