Absolute Value of an Integer
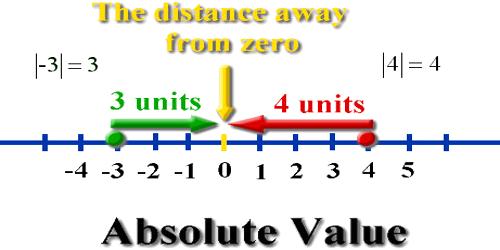
The absolute value of an integer is the numerical value without regard to whether the sign is negative or positive. On a number line it is the distance between the number and zero.
Absolute value describes the distance of a number on the number line from 0 without considering which direction from zero the number lies. The absolute value of a number is never negative. The absolute value of 5 is 5.
The absolute value of -15 is 15. The absolute value of +15 is 15
The symbol for absolute value is to enclose the number between vertical bars such as |-20| = 20 and read “The absolute value of -20 equals 20”.
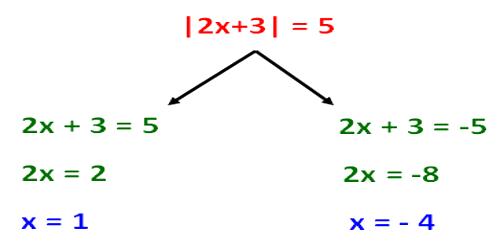
Absolute value describes the distance of a number on the number line from 0 without considering which direction from zero the number lies. The absolute value of a number is never negative.
Symbol used in absolute value
The symbol used to denote the absolute value is, two vertical lines (| |), one on either side of an integer.
Therefore, if ‘a’ represents an integer, its absolute value is represented by |a| and is always non-negative
Note:
(i) |a| = a; when ‘a’ is positive or zero.
(ii) |a| = -a; when ‘a’ is negative.
Examples on absolute value of an integer:
(i) Absolute value of – 7 is written as |- 7| = 7 [here mod of – 7 = 7]
(ii) Absolute value of + 2 is written as |+ 2| = 2 [here mod of + 2 = 2]
(iii) Absolute value of – 15 is written as |- 15| = 15 [here mod of – 15 = 15]
(iv) Absolute value of + 17 is written as |+ 17| = 17 [here mod of + 17 = 17]
Sample Problem
What’s the value of -|-5|?
We’ve got two negative signs and an absolute value sign. Let’s work our way from the inside out. Remember, anything inside those absolute value bars is positive.
-|-5| = -(5) = -5
Information Source: