1.4 Methodology of the Study:
Different data and information are required to meet the goal of this report. Those data and information where collected from various sources, such as, primary and secondary which is showed below:
Table no-1
Departments | Duration |
General Banking | From 15th October – 14 November |
Investment Department | From 15th November – 14 December |
Capital:
The bank started with an authorized capital of TK. 100 million in 1999 and as on 31st December 2000 paid up capital stood at TK. 22.50 million. The paid up capital stood at TK. 31.39 million as on 31st december2000
Table no-2
Authorized Capital (TK) in Million | Year | Paid Up Capital(TK) In Million |
1000 | 2007 | 878.85 |
1000 | 2006 | 627.75 |
1000 | 2005 | 313.88 |
1000 | 2004 | 253.13 |
1000 | 2002 | 225.00 |
Diagram Capital position of Exim Bank:
Source: Annual Reports-2004, 2005, 2006 and 2007
2.3 Components of Capital Structure and correspondent Contribution: Figures of different components of the capital structure for the year 2002, 2003 and 2004,2005 are shown below.
Table no-3
Figures in million TK
| Components of capital | 2003 | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 |
| Paid up capital | 253.13(75.82%) | 313.88(48.7%) | 627.75(45.91%) | 878.85(41.94%) |
| Proposed issue of bonus share | —— | 28.125(6.09%) | 60.750(11.02%) | —– |
| Share premium | —— | 15.750(3.41%) | 82.575(14.98%) | 82.575(11.03%) |
| Statutory reserve | 16.045(5.41%) | 64.896(14.05%) | 132.501(24.03%) | 228.202(30.5%) |
| Other reserve | 23.612(7.96%) | 54.718(11.84%) | —— | —— |
| Proposed cash dividend | 31.500(10.62%) | 56.250(12.18%) | 20.250(3.67%) | —— |
| Retained earnings | 0.590(0.2%) | 17.227(3.73%) | 2.131(0.39%) | 123.622(16.53%) |
| Total | 296.747(100%) | 461.966(100%) | 551.332(100%) | 748.274(100%) |
Exim Bank Limited annual report of the year 2000, capital structure did not contain any value for the component of proposed cash dividend, but in the annual report of the year 2001, it was maintained that proposed cash dividend was 31.5 million taka for the year 2000. Annual reports- 2003, 2004, 2005 and 2006 From the table in the last page, paid up capital was the largest component of the bank’s capital structure for each year though contribution of this component in the capital structure was declining gradually. Two components of the capital structure, proposed issue of bonus share and share premium had no contribution in the capital structure in the year 2000. It is observed that in the year 2003 there is neither proposed issue of bonus share nor proposed cash dividend. Instead of these two things the amount of retained earnings becomes too large.
Table no-4
Year | Amount of Deposit ( TK in Million) |
2006 | 28329.21 |
2005 | 19078.18 |
2004 | 15242.97 |
2003 | 9945.23 |
Source: Annual Reports- 2003, 2004, 2005and 2006
Deposit in EXIM Bank:
Loan and Advance position of Exim Bank:
Table no-5
Year | Amount ( TK in Million) |
2006 | 26046.34 |
2005 | 19332.44 |
2004 | 12289.10 |
2003 | 7954.56 |
2002 | 5131.55 |
Source: Annual Reports- 2003, 2004, 2005and 2006
2.7 Investment:
On December 31, 2005 the total amount of investment is 2377.07 million taka, which was 1419.00 million taka last year. The amount has increased by 958.07 million taka. The notable investment represents development in Treasury bills and shares, Prize bond and others. Table no-6
Year | Amount ( TK in Million) |
2006 | 1633.03 |
2005 | 1542.99 |
2004 | 2377.073 |
2003 | 1419.00 |
2002 | 829.060 |
Source: Annual Reports- 2003, 2004, 2005and 2006
Investment Activities of EXIM Bank
2.8 Import Business:
The total import business handled by the bank during the year 2002 was TK. 13152.50 million. Imported Tk.19260 million of goods.
Handing the amount of Import Business:
Table no-7
Year | Amount ( TK in Million) |
2006 | 41432.07 |
2005 | 26781.70 |
2004 | 19260.01 |
2003 | 13152.50 |
2002 | 8519.70 |
Source: Annual Reports- 2003, 2004, 2005and 2006
Handling of Import Business in EXIM Bank:
Table no-8
Year | Amount ( TK in Million) |
2006 | 31285.37 |
2005 | 22418.50 |
2004 | 15124.60 |
2003 | 10088.30 |
2002 | 7442.20 |
Source: Annual Reports- 2003, 2004, 2005and 2006
Source: Annual Reports- 2003, 2004, 2005and 2006
2.10 Launching of Islami Banking:
Considering the inherent desire of the religious Muslims, Exim Bank has launched Islami banking system and inaugurates two Islami banking Branches in the year 2002. The Islami banking branches perform their activities under the guidance and supervision of a body called “SHARIAH COUNCIL”. 2.11 SWIFT Service: The SWIFT service helped the bank in sending and receiving the messages and instruction related to our NOSTRO account operations and L/C related matters. We have brought 6 of our branches under SWIFT network. Other branches will come under the network hopefully by the year 2004. Besides we have BKE arrangements with 430 bank branches in 100 countries.
Organizing:
Exim Bank is organized as per the existing business location. It has twenty- four branches each of which is a separate entity. Each unit is responsible for own performance and a senior vice president (SVP) followed by manager heads each. He is responsible for the performance of their unit.
Directing and Controlling:
The management approach in Exim Bank is top down. Information just seeks through lower management layer. Works are designed in such a way that one cannot leave without clearing the tasks as he is assigned for a day. Sitting arrangement in all office is done in a way that the superior can monitor the subordinate all time. Budgeting rewarding, punishing, etc. are also practiced as control mechanism.
F. Jessor Branch
2.17 Exim Bank at a Glance:
Export Import Bank of Bangladesh Limited
EXIM BANK AT A GLANCE
Table # 01 Amount in crore
| SL No. | Particular | 2004 | 2005 | 2006 | % of Growth |
| 01. | Authorize Capital | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 | 0.00% |
| 02. | Paid-up capital | 31.39 | 62.78 | 31.39 | 100.00% |
| 03. | Reserve Fund | 30.05 | 35.73 | 30.05 | 18.90% |
| 04. | Deposit | 1524.29 | 1907.81 | 1526.15 | 18.90% |
| 05. | Investment (General) | 1228.91 | 1933.24 | 1228.91 | 57.31% |
| 06. | Investment (Share & Bonds) | 237.70 | 154.29 | 237.70 | -35.09% |
| 07. | Foreign Exchange Business | 3461.97 | 4931.39 | 3461.97 | 42.44% |
| a) Import Business | 1926.01 | 2678.18 | 1926.01 | 39.05% | |
| b) Export Business | 1512.42 | 2241.84 | 1512.46 | 48.22% | |
| c) Remittance | 23.50 | 11.37 | 23.50 | -51.61% | |
| 08. | Operating Profit | 56.26 | 83.58 | 60.64 | 48.52% |
| 09. | Fixed Assets | 12.77 | 15.08 | 12.77 | 18.08% |
| 10. | Loan as a % of total deposit | 80.62% | 92.68% | 80.52% | 14.96% |
| 11. | No. of Foreign Correspondents | 185 | 190 | 185 | 2.70% |
| 12. | Number of Employee | 627 | 768 | 627 | 22.49% |
| 13. | Number of Branches | 19 | 28 | 19 | 47.37% |
| 14. | Cost of Fund | 9.26% | 8.40% | 9.26% | -9.28% |
| 15. | Cost of Fund with E.C | 11.30% | 11.00% | 11.30% | -2.65% |
| 16. | Return on Assets | 3.15% | 3.44% | 3.39% | 9.20% |
Source: Annual Report-2003, 2004, 2005 and 2006
2.18 Export Import Bank of Bangladesh Limited
Year- wise comparative net profit position of Bank
Table # 02 (Amount in Crore)
Particulars | Year 2002 | Year 2003 | Year 2004 | % of Growth | |
| SS | Investment Income Investment Expense | 98.58 72.72 | 139.60 112.13 | 182.02 142.55 | 30.39% 27.13% |
| DD: | Net Investment Income Exchange, Commission & Others | 25.86 33.41 | 27.47 56.59 | 39.47 82.43 | 43.68% 45.66% |
| SS | Administrative Expenses | 59.27 18.87 | 84.06 27.79 | 121.90 38.32 | 45.01% 37.89% |
| Net position | 40.40 | 56.27 | 83.58 | 48.53% | |
Source: Annual Report-2003, 2004, 2005 and 2006
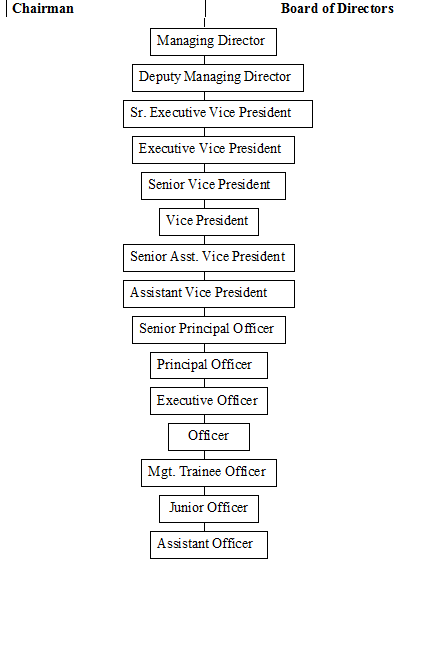
2.19 Hierarchy of position in Exim Bank Ltd.
OVERALL GENERAL ACTIVITIES OF EXIM BANK IBB
General Banking
3.1 Introduction:
Exim Bank General Banking department does the most important and basic work of the bank. Its other departments are liked with this department. Exim Bank also played a vital role in deposit mobilization of the branch. According to customer demand Exim Bank provides different types of account and special types of saving scheme under general banking. On the basic of customer demand and its proper functioning and excellent customer service this department is divided into various sections namely as below:
►Accounts Opening Section
►Cash Section
►Deposit Section
►Bills and Clearing Section
►Remittance section
►FDR Section
►Accounts Sections
Accounts Opening Section:
This section deals with opening of different types of accounts. It is also deals with issuing of checkbooks and different accounts openers. A customer can open different types of accounts though this department such as:
1. CD-AI- Wadiah Current Deposit
2. SB- Mudaraba Saving Deposit
3. STD- Short Term Deposit
4. MTD- Mudaraba Term Deposit
5. SS- Short scheme
a) MSS – Monthly saving Scheme
b) MPSS – Multi plus Super Saving Scheme
c) SSS – Super Saving Scheme
6. ESS- Education Saving Scheme.
7. INV – Investment Account
8. FC – Foreign Currency Account
9. BCD – bearer certificate Deposit
10. Exim Bank Hajj Account project.
As it is an Islami banking Branch the following rules are applied here:
a) Current deposit will be received on Al- Wadiah principal & the same will not get any profit.
b) Savings deposit will be accepted on Mudaraba principal & such deposit will bear 0.62-weight age.
Islami Banking Terms:
In Bangladesh their few banks whop have Islami Banking Deposit, Exim Bank is one of them. For the convenient of the reader who are not familiar with the Islami Banking
Term, the following are some terms of Islami Banking for mobilization of deposit and the schemes are becoming popular day by day.
Al Wadiah Account:
The characteristics of this account are almost similar to current of conventional banks. The owner of the fund does not enjoy any profit nor bear any loss. But the bank obtains the permission from the depositors so that the bank has the option to use the fund when it is necessary.
Mudaraba Saving Account:
Mechanism is almost similar to the saving account of the conventional bank. The basic difference in this case is that the bank and the owner of the fund will share the profit from the investment while the loss from the investment will be borne by the owner of the fund unless the loss is incurred due to the negligence or convenience of the bank. His account. Generally, current account is opened for business and traders
3.2 Revised Rate of interest for Non Islamic Bank affected from 12.01.2004:
Particular | Deposit Rates |
|
Types of Deposit
a) 3 months b) 6 months c) 1 Year |
0.00% 7.50% 6.00% Up to 50 Lac 8.75% 9.25% 9.75% |
Up to 50 Lac 9.00% 9.50% 10.00% |
3.3 Existing Rate of Profit:
MIS ( MONTHLY SAVING SCHEME)
AMMOUNT ON MATURITY AGAINST SAVINGS SCHEME
Terms | Monthly Installment | Monthly Installment | Monthly Installment |
Tk. 1000.00 | Tk.2000.00 | Tk.5000.00 (App) | |
5 Years | Tk. 78258.00 | Tk. 156315.00 | Tk.390788.00 (App) |
8 Years | Tk. 148810.00 | Tk. 297620.00 | Tk.744051.00 (App) |
10 Years | Tk. 210208.00 | Tk. 420417.00 | Tk.1051042.00 (App) |
12 Years | Tk. 286417.00 | Tk. 572835.00 | Tk.1432087.00 (App) |
MIS (MONTHLY INCOME SCHEME)
Deposit Amount | Income |
Tk. 115000 | Tk.1000 (App) |
Tk. 230000 | Tk.2000 (App) |
Tk. 460000 | Tk.4000 (App) |
SSS (SUPER SAVING SCHEME)
Deposit | Term | Payable at Maturity | Payable amount |
10000/- | 7 Years | Double | Tk. 20000/- (App) |
20000/- | 7 Years | Double | Tk. 40000/- (App) |
50000/- | 7 Years | Double | Tk. 100000/- (App) |
100000/- | 7 Years | Double | Tk. 200000/- (App) |
200000/- | 7 Years | Double | Tk. 400000/- (App) |
500000/- | 7 Years | Double | Tk. 1000000/- (App) |
MPSS (MULTI PLUS SUPER SAVINGS SCHEME)
AMOUNT | Tk. 10000.00 | Tk. 20000.00 | Tk. 50000.00 | Tk. 100000/- (App) |
1ST | Tk. 11051.00 | Tk. 22102.00 | Tk. 55255.00 | Tk. 110510.00 (App) |
2ND | Tk. 12212.00 | Tk. 24425.00 | Tk. 61062.00 | Tk. 122125.00 (App) |
3rd | Tk. 13496.00 | Tk. 26992.00 | Tk.67480.00 | Tk. 134960.00 (App) |
4th | Tk. 14914.00 | Tk. 29829.00 | Tk. 74572.00 | Tk. 149144.00 (App) |
5th | Tk. 16482.00 | Tk. 32964.00 | Tk. 82410.00 | Tk. 164819.00 (App) |
6th | Tk. 18214.00 | Tk. 36428.00 | Tk. 91071.00 | Tk. 182142.00 (App) |
7th | Tk. 20128.00 | Tk. 40257.00 | Tk. 100642.00 | Tk. 201285.00 (App) |
8th | Tk. 22244.00 | Tk. 44488.00 | Tk. 111220.00 | Tk. 222440.00 (App) |
9th | Tk. 24582.00 | Tk. 49164.00 | Tk. 122909.00 | Tk. 245818.00 (App) |
10th | Tk. 27165.00 | Tk. 54331.00 | Tk. 135827.00 | Tk. 271654.00 (App) |
11th | Tk. 30020.00 | Tk. 60041.00 | Tk. 150102.00 | Tk. 300205.00 (App) |
3.4 The following procedures are maintained for issuing of a check book:
► At first the customer will fill up the check requisition form.
► The leaves of the check book under issue shall be counted to ensure that all the levels and the bank requisition slip are intact and the name and account number shall be written on the cover page on check book. The account number of the customers shall be entered on all the leaves of the check book and its requisition slip.
► The name and account number of the customers shall be entered in the check book register against the particular check book series.
► Then the register check book and the requisition slip are signed by the officer in charge of the deposit department.
► Then the check book is handed over to the customer after talking acknowledgement on the requisition slip and the register book.
A cover file containing the requisition slip shall be effectively preserved as vouchers. If the ledger keeper notices any defect, he will make a remark to that effect on the requisition slip and forward it to the cancellation officer to decide whether a new check book should be issued or not.
3.5 Cash Department:
Cash section of any bank plays a vital role in general banking procedure. Because it deals with the most liquid assets. There is several counters work simultaneously in cash section of EXIM bank, Rajuk Avenue Branch. There is also some electronic counting machines by which a huge amount of cash money can be counted within a few minutes.
3.6 Cash Receiving Procedure:
The work of cash receiving counter is examining deposit slip.
Depositor uses the prescribed deposit slip supplied by the bank for deposit cash, check, draft pay order etc. in all types of deposits the teller must check the following things.
►The slip has been property filed up.
►The title of the account and in its number.
►The amount in figure and in words is same.
►Instrument signed by the depositor.
►Date of the instrument.
After checking all these things the teller will accept cash, check, draft, pay order etc. against deposit slip. The teller will place the cash in the cash in drawer according to denominations. The teller will place signature and affix cash receipt, rubber stamp seal and record in the cash received register book against the account number. At the end of this procedure. The cash officer passes the deposit slip to the computer section for positing purpose and returns the customer’s copy.
3.7 Cash payments procedures:
In order to safe guard the position the paying banker has observe the following precaution before honoring a check:
► A check must be looked whether it is an opened or crossed check.
► The paying officer should see whether the check is drawn on his/her branch.
► He must see if the check is post dated or pre dated. A letter must not pay any post-dated cheque.
► The office must carefully see the apartment tenor of the check. If it is mutilated or materially altered then the officer must not honor it.
► The officer must compare the signature of the check with the signature on the specimen signature card.
► The officer must verify the regularity of the endorsement.
► The officer may allow overdue against a check if prior arrangement is done with the bank.
3.8 Cash Section:
Banks as a financial institution, accept surplus money from the people as deposit and given them opportunity to withdraw the same by cheque, etc. but among the banking activities, cash department plays an important role. It does the main function of a commercial bank i.e. receiving the deposit and paying the cash on demand. As this department deals directly with the customer, the reputation of the bank depends much on it. The functions of a cash department are described bellow:
Function of cash Department
| Cash Payment |
|
| Cash Receipt |
|
Cash packing:
After the banking hour cash is packed according to the denomination. Notes are counted and packed in bundles and stamps with initial.
Allocation of Currency:
Before starting the banking hour all tellers gave requisition of money though “Teller cash proof Sheet”. The head teller writes the number of the packet denomination wish in “Reserve Sheet” at the end of the day; all the notes remained are recorded in the sheet.
Local remittance Section:
Carrying cash money is troublesome and risky. That’s why money can be transferred from one place to another through banking channel. This is called remittance. Remittances of funds are one of the most important aspects of the commercial banks in rendering services to its customers.
Types of remittance:
► Between banks and non banks customer
► Between banks in the same country
► Between banks in the different centers
► Between banks and central bank in the same country
► Between central bank of different customers.
The main ways used by Exim Bank for remitting funds are:
► Payment order (PO)
► Demand Draft (DD)
►Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
3.9 The Basic Three Types Of Local Remittances Are Discussed Below:
| Points | Pay Order | Demand Draft | TT |
| Explanation | Demand Draft is an order of issuing bank on another branch of the same bank to pay specified sum of money to payee on demand | Issuing branch requests another branch to pay specified money to the specific payee on demand by telegraph/ telephone | |
| Payment from | Payment from issuing branch only | Payment from ordered branch | Payment from ordered branch |
| Generally used to Remit fund | Within the clearinghouse are of issuing branch. | Outside the clearinghouse area of issuing branch. Payee can also be the purchaser. | Anywhere in the country |
| Payment process of the paying bank | Payment is made through clearing |
| |
| Charge | Only commission | Commission + telex charge | Commission + telephone |
Test-key Arrangement:
Test key arrangement is a secret code maintained by the banks for the authentication for their telex messages. It is a systematic procedure by which a test number is and the person to whom this number is given can easily authenticate the same test number by maintaining that same procedure. Exim Bank has test key arrangement with so many banks for the authentication of LC message and for making payment.
Commission for PO:
Exim Bank charges different amount of commission on the basis of payment order amount. The bank charges for pay order are given in the following chart:
Table no 9
Commission & VAT for PO
Total amount of PO | Commission | VAT |
Up to Tk. 10000.00 | Tk. 15.00 | Tk. 3 |
Tk. 10001.00-Tk. 100000.00 | Tk. 25.00 | Tk. 4 |
Tk. 100001.00-Tk. 500000.00 | Tk. 50.00 | Tk. 8 |
Tk. 500001.00 and above | Tk. 100.00 | Tk. 15 |
Source: Annual report 2005
Commission for DD
Firstly bank cheques the ‘Test Code’ mentioned on the draft. If “Test Code” agrees then believe that DD is not forged and makes payments. For future confirmation, the issuing bank sends an advice about the DD to the paying branch. For DD commission is taken in the following way:
|
Commission for TT
|
This service is only provided for valued customers. Who is very reliable and have long-standing relationship with bank, TT commissions are:
Source: Annual report 2005
Passing the check:
After verifying the above – mentioned things the officer passes it to the computer section for more verification. After that it is passed to the officer to make payment. By putting “seal the cash officer make it clear to pay. The cash officer gives the cash amount to the holder and record in the cash paid register.
Dishonor of Check:
A bank cans dishonor a Check in the Following Situation:
► Insufficient fund
► Payment stopped by drawer.
► Alteration required drawer signature.
► Effect not clear in the check.
► Exceed arrangement in check
► Full cover not received.
► Payee’s endorsement irregular/illegible/required.
► Drawer signature different and required.
► Check is post dated/mutilated/out of data.
► Crossed check must be presented through a bank.
►Clearing stamp required cancellation.
3.10 Deposit Section:
The function of the deposit section is very important. It is fully computerized. The officer of the deposit section maintains account number of all the customer of the bank. They are used different code number for different account. By this section a depositor/drawer can know what the present position is if his/her account. The officer makes posting three types of transactions such as cash, clearing and transfer. This section performs the following tasks:
► Post all kind of transaction.
► Provide on demand report.
► Check maintenance
► Preparation of day transaction position.
► Preparation of closing monthly transaction.
3.11 Bill and clearing Section:
For safety and security in financial transaction people use financial instruments like DD, PO, and Check etc. Commercial banks duty is to collect these financial instruments on behalf of their customer. This process that the banks use is known as clearing and collection. The main function of this section is to collect instruments on behalf of the customers though Bangladesh Bank Clearing House, outside bank Clearing (OBC), inters Branch Clearing (IBC). Upon the receipt of the instruments this section examines the following things:
► Whether the paying bank within the DhakaCity.
► Whether the paying bank outside the DhakaCity.
► Whether the paying bank is their own branch.
3.12 Outward Clearing:
Outward clearing held if the instruments collected by specific branch within the Dhaka city and not of their own branch. Here the following procedures are followed:
► The clients receive the duty signed instrument.
► Checked for any apparent discrepancy.
► Clearing stamps are affixed on the instruments and on the deposit slip.
► Branch code number also affixed on the instrument.
► The authorized signature endorses instruments.
► Particulars of the instruments and vouchers are recorded in the outward clearing register.
► The instruments with schedules send to the main branch of Exim Bank Bangladesh Ltd. With issuing an inter branch debit advice (IBDA).
3.13 Essential things for clearing the instruments:
There are three essential things required from clearing the instruments:
- Crossing seal.
- Endorsement Seal.
- Clearing Seal.
3.14 Account Section:
This is very much crucial department for each branch of a commercial bank. Records of all the transaction of very department are kept here as well with other respective branches. Accounting department verifies all financial amounts and contents of transactions. If any discrepancy arises regarding any transaction this depart report to the concerned department.
3.15 Tasks of accounts department:
Accounts department pays a vital role in commercial banking. In private banking sector accounts department of Exim Bank Bangladesh Ltd. performs its tasks property. The activities of account section are as follows:
► Record all transaction in the cashbook.
► Record all transaction in the general and subsidiary ledger.
► Prepare daily fund function, weekly position, periodic statement of affairs etc.
► Prepare necessary statement for reporting purpose.
► Pay all expenditure on behalf of the branch.
► Make salary statement and pay salary.
► Branch to branch fund remittance and support for accounting treatment.
► Budgeting for branch.
► Make charges for different types of duties.
3.16 Product information Of EXIM Bank

Foreign Exchange:
● Non-resident foreign currency deposit account (NFCD)
● Foreign currency deposit Account
Saving Scheme:
● Monthly Savings Scheme (Money Grower)
● Monthly Income Scheme (Steady Money)
● Double the deposit in 6 years (Super Savings)
● 10 years deposit – more than triple (Multiplies Saving)
● Education Saving Scheme
We emphasize on non-fund business and free-based income. Bid Bond/ bid Security can be issued at customer’s request.
Our Bank is posted to extend L/C facilities to its importers/Exporters through establishment of correspondent relation and Nostrum Accounts with leading banks all over the world.
Moreover, customers can deposit their telephone bill of Grameen Phone in all the branches except Rajuk and the consumers of pallid Budded smithy of Gazipur can deposit their electricity bill to Gazipur branch.
3.17 Super Saving Scheme:
Saving helps to build up capital and capital is the prime source of business investment in a country. Investment takes the country toward industrialization, which eventually creates wealth. That is why saving is treated as the very foundation of department. To create more awareness and motivate people to save. Exim Bank Offers SUPER
Terms and conditions of the Scheme:
- Any Individual, company, educational, institution, government organization, NGO, trust, security etc may invest their savings under this scheme.
- The deposit can be made in multiples of Tk 10000.
- The period of deposit is for six years.
- Any customer can open more than one account in branches in his name or in joint names.
- If the deposit is withdrawn before six-month terms, then saving interest rate +1% will be applied before payment is made.
- A depositor can avail up to 80% of the deposited amount under this Scheme.
- In case of death of the depositor, before the term, the deposit (with interest at savings rate +1%) will be given to the nominee.
In case of issuing a duplicate deposit receipt the rules of issuing duplicate receipt of term deposit will be applicable.
3.18 MONEY GROWER:
Savings period and monthly installment rate:
The savings period is for 5,8,10 or 12 years. Monthly installment rate is Tk. 1000/-, 2000/- or 5000/-
Monthly installment deposit:
► The saving amount is to be deposited within the 10th of every month. In case of holidays the deposit amount is to be made on the following day. May also be made in advance.
► The deposit may also be made in advance.
► The depositor can have a separate account in the bank from which a standing instruction can be given to transfer the monthly deposit in the scheme’s account.
► In case the depositor fails to make the monthly installment in time, then 5% on overdue installment amount will be charged. The charge will be added with the following month(s) installment and the lowest charge will be Tk. 10/-
Table-10
| Monthly Installment | |||
| Profit rate % | 1000/- | 2000/- | 5000/- |
5 Years | 10.00 | 82800 | 165000/- | 414000/- |
8 Years | 10.15 | 163600 | 327200/- | 818000/- |
10 Years | 10.30 | 236400 | 472800/- | 1184500/- |
12 Years | 10.50 | 331986 | 663973/- | 1659932/- |
Withdrawal:
► Generally withdrawal is not advised before a 5-year term, but if it is withdrawn before the above term, then interest will be paid at saving rate. However, no interest will be paid if the deposit is withdrawn within 1 year of opening the account.
► In case the deposit wishes to withdraw between the 5,8,10 or 12- year period then full interest will be paid for a completed term and savings rate will applicable for the fractional period.
Loan Advantage
After three years of savings in this scheme the depositor ( if any adult) is eligible for a loan up to 80% of this deposited amount. In that case, interest rates on the loan will be applicable as per prevailing rate at that time.
Reasons for disqualification from this Scheme:
► If the depositor fails to pay 3 installments in a row, then he will be disqualified from this scheme and interest will be applicable as mentioned in withdrawal clause.
► If a depositor fails to pay 5 installments in a row after completion of 5-year term, then the bank reserves the right to close the account and interest will be paid as, mentioned in withdrawal clause.
►In case of death of the depositor the scheme will cease to function. The amount will be handed over to the nominee of the deceased depositor. In case of absence of the nominee the bank will handover the accumulated
► Amount to the successor of the deceased
3.19 Monthly Income Scheme:
Highlights of the Scheme
► Minimum deposit Tk. 25000/-
► Higher monthly income for higher deposit
► The Scheme is for a 5-year period.
Monthly income will be created to the depositor’s account on the 5th of each month.
Table No- 11
Monthly Income Scheme
Deposit Amount | Monthly Income |
Tk. 25000/- | Tk. 250 |
Tk. 50000/- | Tk. 500 |
Tk. 100000/- | Tk. 1000 |
Tk. 200000/- | Tk. 2000 |
Tk. 500000/- | Tk. 5000 |
Tk. 1000000/- | Tk. 10000 |
Objectives of the Scheme:
► An account is to be opened by filling up a form.
► The bank will provide to the customer a deposit receipt after opening the account. This receipt is non-transferable.
► If the deposit is withdrawn before a 5-year term, then saving interest rate will be applicable and paid to the depositor. However, no interest will be paid if the deposit is withdrawn within 1 year of opening the account and monthly income paid to the customer will be adjusted from the principal amount.
A depositor can avail loan up to 80% of the deposit amount under this scheme. In this case, interest, will be charged against the loan as per Bank’s prevailing rate.
3.20 Smart Saving:
Smart saver is a high return investment plan, which helps a customer build up sizeable amount in a period of 5 years. This scheme offers a customer to by smart saver term deposit 5 times the invested amount. Smart saver is a 5-year term deposit Scheme.
Terms and condition:
- One unit of smart saver term deposit is 25000.
- During the tenure of the loan the term deposit will be kept in bank as security.
- The customer will have to open an account and monthly installment of loan will be debited from the account commencing from 30 days after opening loan account.
- Within the 1st year if the customer fails to repay 3 consecutive installments then only the principal amount of smart saver term deposit will be encased and the lone will be liquidated inclusive of accrued interest and balance paid to the customer. After completion of 1year, saving rate will be added to the principal amount of smart saver term Deposit. In both cases closing charge will be Tk. 500.
- For missed installments on due date customer will be charged Tk. 25 per unit per month.
- In the event of death of the customer, the bank shall be entitled to encase the term deposit and adjust the dues first before any refund is made to the nominees/ successors.
The bank reserves the right to amend the rules and rates as and when deemed necessary.
Multiplus Savings:
Saving helps to build up Capital and capital is the prime sources of business investment in a country. Investment takes the country towards industrialization, which eventually creates wealth. That is why saving is treated as the very foundation of development. To create more awareness and motivate people to save, Exim Bank Offers MULTIPLUS SAVINGS Scheme.
Terms and condition of the Scheme:
- Any individual, company, educational institution, government Organization, NGO, Trust, society etc may invest there savings under this scheme.
- The deposit can be made in multiples of Tk. 10000.00
- The period of deposit is 10 years. But the deposit can be withdrawn at any year with interest. As an example, if deposit is withdrawn after completion of 1 year but before 2 years then deposit with interest will be paid for 1 year only. The same rule will apply for other years. If deposit is withdrawn before 1st year then no interest will be paid.
Any customer can open more than one account in a branch in his name or in joint names. A deposit will be issued at the time of opening the account.
- The depositor can avail lone up to 80% of the deposit under this Scheme.
- In case of issuing duplicate receipt the rules of issuing a duplicate receipt of term deposit will be applicable.
- In case of death of depositor before the term, the deposit (with interest at savings rate) will be given to the nominee. In the absence of nominee, the heirs/ successors will be paid on production of succession certificate.
- The nominee may, at his option continue the scheme for the full term.
OVERALL BANKING ACTIVITIES OF EXPORT IMPORT BANK OF BANGLADESH LIMITED
CHAPTER FOUR
LAUNCHING ISLAMI BANKING
ISLAME BANKING
4.1 Launching of Islami Banking and its Objectives:
Considering the inherent desire of the religious Muslims, Exim Bank has launched islami banking system and inaugurates two islami banking branches in the year 2002 but from 1st July 2004 they started to follow Islami banking system. All the branches perform their activities under the guidance and supervision of a body called “ SHARIAH COUNCIL”. This council is consisting of 16 members.
Objectives:
- Islami Banking system plays very important role in the Muslim nation. As 90% people of our country are Muslim the bank wants to compete the market.
- For interest free banking financing arrangements.
- To follow Quran, Sunnah and Shariah Rules.
- Due to profit sharing features of Islamic Banking Banks and entrepreneurs have a shared interest in the outcome of an investment, which fortes economic development.
- To establish equity & justice in the society through the legitimate business & income.
- Try to bring diversity in the investment portfolio in accordance with the need and demand of the time and nature of business by introducing various investment methods & techniques.
- Co- ordinate the economic development with the social development.
4.2 Concept of Islamic Banking:
The concept of Islamic banking represents a radical departure from traditional banking. Islamic Banking has to derive its inspiration from the religious edicts of Islam and has to would its operations within the framework of the teaching of Islam. The most distinctive feature of Islamic Banking is the prohibition of interest (Riba) in all forms to transaction. Because “Allah” forbids ribs (interest) but permits trade. The most important verses read as follows “ O believes, take not double and redoubled interest and fear God so that you may prosper ( Sura 3 [ Al-Imran] verse 130). The Islamic banks organize their operations on the basic of profit/ Loss sharing and other modes, which are permitted in islam.
Islamic banking has been defined in a number of ways:
The definition of Islamic bank approved by the General Secretariat of the OIC is “An Islamic bank is a financial institution whose status rules and procedures expressly state its commitment to the principal of Islamic shariah and to the banning of the receipt and payment of interest on any of its operations.
According to Dr Shawki Ismail Shehta. “It is there\ fore natural and indeed imperative for an Islamic bank to incorporation in its functions and practices commercial investment and social activities as an institution designed to promote the civilized mission of an Islamic Economy”.
Dr Ziauddin Ahmed opined that “Islamic Banking is essential a normative concept and could be defined as conduct of banking in consonance with the ethos of the value system of Islam”
It is clear from the definitions given above that an Islamic bank is not merely a financial intermediary; it involves direct participation in business on the principals of sharing of profit and losses aiming at ensuring social equity and justice.
4.3 Important Objectives Of Islamic Banking:
The important objectives of Islamic banking are:
► Make the best effect to penetrate into the entire society with particular emphasis on low-income groups
► Allocate part of the savings collected in each community to project directly related to the community itself.
► Allocate part of the available funds to the artisans and small enterprises and not only to save big business and procedures
► Be aware that when managing its zakat funds the Islamic banks should allocate to overcome part of these funds to securing Qard Hasan(interest free loans). This Qard Hasan Should is directed to opportunities that would serve development, such as creating jobs in order to convert unemployed persons into productive elements within the society or assisting small businesses their financial problems.
► Make effort to turn banking institution as business share institutions from merely loan institutions.
► Try to bring diversity in the investment portfolio in accordance with the need and demand of the time and nature of business by introducing various investment methods & techniques
► Create efficient management engineer through conducting jointly the business Enterprises and production activities.
► Link loans and advances with efficiency based method in Lieu of security oriented. As a result a large number of potential but efficient poor entrepreneurs be able to deploy there service and labor for the productive and innovative activities.
► Establish equity and justice in the society thought the fair distribution of profit Loss Sharing.
► Implement a compulsory ruling of sharia by abolishing the interest mechanism from the banking system.
► Establish priority of labor and production as a source of profit earning and Growth of capital.
► Finance in income generating activities for fulfillment of the basic needs of the poor mass.
► Finance for the balanced development of the country’s agricultural industrial and commerce sectors to help reduce the ill effects of discriminating investment or development narrowed down the gap between the rich and poor and frame and investment plan on micro level basis.
► Discard various types of corruption fraud forgeries misuse or under use of potential recourses and establish strong culture of moral discipline in conformity with the tenets of Islamic Sharia.
► Invest in the country’s potential utilized sector insuring the best uses of the Endowed resources by the God and
► Co ordinate the economic development with the social development.
4.4 Features Of Islamic Banking:
The main features of Islamic banking may be grouped as under
► Prohibition of interest in all forms of transaction.
► Undertaking business and trade activities on the basis of fair and legitimate (Halal) profits.
► Giving Zakat
► Prohibition of monopoly.
► Investment pattern is designed to promote welfare of the disadvantaged and
4.5 Characteristics Of Islamic Banking:
► The distinct characteristics of Islamic Banks may be explained as under. The basis of interest whether it is fixed floating, prepaid, deferred, deducted or in any other form.
► The relationship between Islamic banks and their customers is not that of creditor and debtor but one of participation in risks and rewords.
► Unlike conventional bank, which pool capital funds and depositor’s funds, an Islamic bank keeps the two segregated in order not to mix the profit corned on its own fund (capital plus current balances repayment or which is guaranteed) with the profit corned on investor’s funds which are accepted on a profit and loss sharing basis. This enables the banks to calculate the profit due to investors correctly.
► Islamic banks are multipurpose banks since they pay the role of commercial Bank, Investment banks and development banks.
► When Islamic banks employ their resources for production purposes they do not offer cash loans, as is the cash with conventional banks, but operates though participation (Musharaka) or
► Some other form of Islamic contract, such as Mudaraba, Murabaha, Ijara etc.
While the role of non-Islamic banks is to attract financial resources and lend them so as to make profit the Islamic banks mobilize financial resources in Order to use them to develop the society as a whole. Profit is no doubt, kept in sight but that is not the sole objective of investment.
4.6 Profit of Islami Banking and Interest for Non-Islami Banking Branch:
Rate of profit on Deposit accounts of Islami banking branch affected from 10.01.2004
SL No | Nature of Deposit | % |
1. | Mudaraba Term Deposit a) For 03 months and above but less than 6 months b) For 06 months and above but less than 12 months c) For 12 months and above but less than 24 months d) For 24 months and above but less than 36 months e) For 36 months and above | 8.87% 9.38% 9.87% 10.00% 10.20% |
2. | Mudaraba Saving Deposit | 8.51% |
3. | Mudaraba Short Term Deposit | 7.04% |
4. | Steady Money | 13.05% |
5. | Super Saving | 13.28% |
6. | Multi plus Saving | 13.28% |
7. | Money Grower 05 Years 08 Years 10 Years 12 Years | 13.16% 13.28% 13.39% 13.50% |
8. | Education Savings | 12.94% |
Shariah Council:
Chairman: Professor Maulana mohammad Uddin
Member: Professor Maulana Abdul Qasem Muhammad
Member: Maulana Mahammed Sadequl Islam
Member: Professor H.M. Shahidul Islam Barakaty
Member: Mr. A.S.M.Fakhrul Ahsan
Member: Hafiz Maulana Mufti Mohammad Khairullah
Member: Hafiz Quari Maulana Mufti mohammad Nuruddin
Member: Mr.Md. Nazrul Islam Mazumder
Member: Mr.Md. Altaf Hossain
Member: Engr. Aminur Rahman Khan
Member: Mr. A.K.M. Nurul Fazal Bulbul
Member: Mr.Md. Abdul Mannan
Member: Mr.Md. Fahim Zaman Pathan
Member: Mr.Zubayer Kabir
Member: Mr. Mohammed Lakiotullah
Member: Secretary Mr. Muhd. Mubarak Hussein
► While conventional bank are satisfied with the traditional review of accounts by certified auditors, Islamic banks are subject to additional review to ensure that money is being utilized and invested in ways that conform to Islamic principle.
► The religious supervisor Board/Sharia Council has to approve each type of transaction that the bank undertaker, and also has authority to look into individual transactions to the extend needed to satisfy itself on their compliance with sharia requirements
4.7 Difference between Conventional Financial System (CFS) and Islamic Financial System (IFS):
Conventional Financial System (CFS):
A financial system which is traditionally based and working on Riba or interest principle which is irrelevant of or ignores or separates the religious life of a man from the economic life can be defined as CFS. The conventional financial system is of two types:
1) Socialistic F.S & 2) Capitalistic F.S – both systems have been provide inefficient to establish economic balance in the society.
Islamic financial System (IFS):
A financial system that is based on Islamic principles & values, which eliminates Riba and ensures a profit sharing mechanism in the financial system is called IFS. It may be characterized by the absence of interest bared financial institution & transactions, doubtful transactions or gharry, stock of companies dealing in unlawful activities, unethical or immoral transaction such as market manipulation insider trading, short selling etc.
4.8 Differences between CFS & IFS are as follows:
Basis of Difference | CFS | IFS |
Religious Belief | Secular & Separates religion from other parts of human life | Belief in unity of God & relates this belief to economic life of a man |
Freedom of economic activity | In socialism govt. enjoys economic freedom but in capitalism individuals enjoy freedom. | Restrictive freedom is allowed in the light of shariah both by the Govt. & or individual. |
Ownership of system | Socialism-state ownership Capitalism-individual ownership | Allah is the exclusive owner. Man is the caretaker of the property |
Goal of financial system | Socialism-Profit of the Society Capitalism-Individuals profit | Welfare of both here and hereafter. |
Competition | Socialism-No competition. Capitalism-legal & unethical Competition | Logical competition and financial co operation |
Wealth distribution | Socialism-equal Capitalism-unequal | Equitable |
Basis of economic system | Riba or interest | Interest free; PLS. Zakat & compensation based |
Sources of the system | Intellectuals brain, storming of the economic problems of mens life | Devine book “Al Quran” & prophet’s speeches. |
Result | Concentration of income & economic power in few hands | Maximum & equitable distribution of economic opportunities & higher production in the society. |
Social & environmental welfare | Do not consider the social & environmental welfare | Ensure social & environmental welfare. |
Owners trpectation in spect of welfare | Dividend or part of profit in case of equity financing | Part of profit or loss |
Lender or links expectation in lerms of debt | Interest | Profit or loss sharing. |
Mode of | Lone, Overdraft & cash Credit. | Mudarabah, Musharaaka, |
4.9 Accounts Opening Section:
This section deals with opening of different types of account. It is also deals with issuing of checkbook and different accounts openers. A customer can open different types of accounts though this department such as:
► CD- Al- Wadiah Current Deposit
► SB- Mudaraba Saving Deposit
► STD-Short term Deposit
► MTD- Mudaraba Term Deposit
► SS- Short Scheme
● MSS-Monthly Saving Scheme
● MIS-Monthly Income Scheme
● MPSS-multi plus super Saving Scheme
● SSS- Super Saving Scheme
► ESS- Education Saving Scheme
► INV- Investment Account
► FC-Foreign currency Account
► BCD-Bearer Certificate Deposit
► Exim Bank Hajj Account Project.
As it is an Islami Banking Branch the following rules are applied here:
> Current deposit will be received on Al-wadiah principle & the same will not get any profit.
> Saving deposit will be accepted on Mudaraba principle & such deposit will Bear 0.62 weight age.
Islami Banking Terms:
For the convenient of the reader who are not familiar with the Islami banking Term, the following are some terms of Islami banking for mobilization of deposits and the schemes are becoming popular day by day:
Al Wadiah Account:
The characteristics of this account are almost similar to current account of conventional banks. The owner of the fund does not enjoy any profit nor bear any loss. But the bank obtains the permission from the depositor so that the bank has the option to use the fund when it is necessary.
Mudaraba Savings Account:
Mechanism is almost similar to the saving account of the conventional banks. The basic difference in this case is that the bank and the owner of the fund will share the profit from the investment while the loss from the investment will be borne by the owner of the fund unless the loss is incurred due to the negligence or convenience of the bank.
4.10 Hajj Saving Account:
Hajj is one of the fifty rukan in Islam. In the socio- economic perspective of our country low-income group cannot provide necessary money in together for Hajj. For not taking profit rather for meeting their desires and hopes Exim Bank has introducing “ Exim Bank Hajj Account Project”
Requirement of opening an Account:
There are some requirements that have to be completed for opening an account.
SL No | Types of Account | Papers to be obtained |
1 | Joint Account | From No GB- 68 |
2 | Proprietorship Account | From No GB-15 |
3 | Partnership A/C | From No GB-8, copy of partnership deed. |
4 | Public/ Private Ltd. Co. | From No GB-69, Memorandum & Articles of Association, certificate of commencement of Business (in case of public Ltd. Co.) |
5 | Association, clubs, Societies, trusts, Schools Colleges etc. | From No GB-67 & a list of managing committee/Executive committee |
6 | Mandate of authority to operate the A/C by third parties. | From No GB- 11 |
4.11 Al-Wadiah Current Account:
Current Account is an account where the account holders can makes numerous transactions within a working day. There is no restriction on the number and the amount of withdrawals from the current account within the availability of funds. As the banks is under the obligation to repay this deposit on demand no profit is paid in
► Minimum opening deposit of TK.1000/- is required;
► There is no withdrawal limit.
► No interest is given upon the deposited money;
► Minimum TK.1000/= balance must always maintain all the time;
4.12 Mudaraba Term Deposit Receipt (MTDR):
It is like a fixed deposit in the conventional baking system but it does not receive or accept interest father, this account give profit and collect deposit. In this mode less that TK. 1 crore or TK. 1 crore and above can be deposited against client will get non-transferable instrument of equal amount. If a customer withdraw his/her money before one month then he/she will not get any kind of profit . if a depositor would like to withdraw his profit after six month he/she will get the profit accordance with previous years profit rate. After the announced yearly profit or loss, if bank felt in loss positing then the depositor bound to incur the loss. In absence of account holder the selected nominee will get the money. Account holder bound to bear any kind of tax or excise duty according to government circular. The profit rates of this account are:
Table No-12
Mudaraba: Fixed Deposit (FDR) | Provisional Rate of Profit | Minimum Deposit Requirement |
1(One) month | 10.25% | Any Amount |
3(Three) months | 13.50% | Any Amount |
6(Six) months | 13.50% | Any Amount |
01 (One) Year | 13.50% | Any Amount |
02 (Two) Years | 13.50% | Any Amount |
03 (Three) Years | 13.50% | Any Amount |
Source: Annual Report 2007
4.13 Mudaraba Short Term Deposit(MSTD) Account:
Normally various big companies, organizations, Government deposit keep money in MSTD account. Frequent withdrawal is discouraged and requires prior notice the deposit should be kept for at least seven days to get interest. The interest offered for MSTD is less than that of savings deposit. Interest is calculated based on daily minimum product and paid two times in a year. Interest rate is 6%.
Account opening procedure:
| Step 1 | The account should be properly introduced by Any one of the following:
|
| Step 2 | Receiving filled up application in banks prescribed from mentioning what type of account is desired to be opened |
| Step 3 |
|
| Step 4 | Authorized officer accept the application |
| Step 5 | Minimum balance is deposited-only cash is accepted |
| Step 6 | Account is opened and a cheque book and pay-in-slip book is given |
4.14 Comparative position of new generation private bank
Comparative position of new generation private banks as on December 31,2003
| SL No | Name of the Bank | Total Deposit | Call Deposit | Bank Deposit | Core Deposit | Advance | A/D Ratio | Profit/Loss | No. of Branches |
| 01 | EXIM Bank | 1524.29 | 82.00 | 110.81 | 1331.48 | 1229 | 80.62% | 56.27 | 19 |
| 02 | Mercantile Bank Ltd. | 1627 | – | 203 | 1424 | 1077 | 75.63% | 63.65 | 20 |
| 03 | Bank Asia Ltd. | 1075 | – | – | 1075 | 814 | 75.72% | 43.1 | 14 |
| 04 | First Security Bank Ltd. | 944 | – | – | 944 | 602 | 63.77% | 24.13 | 11 |
| 05 | Standard Bank Ltd. | 600 | – | – | 600 | 495 | 82.50% | 29.5 | 15 |
| 06 | The Premier Bank Ltd. | 1000 | – | – | 1000 | 895 | 89.50% | 40.09 | 17 |
Source: Annual Reports-2004, 2005,2006 and 2007
4.15 Documents Required for Opening Account:
Individual/Joint Account:
► Introduction of the account.
► Two photographs of the signatories duly attested by the introducer
► Identity (copy of Passport).
► Joint Declaration Form(For joint A/C only)
► Employee’s certificate ( in case of Service Holder).
Partnership account:
► Introduction of the account.
►Two Photograph of the signatures duly attested by the introducer.
►Partnership latter duly signed by all partners (sign should be similar as stated in
►Partnership Deed.)
►Partnership Deed duly certified by notary public.
►Registration (if any)
►Updated Trade license.
Proprietorship account:
►Introduction of the account
►Two photographs of the signatories duly attested by the introducer.
►Valid copy of trade license.
►Rubber-stamp.
►TIN number certificate.
►Identity(Copy of passport).
►Permission letter from DC/Magistrate (in case of newspaper)
Limited Company:
►Introduction of the account
►Two photographs of the signatories duly attested by the introducer.
►Valid copy of Trade License.
►Certificate of incorporation
►Certificate of commencement (in cash of Public limited company).
►Certified (joint Stock) true copy of the Memorandum and Article of association of the Company duly attasted by chairman or managing Director.
►List of directors along with designation & specimen signature.
►Latest certified copy of form – xii (to be certified by register of joint stock companies) (In case of Directorship Change).
►Rubber-stamp (Seal with designation of each person).
►Certificate of registration (in cash of Insurance company obtained from department of insurance from the peoples republic of BD).
Club / Societies Account:
►Introduction of the account.
►Two photographs of the signatories duly attested by the introducer.
►Board Resolution for Opening A/C duly certified by president/Secretary.
►List of Existing managing Committee.
►Registration (if any).
►Rubber-stamp.
►Permission letter from bureau of N.G.O (In case of N.G.O. A/C).
4.16 Problems related to Macro Operation of the Islamic Banks:
- Liquidity and Capital.
- Valuation and bank Assets.
- Financial stability
- The ownership of the banks
- Lack of capital market and investment- free financial instruments.
- Insufficient legal protection.
- Controlling and supervision by the central banks on the basis of Islamic Shariah
- Lack of unified Shariah rulings
- Absence of Islamic inter-bank money market.
- New banking regulation.
- Accounting principles and procedures
- Shortage of supportive and link institutions
- Shortage of skilled and trained manpower in Islamic Shariah banking
- Lake of Co- Operation among the Islamic Banks
- Lack of Familiarity by international financial and non-financial sector with Islami products and procedure.
- Severe competition in the financial sector.
- Economics slowdown and political situation of the country
- Inadequate track record of Islamic banking
- Absence of infrastructure for international Islamic trade financing
- Defaulting culture of the borrowers
- Short-term asset concentration in the Islamic banks.
- Lack of Course or paper on Islamic Economics, Banking and finance at the Educational institutions.
- Lack of Uniform operational procedure of Islamic Banking
- Lack of Specialized Islamic Banks and Non- Bank financial institutions
- Lack of consortium or syndication of the Islamic Banks
- Lake of Harmonization of Islamic financial practices
- Lack of inter- country study on the practical operations of Islamic banking
- Lack of secondary securitization Market.
- Lack of coordinated research work on Islami Economic, banking and finance
- Lack of Apex Training Institute for the Islamic banks.
4.17 Problem Related to Micro Operation of the Islamic Banks:
- Increased Cost of Information.
- Control over Cost of Funds.
- Make-up financing and corrupted Mark-up
- Excess resort to the Murabaha mode of Financing.
- Utilization of interest rate of fixing the profit Margin in Bai-Modes
- Financing Social Concerns.
- Lack of positive response to the requirement to government Financing.
- Failure of Islamic banks of finance High return projects.
- Sacrifice of a locative efficiency
- Loss of distributive efficiency.
- Depression of profit.
- Lack of full-fledged Shariah Audit.
- Fraud-Forgery or corruption in Islamic Banks.
- Minimum Budget for Research and Development.
- Working Environment.
- Issuance of letter of Guarantee (L/G).
- Minimum Budget for Research and Development.
- Lack have Shariah manual or Guidelines.
- Islamic Investment Risk Analysis and measurement methodology.
- Non-exemption of stamp Duty for purchasing property by Banks.
- Lack of Co-operation between Islamic banks and Islamic NGOs for extending Micro Credit.
- Lack of Establishment of links with other Training institutes and Shariah Supervisory Bodies.
- Lack of intention of the Management to be Strict with Shariah Guidelines.
The above problems are some of the burning problems confronting the Islamic banks in Bangladesh. However it is felt that much operational work and in – depth research work has to be undertaken to allow the Islamic banks to flourish with highest quality and strength.
5.1 Introduction:
This is the survival unit of the bank because until and unless the success of this department is attained, the survival is a question to every bank. If this section does not properly work the bank it may because bankrupt. This is important because this is the earning unit of the bank. Banks are accepting deposits from the depositors in condition of providing profit to them as well as safe keeping their interest. No the question may gradually arise how the bank will provide profit to the clients and the simple answer is loans & Advance.
Why the bank provides advances to (he Borrowers)
► To earn profit from the borrowers and give the depositors profit.
► To accelerate economic development by providing different industrial as well as agricultural advances.
►To create employment by providing industrial loans.
► To pay the employees as well as meeting the profit groups.
Credit is continuous process. Recovery of one credit gives rise to another credit. In this process of revolving of funds, bank earns income in the form of profit. A bank can invest its fund in many ways. Bank makes loans and advances to traders, businessman, and industrialists; moreover nature of credit may differ in terms of security requirement, disbursement provision, terms and conditions etc.
Lending Principle:
The principle of lending is a collection of certain accepted time tested standards, which ensure the proper use of loan fund in a profitable way and its timely recovery. Different authors describe different principles for sound lending.
►Safety
►Security
►Liquidity
►Adequate yield
►Diversity
Safety:
Safety should get the prior importance in the time of sanctioning the lone. At the time of maturity the borrower may not will or may unable to pay the loan amount. Therefore, in the time of sanctioning the loan adequate securities should be taken from the borrowers to recover the loan. Banker should not sacrifice safety for profitability.
Exim Bank Ltd- exercises the lending function only when it is safe and that the risk factor is adequately mitigated and covered. Safety depends upon:
►The security offered by the borrower and
►The repaying capacity and willingness of the debtor to repay the loan with interest.
Liquidity:
Bank should consider the liquidity of the loan in time of sanctioning it. Liquidity is necessary to meet the consumer need.
Security:
Banker should be careful in the section of security to maintain the safety of the loan. Banker should properly evaluate the proper value of the security. If the estimated value is less than or equal to loan amount, the loan should be given against such securities. The more the cash near item the good the security, in the time of valuing the security, the banker should be more conservative.
Adequate Yield:
As a commercial origination. Banker should consider the profitability. So banker should consider the interest rate when go for lending. Always Banker should fix such an interest rate for it’s lending which should be higher than its saving deposits interest rate. To ensure this profitability banker should consider the prospect of the project.
Diversify:
Banker should minimize the portfolio risk by putting its fund in the different fields. If banks put its entire loan able fund in one sector it will increase the risk. Banker should distribute its loan able fund in different sectors. So if it faces any problem in any sector it can be covered by the profit of another sector.
5.2 Reasons for Loan Default:
There are many reasons for loan default. The principle reasons are:
Sick management Sick operation
Integrity Efficient Machinerys
Cooperation Skilled
Financial/Marketing Labor/supervision good
Knowledge/Technical Labor relation Utilities of
Knowledge/Experience Raw materials
Endurance and judgement Sick Finance
Sick market working capital
Freedom Repayment period
Openness Flexible rate of interest
Growth Assets matching to
Stability liabilities collaterals capital market
Sick product Other reasons
Quality Reputation
Competitiveness Analysis of balance
Demand Sheet
Durability Lenin risk analysis
5.3 Process of Loan:
Heads | Characteristics |
Application | Applicant applies for the loan in the prescribed from of the bank describing the types and purpose of loan |
Sanction | 1. Collecting credit information about the applicant to determine the credit worthiness other borrower. Sources of information 2. Personal investigation, confidential report from other bank. Head office/ branch/chamber of commerce. 3. CIB (Central Information Bureau) report from central Bank. i. Evolution of compliance with its lending policy. ii. Evaluating the proposed security. 4. LRA is most for the loan exceeding one cror- as ordered by Bangladesh bank. 5. if everything is in accordance the loan is sanctioned. |
Documentation | Then bank prepare a loan proposal which contains terms and conditions of loan for approval of 11.0-or manager. Takes the necessary papers and signatures from borrower. |
Disbursement | A loan Account is opened. Where Customer A/C Dr. Respective Loan A/C Cr. |
5.4 Types of Loans and Advances:
The different types of loans and advance that EX1 M bank offers are as follows:
► Secured Overdraft (SOD)
► Loan against imported Merchandise (LTM) t 3. Loan against Trust Receipt (LTR)
► Payment against Document (PAD)
► HouseBuilding Loan
► HouseBuilding Loan (Staff)
► Term Loan. 8. Loan (general) 9. Bank Guarantee 10. Export Cash credit.
► Cash credit (pledge)
► Cash credit (Hypo)
Foreign Documentary Bill Purchase (FDBP) 14. local Documentary Bill purchase (LDBP)
►Secured Overdraft (SOD):
It is a continous advance facility. By this agreement, the banker allows his customer to overdraft his current account up to his credit limits sanctioned by the bank. The interest is charged on the amount, which he withdraws, not no the sanctioned amount. Exim Bank sanctions SOD against different secutity.
►SOD (general):
Advanced allowed to individual/firm against financial obligation (i.e. lien on FDR/DR/PSP/BSP/ insurance policy share etc.) this may or may not be a continuous credit.
►SOD (others):
Advance allowed against assignment of work order or execution of contractual works falls under this head. This advance is generally allowed for a definite period and specific purpose i.e. it is not a continuous credit. It falls under the category “others”
►SOD (Export):
Advance allowed for purchasing foreign currency for payment against L/Cs (Back to Back) where the exports do not materialize before the import payment. This is also an advance for temporary period, which is known as export finance and under the category “commercial lending”
►LIM (Loan against imported merchandise:
Advanced allowed for retirement of shipping documents and release of goods imported through L/C taking effective control over the goods by pledge in go downs under banks lock & key fall under this type of advance. This is also a temporary advance connected with import, which is known as post-import financing, falls under the category “commercial lending”
►LTR (Loan against trust receipt):
Advanced allowed for retirement of shipping documents, release of goods imported through L/C falls under trust with the arrangement that sale proceed should be deposited to liquidate within a given period – This is also a temporary advance connected with import, which is known as post-import financing, falls under the category “commercial lending”
►PAD (payment against document):
Payment made by the bank against lodgment of shipping documents of goods imported thought L.C falls under this head. It is an interim advance connected with import and is generally liquidated against payments usually made by the part for retirement of the documents for release of imported goods from the customer’s authority. It falls under the category “Commercial Bank”
►House building Loan (General):
Loans allowed to individual/ enterprise construction of house ( residential or commercial) fall under this of advance. The amount is repayable by monthly installment within a specified period, advances are known as Loan (HBL-GEN).
Introduction:
House building loan is one of the common credit policies of banking sector. There was only one institution in our country, which is specified in HBFC, Bangladesh commercial bank and leasing company provides house-building loan to the customers.
Interest rate:
Interest rate may changes from time to time depending on the market interest rate. From the customer point of view this changes have an advance impact on the customer. Some times if they have to bear a higher interest on the principal amount which causes a great burden on them.
Disbursement procedure:
The disbursement procedure or timing of disbursement depends on the client or the progress of work of the construction. The disbursement can be made two or three stages or more depending on the above conditions.
Made of repayment:
The loan shall be adjusted by monthly interest basis. The repayment will start from 6 (six) months, of the date of first disbursement) it may change according to the terms and conditions of the agreement).
Collateral:
The land and the constriction on the land arc normally given as collateral. It may changes:-
The documents to be obtained:
- DP note
- Letter of disbursement.
- Letter of installment.
- Letter of guarantee.
- Letter of under taking.
- Letter of agreement.
- Irrevocable general power of attorney.
- Memorandum of deposit of title deed.
- Any other documents if considered
►House building loans (staff):
Loans allowed to the bank employees for purchase/construction of house shall be known as staff loan (HBFC-STAFP).
►Term Loan
Exim Bank considers the loans. Which are sanctioned for more than one year as term loan. Under this facility, an enterprise is financed from the starting to its finishing, i.e. from installation to its production.
►Loan (general):
Short term and long term loans allowed to individual/firms/industries for a specific purpose but a definite period and generally repayable by the installments fall under this head. These types of lending are mainly allowed to accommodate financing under the categories.
a) Large and medium Scale Industries-
b) Small and cottage industries, very often term financing for agriculture and others are also included here.
►Bank guarantee:
The bank is very often requested by his customer to issue guarantees on their behalf to a third party- committing to make an unconditional payment of certain amount of money to the third party, if the customer (on whose behalf it gives guarantee) becomes liable, or creates any loss or damage to the third party.
►Export Cash Credit (ECC):
Financial accommodation allowed to customer for exports of goods falls under this head is categorized as “Export Credit”. The advances must be liquidated out of export proceeds within 180 days.
►Cash credit (Hypothecation):
The mortgage of movable property for securing loan is called hypothecation. Hypothecation is a legal transaction whereby goods are made available to the lending banker as security for a debt without transferring either the property in the goods or either possession. The banker has only equitable charge on stocks, which partially means nothing. Since the goods always remain in the physical possession of the borrower, there is much risk to the bank. So, it is granted to parties of undoubted means with the highest integrity.
►Cash Credit (Pledge):
Bailer in this case is called the “Paw nor” and the bailee is called the “Pawnee”. In a contract of pledge, neither paws nor must deliver the goods pledged to the Pawnee either actually or constructively. Transfer of possession in the judicial sense is essential in the valid pledge. In case of pledge, the bank acquire the possession of the goods or a right to hold goods until the repayment for credit with a special right to sell after due notice to the borrower in the event of non-repayment.
The formalities for opening cash credit:
The intending cash credit holder should submit the following documents and being fulfill property:
- Stock report. Rent receipt.
- Trade license.
- Up to date income tax clearing certificate.
- Charge documents
- Letter of continuity
- Letter of arrangement
- DP (demand promissory) note.
- Letter of guarantee.
- Letter lien.
- Limit sanctions advice.
- Non-encumbrance certificate.
Observing the documents the bank authority prepares a CC proposal from that contains the following information.
> Nature of business.
> Banking with EXIM
> Transaction with CD account by the client.
> Allied deposit with SB/STD account.
> Number of adjustment (S) (applicable only for renewal of CC)
►Lending Authority:
As sure proper and orderly conduct of the business of the bank, the Board of Directors will empower the managing director and other Executives of the Bank to lend up certain amount under certain terms and conditions at their discretion. The lending officer is broadly categorized as follows:
> Managing Director
> Deputy Managing Director
> Executive Vice President Asst.
> Senior Vice President
> Vice President
> Senior Asst. Vice President
> Asst. Vice President
The amount and scope of each Officer lending authority is a function of the amount and extent of authority required by the officer to carry out his/her responsibilities to the bank and its clients may prudent, effective manner. It must be emphasized that an officer will not be delicate-lending authority only on the basis of his position. In other words an officer does not automatically get lending authority by virtual of his corporate and /or functional title. Specified lending authority will be delegated by the Managing Director to various Executives after taking into consideration his proven credit judgment, knowledge and experience. The amount of lending authority approved by the Board for various executives from the upper limits of the authority that may be delegated to an officer holding corporate title. Each individual lending authority will be delegated to him in writing. The Managing Director with the Executive Committee/ Board will review all lending authorities periodically.
CIB:
Bangladesh Bank has established within itself credit information Bureau (CIB), which collects credit information from the banks. Banks are required to furnish such information in respect of credit limit of TK. 50000 and over. They mention the name of facility, security and charge along with outstanding balance. After consolidating such information in respect of each customer, the central bank supplies to the total limits sanctioned to and the number of banks dealing with a party. Thus the banks can find out if any of their customers is having excessive borrowings from the banking system at any particular time.
5.5 Investment Classification:
Investment classification is a process by which the risk or loss potential associated with the investment accounts of a bank on a particular data is identified and quantified to measure accurately the level of reserves to be maintained by the bank to provide for the probable loss on account those risky investment.
Like other banks, all types of investments of Exim Bank fall into following four scales:
►Unclassified: Repayment is regular.
►Substander: Repayment is stopped or irregular but has reasonable prospect of improvement.
►Doubtful debt: Unlikely to be repaid but special collection efforts may result in partial recovery.
►Bad/Loss: Very little chance of recovery.
5.6 Creation of a charge for securing Investment:
For the safety of investment, bank requires security from the investment so that it cans recovery the investment by selling security if borrower fails to repay. Creation of a charge means making it available as a cover for an advance. The method of charging should be legal, perfect, and complete. Importance of charging security
►Protection of profit.
►Ensuring the recovery of the money lent
►Provision against unexpected change
►Commitment of the borrower
Security:
To make the investment secured, charging sufficient security on the credit facilities is very important. The banker cannot afford to take the risk of non-recovery of the money lent. Exim Bank charges the following two types of security.
►Primary security: these are the security taken by the ownership of the items for which bank provides the facility.
►Collateral security: collateral securities refer to the securities deposited by the third party to secure the advance for the borrower in narrow sense. In wider sense, it denotes any type of security on which the bank has a personal right of action on the debtor in respect of the advance.
5.7 Modes of charging security:
There are different modes of charging the bank exercises security:
Pledge:
Pledge is the bailment of the goods as security for payment of a debt or performance of a promise. A pledge may be in respect of goods including stocks and share as well as documents of title to goods such as railway receipt, bills of landing, doc warrants etc. duly endorsed in banks favor.
Hypothecation:
In case of hypothecation the possession and the ownership of the goods both rest the borrower. The borrower to the banker creates an equitable charge on the security. The borrower does this by executing a document known as agreement of Hypothecation in favor of the lending bank.
Lien:
Lien is the right of the banker to retain the goods of the borrower until the investment is repaid. The banker’s lien is general line. A banker can retain all security in his possession till all claims against the concern person are satisfied.
Mortgage:
According to section (58) of the transfer of property Act. 1882 mortgage is the “transfer of an profit in specific immovable property for the purpose of securing the payment of money advanced or to be advanced by way of investment, existing or future debt or the performance of an engagement which may give rise to a pecuniary liability”. In this case the mortgagor does not transfer the ownership of the specific immovable property to the mortgage only transfer some of his rights as an owner. The banker exercises the equitable mortgage.
5.8 Documentation:
Documentation can be described as the process or technique of obtaining the relevant document. In spite of the fact that banker lends credit to a borrower after inquiring about the character, capacity and capital of the borrower, he must obtain proper documents executed from the borrower to protect him against willful defaults. Moreover, when money is lent against some security of some assets. The document must be executed in order to executed in order to given the banker a legal and binding charge against those assets. Documents contain the precise terms of granting investments and they serve as important evidence in the law courts if the circumstance so desire. That why all approval procedure and proper documentation shall be completed prior to the disbursement of the facilities.
5.9 Credit Disbursement:
Having completely and accurately prepared the necessary investment documents, the investment officer ready to disburse the investment to the borrower’s investment account. After disbursement, the investment needs to be monitored to ensure whether the terms and conditions of the investment fulfilled by both bank and client or not.
5.10 Administration/ Monitoring:
The administration of the investment process shall ensure. Compliance with all laws and regulations at both local and global levels including bank policy as set out in this document and the banks credit manual/circulars.
Proper analysis of credit proposal is complex and requires a high level of numerical as well as analytical ability and common sense to ensure effective understanding of the concepts and thus common sense. To ensure effective understanding of the concepts and thus to make the overall credit portfolio of the bank healthy proper staffing of the credit departments shall be done through placement of qualified officials who have got the right aptitude, formal training in finance, credit risk analysis. Bank credit procedures as well its required experience. Where repayment and profit servicing performance of a credit deteriorates shall be identifies at an early state and closely monitored to avoid low losses.
Investment facilities, where appropriate and related security shall be monitored and reviewed by a separate unit unconnected with the credit approval process on a regular basis in order to assess the credit ability of the investment and effectiveness of the security. This unit will report to the managing Director or his designed officer.
Foreign Exchange
6.1 Introduction:
Foreign exchange is the means and methods by which right to wealth in a countries currency are converted into rights to wealth in another country’s currency. In banks when we talk of foreign exchange, we refer to the general mechanism by which a bank converts currency of one country into that of another. Foreign Exchange Department (FED) is the international department Bangladesh bank issues license to scheduled banks to deal with foreign exchange. These banks are known as authorized Dealers. If the branch is authorized dealer in foreign exchange market, it can remit foreign exchange from local country to foreign country. So EXIM Bank, principal branch is an authorized dealer.
There are three kinds of foreign exchange transaction:
- Import
- Export
- Remittance.
6.2 Import:
To Import, a person should be competent to be and importer. According to import and Export Control Act, 1950, the office of chief controller of import and export provides the registration (IRC) to the importer. In an international business environment, buyers and sellers are generally unknown to each other. So seller of goods always seeks security for the payment of his exported goods. Bank gives export guarantee that it will pay for the goods on behalf of the buyer if the buyer does not pay. This guarantee is called letter of credit. Thus the contract between importer and exporter is given a legal shape by the banker by ‘Letter of Credit’.
Letter of Credit:
A conditional written undertaken issued by the importer’s (applicant) bank to the export (beneficiary) at the request of the importer to effect payment up to a stated amount within a stated time period against presentation of complaint document.
The LC is governed by international Chamber of Commerce (ICC) publication no. 500.
Parties of the L/C:
Importer | Who Applies for L/C |
Issuing Bank | It is the bank which opens/issues a L/C on behalf of the import |
Confirming Bank | It is the bank, which adds its confirmation to the credit and it, is done at the request of issuing bank. Confirming bank may or may not be advising bank. |
Advising or Notifying Bank | It is the bank through which the L/C is advised to the exporters. This bank is actually situated in exporters country. It may also assume the role of confirming and/or negotiating bank depending upon the condition of the credit. |
Negotiating Bank | It is the bank, which negotiates the bill and pays the amount of the beneficiary. The advising bank and the negotiating bank may or may not be the same. Sometimes it can also be confirming bank. |
Accepting Bank | It is the bank on which the bill will be drawn (as per condition of the credit). Usually it is the issuing bank. |
Reimbursing Bank | It is the bank, which would reimburse the negotiating bank after getting payment- instructions from issuing bank. |
Steps for import L/C operation – 8 steps operation
Step 1-registration with CCI & E:
►For engaging in international, trade, every trader must be first registered with the chief controller of import and export,
►By paying specified registration fees to the CCI & E. the trader will get RC/ERC (Import/Export registration certificate), to open L/C with bank, this IRC is must.
Step 2 – Determination terms of credit:
The terms of the letter of credit are depending upon the contract between the importers and exporter. The terms of the credit specify the amount of credit, name and address of the beneficiary and opener, tenor of the bill of exchange, period and mode of shipment and of destination, nature of credit, expire date, name and number of sets of shipping documents etc.
Step 3 – Proposal for opening of L/C:
To have an import LC limit an importer submits an application to department to Exim Bank The proposal contains the following particulars:
►Full particulars of the bank account
►Nature of business
►Required amount of limit
►Payment terms and conditions
►Goods to be imported
►Offered security
►Repayment Schedule
Step 4 – Application by importer to the banker to open letter of credit
►For opening L/C, the importer is required to fill up a prescribed application from provided by the banker along with the following document:
Table No-13
| 1. L/C Application form 7. Authority to debt account. 2. Filled up LCA form 8. Filled up amendment request form 3. Demand Promissory Note 9. IMP form 4. Pro-forma invoice 10. Insurance cover note and money receipt. 5. Tax identification number 11. Membership certificate 6. Import registration certificate 12. Rate fluctuation undertaking |
Step 5 – Opening of L/C by the bank for the opener:
►Taking filled up application form the importer.
►Collects credit repots of exporter from exporters country thought his foreign correspondence there.
►Opening bank then issues credit by air mail/TEL EX/SWIFT followed by L/C advice as asked by the opener through his foreign correspondent or branch as the case may be, at the place of beneficiary. The advising bank advises the L/C to the beneficiary on his own form where it is addressed to him or merely hand over the original L/C to the beneficiary if it is so addressed.
Step 6 – shipment of goods and lodgment of documents by exporter:
►Then exporter ships the goods to destination of the importer country.
►Sends die documents to the L/C opening bank through his negotiating bank.
Generally the following documents are sent to the opening Banker with L/C:
Table No-14
| 1. Bill of Exchange | 6. Packing List |
| 2. Bill of lading | 7. Advice Details of Shipment |
| 3. Commercial Invoice | 8.pre-shipment Inspection certificate |
| 4. Certification of Origin | 9. Vessel particular |
| 5. A certificate stating that each packet contains the description of goods over the packet. | 10. Shipment certificate |
Step 7 – lodgment of documents by the opening bank from the negotiating bank:
After receiving the documents, the opening banker scrutinizes the documents. If any discrepancy found, it informs the importer, if importer accepts the fault, then opening bankers call importer retiring the document. At this time many thing can happen. These are indicated in the following:
►Discrepancy found but the importer accepts- no problem occurs in lodgment.
►Discrepancy found and importer not agreed to accept – in this case, importer protest and send back all the documents to the Exporter and request his to make in the specified manner. Here banker is not bound to pay because the documents send by exporter is not in accordance with the terms of L/C.
►Documents are OK but importer is willing to retire the documents- in this case bank is obligated to pay the price of exported goods. Since importer did not pay for bill of exchange, this payment by bank is one kind of credit to the importer and this credit in banking is known as PAD.
►Everything is O.K. but importer fails to clear goods from the port and request bank to clear – in this case banks clear the goods and takes delivery of the same by paying customer duty and sales tax etc. So, this expenditure is debited to the importers account and in banking it is called LIM.
Step 8 – Retirement:
The importer receives the intimation and gives necessary instruction to the bank for retirement of the import bills or for the disposal of the shipping document to clear the imported goods from the customs authority. The importer may instruct the bank to retire the documents by debiting his account with the bank or may ask for LTR (Loan against Trust receipt). When the officer thinks fit the application to open a L/C, giving the following entries creates the following charge
6.3 Accounting Procedure in case of L/C Opening:
Table No-15
| Particulars | Debit/Credit | Charge in Taka |
| Customers A/C | Debit | |
| L/C Margin A/C | Credit | |
| Commission A/C on L/C | Credit | 50% |
| VAT | Credit | 15% on commission |
| SWIFT Charge | Credit | 3000/- |
| Datamax | Credit | 1000/- |
| Stamp | Credit | 150/- |
| Postage | Credit | 300/- |
| DHL/Courier | Credit | 1500/- |
6.4 Amendment of L/C:
After opening of L/C some times alteration to the original terms and conditions become necessary. These amendments involve change in
- Unit price
- Extension of validity to the L/C
- Documentary requirements etc.
Such amendments can be affected only if all the concerned parties agree i.e. the beneficiary, the importer, the issuing bank and the advising bank.
For any amendment the importer must request the issuing bank in writing duly supported by revised indent/Performa invoice. The issuing bank then advises the required amendment to the advising bank. L/C amendment commission including postage is charged to the clients A/C.
Loan against Trust receipts (LTR)
¨Advance against a trust receipt obtained from the customers are allowed to only first class tested parties when the documents covering an import shipment or other goods pledged to the bank as security are given without payee.
¨However, for such advances prior permission/sanction from head Office must be obtained.
¨The customer holds the goods or their sale-proceeds in trust for the bank, till! Such time, the loan allowed against the trust receipt is fully paid off.
¨The trust receipt is a document that creates the bankers lien on the goods and practically amounts to hypothecation of the proceeds of sale in discharge of the lien.
Loan against Imported Merchandise (LIM)
Advance (Loan) against the security of merchandise imported through the bank may be allowed either on pledge or hypothecation of goods, retaining margin prescribed on their landed Cost, depending on their categories and credit Restriction imposed by the Bangladesh bank, bank shall also obtain a letter of undertaking and indemnity from the parties, before getting the goods cleared through LIM Account.
6.5 Payment Procedure of Import Document:
This is the most sensitive task of the Import department. The Officials have to be very much careful while making payment. This task constitutes the following:
►Date of Payment:
Usually payment is made within seven days after the documents have been received. If the payment is become deferred, the negotiating bank may claim interest for making delay.
►Preparing Sale Memo:
A sale memo is made at B.C rate to the customer. As the T.T & O.D rate is paid to the ID, the difference between these two rates is exchange trading. Finally, an inter branch Exchange Trading Credit Advice is sent to ID.
►Requisition for the Foreign Currency
For arranging necessary fund for payment, a requisition is sent to the international Department.
►Transmission of Message:
Message is transmitted to the correspondent bank ensuring that payment is being made.
6.6 Export:
The goods and services sold by Bangladesh to foreign households, businessmen and Government are called export. The export trade of the country is regulated by the imports and exports (control) Act, 1950. There are a number of formalities, which an exporter has to fulfill before and after shipment of goods. The exports from Bangladesh are subject to export trade control exercised by the Minister Of commerce through Chief Controller of Imports and Exports (CCI & E). No exporter is allowed to export any commodity permissible for export from Bangladesh unless he is registered with CCI & E and holds valid Export registration certificate (ERC). The ERC is required to be renewed every year; the ERC number is to be incorporated on EXP forms and other documents connected with exports. The formalities and procedure are enumerated as following next page.
- Obtaining exports LC: to get export LC form exporter issued by the importer.
- Submission of export document; Exporter has to submit all necessary documents to the collecting bank after shipping of goods
- Checking of export documents; after getting the documents banker used to check the documents as per LC terms.
- Negotiation of export documents; if the bank accepts the document and pays the value draft to the exporter and forward the document to issuing bank that is called a negotiating bank. If the bank does buy the LC then the bank normally acts as collecting bank.
- Realization of proceeds: this is the period when the issuing bank has realized the payment.
- Reporting to the Bangladesh bank: as per instruction by Bangladesh bank the bank has to report to respective department of Bangladesh bank by mentioning latest payment.
- Issue to proceeds realization certificate (PRC): bank has to issue precede realization certificate of export LC to the supplier/exporter for getting cash assistant.
Export Operation:
Bangladesh exports a large quantity of goods and services to foreign household. Readymade textile garments (both knitted and woven). Jut, Jute-made products frozen shrimps, tea are the main goods that Bangladeshi exporters exports to foreign countries. Garments sector is the largest sector that exports the lion share of the countries export. Bangladesh exports most of its readymade garments products to U.S.A and European community (EC) countries. Bangladesh exports about 40% of its readymade garments products to U.S.A. most of the Exporters who export through.
EXIM BANK is a readymade garment exporter. They open export L/Cs here to export their goods, which they open against the import L/Cs opened by their foreign importers.
Export L/C operation is just reverse of the import L/C operation. For exporting goods by the local exporter, bank may act as advising banks and collecting bank (negotiable bank) for the exporter,
►As an advising bank:
It receives documents from the foreign importer and hands it over to the exporter. Sometimes it adds confirmation on the L/C on request from the opening bank. By adding confirmation, it assumes the responsibility to make payment to the exporter.
►As Negotiating Bank:
It negotiates the bills and other shipping documents in favor of the exporter. That is it collects the proceeds of the export-bill from the drawer and credits the exporters account for the same. Collection proceed from the export bill is deposited in the banks NOSTRO account in the importers country. Sometimes the bank purchases the bills at discount and waits till maturity of the bill. When the bill matures, bank presents it to the drawer to encase it.
In our country, Export and Import operation of bank is very much related with one another because of use of Back to Back and maturity of payment for Back-to-Back L/C is set in such that it can be paid out of export proceeds.
Back-To-Back L/C:
- Obtaining exports LC: To get export LC form exporter issued by the importer.
- Submission of export documents: Exporter has to submit all necessary documents to the collecting bank after shipping of goods
- Checking of exports documents: after getting the documents banker used to check the documents as per LC terms.
- Negotiation of export documents: if the bank accepts the document and pays the value draft to the exporter and forward the document to issuing bank that is called a negotiating bank. IF the bank does buy the LC then the bank normally acts as collecting bank.
- Realizations of proceed: this is the period when the issuing bank has realized the payment.
- Reporting to the Bangladesh bank: As per instruction by Bangladesh bank the bank has report to respective department of Bangladesh bank by mentioning latest payment.
- Issue to proceeds realization certificate (PRC): Bank has to issue recede realization certificate of export LC to the supplier/exporter for getting cash assistant.
6.7 Export Operation:
Bangladesh exports a large quantity of goods and services to foreign household. Readymade textile garments (both knitted and woven). Jut, Jute-made products frozen shrimps, tea are the main goods that Bangladeshi exporters exports to foreign countries. Garments sector is the largest sector that exports the lion share of the countries export. Bangladesh exports most of its readymade garments products to U.S.A and European community (EC) countries. Bangladesh exports about 40% of its readymade garments products to U.S.A. most of the Exporters who export through.
EXIM BANK is a readymade garment exporter. They open export L/Cs here to export their goods, which they open against the import L/Cs opened by their foreign importers.
