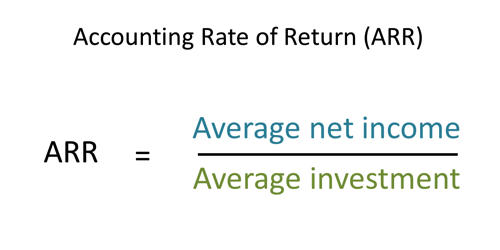Variable costing is a methodology that only assigns variable costs to inventory. This method requires that all overhead costs be charged to expense in the period in which they are incurred, while direct materials and variable overhead costs are assigned to inventory. The variable costing system is commonly used for internal management rather than external reporting. It is more useful for making managerial decisions, profit planning, cost control, pricing, and so on.
Management frequently employs variable costing to assist with a variety of decisions. For example, a break-even analysis could be used to determine the sales level at which a company makes no profit. Another possibility is to use it to determine the lowest possible price at which a product can be sold.
The importance or uses of variable costing system can be expressed as follows:
(1) Profit Planning
It is a method of developing and implementing an operational plan with the goal of exceeding the profit target. It focuses on the contribution margin, which aids in understanding the interdependence of cost, volume, and profit.
Variable costing aids in determining the break-even sales as well as the sales level at which the company will be able to achieve the desired profit. Variable costing also aids in determining the impact on profit of changes in volume, variable and fixed costs, and product mix. The contribution margin allows for the most profitable products, territories, and customers to be chosen.
(2) Cost Control
Standard costing and a flexible budget are the most important cost-control tools. This costing system divides costs into fixed and variable costs in order to control costs. So, the fixed cost is treated as the period cost and deducted from the contribution margin to calculate profit. As a result, variable costing is a critical method for reducing unnecessary costs.
(3) Decision Making
The cost of the product is an important consideration in decision-making. Variable costing identifies and categorizes costs into fixed and variable costs, providing useful information for decision-making. Fixed costs, in general, complicate decision-making due to difficulties in allocating them. They are assumed to be constant in variable costing and are not considered relevant in decision-making.
The fixed costs are treated as period costs, and the profit is the contribution margin above the fixed costs. In a decision involving multiple options, the option with the highest contribution margin is chosen. Pricing decisions, make or buy decisions, product mix decisions, and so on are examples of decision areas where variable costing is particularly useful and relevant.
(4) Pricing Decision
Variable costing assists management in price, volume, or sales mix fixation because variable costing clearly identifies the reasons for profit fluctuation is due to sales fluctuation rather than production fluctuation. Furthermore, it is useful in evaluating the performance of various departments of the firm that generate revenues.
Variable costing has no application in financial reporting because accounting frameworks (such as GAAP and IFRS) require that overhead be allocated to inventory as well. The frameworks do not recommend variable costing because it does a poor job of matching revenues with all related expenses. Under variable costing, overhead costs are charged to expense all at once, rather than when the associated sales occur (which may be in a later period). Consequently, this methodology is only used for internal reporting purposes.