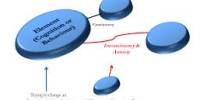
Socialization is known as the process of inducting the individual into the social world. It is the means by which human infants begin to acquire the skills necessary to perform as functioning members of their society. The term socialization refers to the process of interaction through which the growing individual learns the habits, attitudes, values, and beliefs of the social group into which he has been born.
Types of Socialization-
- Group socialization
Group socialization is held that an individual’s peer groups, rather than parental figures, influences his or her personality and behavior in adulthood. Adolescents spend more time with peers than with parents. Therefore, peer groups have stronger correlations with personality development than parental figures do.
- Gender Socialization
Henslin contends that “an important part of socialization is the learning of culturally defined gender roles.” Gender socialization refers to the learning of behavior and attitudes considered appropriate for a given sex. Boys learn to be boys and girls learn to be girls. This “learning” happens by way of many different agents of socialization. Parents play a very significant role in gender socialization.
- Anticipatory socialization and Re-socialization
Anticipatory socialization refers to the processes of socialization in which a person “rehearses” for future positions, occupations, and social relationships. Re-socialization refers to the process of discarding former behavior patterns and reflexes, accepting new ones as part of a transition in one’s life.
- Racial socialization and cultural socialization:
Racial socialization has been defined as “the developmental processes by which children acquire the behaviors, perceptions, values, and attitudes of an ethnic group, and come to see themselves and others as members of the group”.
- Planned socialization and Natural Socialization
Planned socialization occurs when other people take actions designed to teach or train others—from infancy on. Natural socialization occurs when infants and youngsters explore, play and discover the social world around them.
- Positive socialization and Negative socialization
Positive socialization is the type of social learning that is based on pleasurable and exciting experiences. We tend to like the people who fill our social learning processes with positive motivation, loving care, and rewarding opportunities.
- Broad and Narrow Socialization
Arnett proposed an interesting though seldom used distinction in types of socialization. Arnett distinguishes between broad and narrow socialization. Broad socialization is intended to promote independence, individualism, and self-expression; it is dubbed broad because this type of socialization has the potential of resulting in a broad range of outcomes.
- Primary and Secondary Socialization
Primary socialization takes place early in life, as a child and adolescent. Primary socialization for a child is very important because it sets the groundwork for all future socialization. Primary Socialization occurs when a child learns the attitudes, values, and actions appropriate to individuals as members of a particular culture. It is mainly influenced by the immediate family and friends. Secondary socialization refers to the socialization that takes place throughout one’s life, both as a child and as one encounters new groups that require additional socialization. Secondary socialization refers to the process of learning what is the appropriate behavior as a member of a smaller group within the larger society.
Information Source: