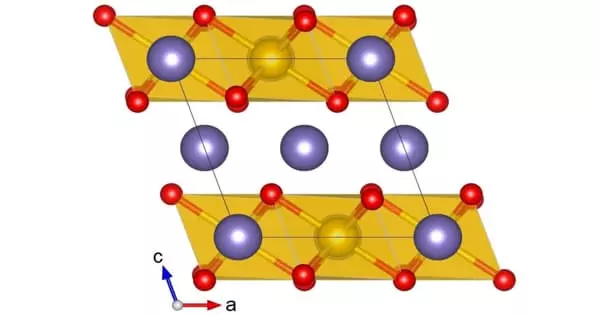
Abswurmbachite is a copper manganese silicate mineral [(Cu,Mn2+)Mn3+6O8SiO4]. Abswurmbachite was discovered in 1990 and named after a German mineralogist, Dr. Irmgard Abs-Wurmbach, a German mineralogist. It is found in Mili, Avia or Andros Island, Greece. It is not radioactive.
It crystallizes in the tetragonal system. Its Mohs scale rating is 6.5 and a specific gravity of 4.96. It has a metallic luster and its color is jet black, with light brown streaks.

Physical Properties
- Cleavage: None
- Color: Black, Dark brown.
- Density: 4.96
- Diaphaneity: Opaque
- Hardness: 6.5 – Pyrite
- Luster: Metallic
- Streak: brownish black
- Transparency: Opaque
- Comment: grey in reflected light.
- Hardness: 6½ on Mohs scale
- Density:4.96 g/cm3 (Calculated)
How to Identify Abswurmbachite
Abswurmbachite can be identified in the field by its brownish-black color. It is opaque, with a hardness of 6.5 (approximate to pyrite), and a density of 4.96g/cm3.
This mineral has a metallic lustre, with no cleavage.
Global Distribution
Abswurmbachite can be found on the islands of Greece at Mili, Evvia Island, and Apikia, Andros Island, and the Cyclades Islands.
Occurrence of Abswurmbachite and Useful Mineral Association
Abswurmbachite occurs in very low-grade, high-pressure metamorphic manganese-aluminum-rich quartzites.
It is often associated with minerals such as quartz, tenorite, ardennite, sursassite, rutile, hollandite, shattuckite, clinochlore, and piemontite.
Information Source: