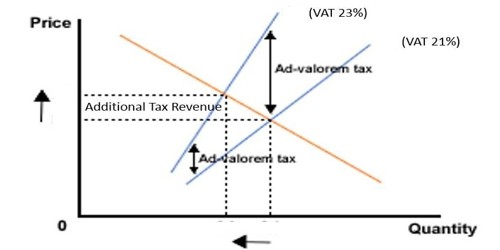
Ad valorem
It means “according to value”; An ad valorem refers to customs duty imposed on certain articles having regard only to the value or quality of articles and not the weight or quantity. It is charged by state and municipal governments, and it is based on the assessed value of a product or property. It is generally calculated as a percentage of the value of the property, rather than on size, weight, or quantity. It can also be imposed on estates and imports, and in other circumstances when a property changes hands, such as inheritance. Sales taxes of broad scope must of necessity have ad valorem rates. The most common ad valorem tax is the property tax, which is charged on real estate and personal property. Example: If the market value of a 2,000-square foot home is $100,000, the ad valorem property tax is based solely on the home’s value, regardless of its relative physical size.
An ad valorem tax is a tax based on the assessed value of an item, such as real estate or personal property. It is charged at the time of the transaction as is the case with Value Added Tax (VAT), which is deducted at the point of purchase. It is calculated according to the price of a product or service, rather than at a fixed rate. The assessed value of the property typically means the annual determination of fair market value, or the price that a potential buyer would pay and a potential seller would accept for a property. Example: Sales tax is a tax charged at the point of purchase of certain goods and services. The tax may be included in the price of the product or added at the point of sale. However, ad valorem taxes may also extend to a number of tax applications, such as import duty taxes on goods from abroad. These taxes comprise one of the primary sources of revenue for the state, county, and municipal governments.