Export L/C operation is just reverse of the import L/C operation. For exporting goods by the local exporter, bank may act as advising banks and collecting bank (negotiable bank) for the exporter,
►As an advising bank:
It receives documents from the foreign importer and hands it over to the exporter. Sometimes it adds confirmation on the L/C on request from the opening bank. By adding confirmation, it assumes the responsibility to make payment to the exporter.
►As Negotiating Bank:
It negotiates the bills and other shipping documents in favor of the exporter. That is it collects the proceeds of the export-bill from the drawer and credits the exporters account for the same. Collection proceed from the export bill is deposited in the banks NOSTRO account in the importers country. Sometimes the bank purchases the bills at discount and waits till maturity of the bill. When the bill matures, bank presents it to the drawer to encase it.
In our country, Export and Import operation of bank is very much related with one another because of use of Back to Back and maturity of payment for Back-to-Back L/C is set in such that it can be paid out of export proceeds.
Back-To-Back L/C:
It is simply issued to the clients against an import L/C. Back-To-Back mechanism involves two separate L/C. One is master export L/C and another is Back-To-Back L/C. on the strength of master Export L/C bank issues Back-To-Back L/C. Back-To-Back L/C. is commonly known as buying L/C. On the Country, master Export L/C is Known As Selling L/C.
Features of Back-To-Back L/C:
►An Import L/C to procure goods/raw materials for future processing.
►It is opened based on Export L/C
►It is a kind of export Finance.
►Export L/C is at sight but Back-To-Back L/C is at Usance.
►No margin is required to open Back-To-Back L/C
►Application is registered with CCI & E
►Application has bonded warehouse license.
►L/C value shall not exceed the admissible percentage of net FOB value of relative master L/C
►Usance period will be up to 180 days.
►The Import L/C is opened for 75% of the value of export L/C.
►Here L/C issued against the lien of Export L/C
►Arrangements are such that Export L/C matures first then out of this export profit, import L/C is paid out.
Documents Required for Opening a Back-To-Back L/C:
In EXTM bank principal branch, followed papers/ Documents are required for opening a Back-To-Back L/C –
- Master L/C
- Valid Import Registration certificate (IRC) and Export Registration certificate (ERC)
- L/C Application and LCAF duly filled in and signed
- Performa invoice or indent
- Insurance cover note with money receipt.
- IMP form duly signed.
In addition to the above documents, the followings are also required to export oriented garment industries while requesting for opening a back-to-back L/C-
- Textile permission
- Valid Bonded warehouse license
- Quota allocation letter issued by the Export Promotion Bureau (EPB) in favor of the applicant for quota items.
Checklist of exports L/C:
Following defective points are usually found in the Master L/C. So, the bank officials so much carefully check these points. These are:
- Name of the advising bank.
- Name of Transferring bank
- Form of Doc. Credit:
►Name of issuing Bank
►Documentary Credit No. and issuing data
►Data of Shipment
►Expire data and place
- Applicant/for order of /On Account.
- Beneficiary/Favoring
- Amount
- Availability of credit
- Partial shipment/transshipment
- Payment condition/draft Sign
- Category.
- Description of goods
- ·Item
- ·Total Qty
- ·Unit price
- B/L Clause
- Reimbursement clause.
- UCPDC Clause
- Net FOB Value.
Payment of back-to-back L/C
In case back to back as 60-90-120-180 days of maturity period, deferred payment is made. Payment is given after realizing export proceeds from the L/C issuing bank.
L/C under EDF:
·Exporter development fund is created by Bangladesh bank to given encourages to the exporter in Bangladesh.
·Generally Back-to-Back L/C is Usance L/C that is here bill of exchange is payable after some maturity date say 90 or 120 days after the date of acceptance/negotiation. But some foreign seller may require sight payment. Here import L/C matures first. In that case Bangladesh Bank gives me fund to the bank to pay the price of imported goods in favor of the local purchaser of raw materials. When export proceeds come, first Bangladesh bank loan to the importer is adjusted and remaining part goes to the importer of raw materials.
6.8 Negotiations of exports documents:
The most common method of financing exporters is negotiation of documents under L/C. it is a post-shipment credit. Here the bank acts as a negotiating bank. After the shipment of the goods, the exporter submits the relative documents to the branch for negotiation. The documents are to submit within the period mentioned in the L/C. after approval of negotiation of the bill the full particulars of the documents are entered into the foreign bill purchased (F.B.P) register. The documents are sent to the L/C opening branch will a forwarding letter. The branch claim reimbursement from the issuing bank or from the reimbursing bank, giving clear instructions to credit the proceeds of the bill to the Exim Bank head office NOSTRO A/C maintained with the named correspondent bank abroad under telex intimation to the principal branch and head Office (International Division).
Negotiation stands for payment of value to the exporter against the documents stipulated in the L/C. if documents are in order, Exim Bank Purchases (negotiates) the same on the basis of banker- customer relationship. This is known as foreign documentary bill Purchase (FDBP).
If the bank is not satisfied with the documents submitted to Exim Bank gives the exporter reasonable time to remove the discrepancies or sends the documents to L/C opening bank for collection. This is known as foreign Documentary bill for Collection (FDBC).
Presentation of exports documents for negotiation/purchase:
After shipment, exporter submits the following documents to Exim Bank for negotiation.
►Bill of exchange
►Bill of lading
►Invoice
►Insurance policy/certificate
►Certificate of origin
►Inspection certificate
►Consular Invoice
►Packing list
►Quality Control certificate
►G.S.P. Certificate.
Payment procedure for FDBP:
i) After purchasing the document, Exim Bank gives the following entries:
FDBP A/C——————————-Dr.(at OD sight rate)
Customer A/C—————————Cr.
(Before realization of proceeds)
Bank would realize only postage charges from the export.
(Subsequently, Bank will send the documents to the L/C opening bank for payment with a forwarding letter detailing the enclosures. Upon realization of proceeds the negotiating bank would pass the following vouchers:
Head Office A/C————————-Dr. (at T.T Clean rate)
FDBP A/C——————————–Cr.
Income A/C Profit on Exchange Trading————-Cr.
(Adjustment after realization of proceeds)
A FDBP register is maintained for recording all the particulars.
Foreign documentary bills for collection (FDBC):
Exim Bank forwards the documents for collection due to the following reasons-
►If the documents have discrepancies.
►If the Exporter is a new client.
FDBC signifies that the exporter will receive payment only when the issuing bank gives payment. Exim Bank make regular follow-up with the L/C opening bank in case of any delay in getting payment.
Settlement of Local Bills:
- The settlement of local bills is done in the following ways
- The customer submits the L/C to Exim Bank along with the documents to negotiate
- Exim Bank official scrutinizes the documents to ensure the conformity with the terms and conditions.
- The documents are then forwarded to the L/C opening bank.
- The L/C issuing bank gives the acceptance and forwards an acceptance letter.
- Payment is given to the customer on either by collection basis or by purchasing the document.
Mode of payment of export bill under L/C:
As per UCPDC 500, 1993 revision there are four types of credit. These are as follows:
►Sight payment credit:
In a sight payment credit, the bank pays the stipulated sum immediately against the exporters presentation of the documents.
►Deferred Payment Credit:
In deferred payment, the bank agrees to pay on a specified future date or event, after presentation of the export documents. No bill of exchange is involved. Payment is given to the party at the rate of D.A 60-90-120-180 as the case may be. But the head office is paid at T.T clean rate. The difference between the two rates us the exchange trading for the branch.
►Acceptance Credit:
In acceptance credit, the exporter presents a bill of exchange payable to him and drawn at the agreed tenor (that is, on a specified future date or event) on the bank that is to accept it. The bank signs its acceptance on the bill and returns it to the exporter. The exporter can then represent it for payment on maturity. Alternatively he can discount it in order to obtain immediate payment.
►Negotiation credit.
In negotiation credit, the exporter has to present a bill of exchange payable to him in addition to other documents that the bank negotiates.
6.9 EXIM BANK LC nature of code:
Cash LC (sight) Foreign -01
Cash LC (Usance) Foreign -02
Inland back to back LC (sight) -03
Inland back to back LC (Usance) -04
Foreign back to back LC (sight) -05
Foreign back to back LC (Usance) -06
LC under AID/Loan ED -07
LC Under STA -08
Import from EPZ (Cash LC) Sight -09
Import from EPZ (Cash LC) Usance -10
Import from EPZ (B/B LC) Sight -11
Import from EPZ (B/B LC) Usance -12
Others (L/C) Cash LC Local sight or usance -99
EXIM BANK BACK-TO-BACK LC COMMISSION:
► Back to Back (Foreign):
1st quarter- 0.50%
(LC issue date to asperity date with in 90 days than
90 days (0.50%+0.30%=80%)
► Back to Back (Foreign) other charge:
Data max charge -1000
Swift -3000
Stamp -150
►Back to Back (Local):
1st quarter- 0.50%
(LC issue date to expire date with in 90 days than
90 days (0.50%+0.30%=80%)
►Back to Back (Sight Local):
1st quarter- 0.50%
(LC issue date to expire date with in 90 days than
90 days (0.50%+0.30%=80%)
►Export Development Fund:
1st quarter- 0.50%
(LC issue date to expire date with in 90 days than
90 days (0.50%+0.30%=80%)
►Export processing Zone:
1st quarter- 0.50%
(LC issue date to expire date with in 90 days than
90 days (0.50%+0.30%=80%)
►Export processing Zone other charge:
Data max charge -1000
Courier Charge -200
-0.50%
(LC issue date to asperity date with in 90 days than
90 days (0.50%+0.30%=80%)
►Back to Back (Foreign) other charge:
Data max charge -1000
Swift -3000
Stamp -150
6.10 Foreign Remittance:
This bank is authorized dealer to deal in foreign exchange business. As an authorized Dealer, a bank must provide some services to the clients regarding foreign exchange and this department provide these services.
The basic function of this department are outward and inward remittance of foreign exchange from one country to another country. In the process of providing this remittance service, it sells and buys foreign currency. The conversion of one currency into another takes place at an agreed rate of exchange, which the banker quotes, one for buying and another for selling. In such transactions the foreign currencies are like any other commodities offered for sales and purchase, the cost (convention value) being paid by the buyer in home currency, the legal tender.
Remittance procedures of foreign currency:
There are two types of remittance:
- Inward remittance
- Outward remittance.
Inward foreign remittance:
Inward remittance covers purchase of foreign currency in the form of foreign T.T., D.D and bills, T.C. etc. sent from abroad favoring a beneficiary in Bangladesh.
Purchase of foreign exchange in to be reported to exchange control department of Bangladesh bank on form-C.
Outward Foreign Remittance:
Outward remittance covers sales of foreign currency through issuing foreign T.T draft, travelers check etc. as well as sell of foreign exchange under L/C and against import bills retired.
Working of this department:
- Issuance of TC, Cash Dollar/Pound
- Issuance of FDD, FTT & purchasing, payment of the same.
- Passport endorsement.
- Encashment certificate
- F/C Account opening & filling.
- Opening of export FC retention Quota A/C & maintain.
- Maintenance of ledger of cash Dollar, FC Department A/C & TC.
- Maintain FBC register & follow up FBC.
- Opening of Student fill & maintain.
- Preparation of all related statement, Voucher & posting.
- Preparation of Weekly, Monthly, Yearly Statement for Bangladesh bank returns timely.
- Attending all related correspondence to other Bank or institutions.
Modes:
The remittance process involves the following four modes
Cash Remittance Dollar Pound | Sell | Bank sells dollar / Pound for using in abroad by the purchaser. The maximum amount of such sell is mentioned in the Bangladesh bank publication of ‘Convertibillity of taka for Currency Transaction in Bangladesh! |
Purchase | Bank can purchase dollar from resident and non-resident Bangladeshi and foreigner. Most dollars purchased comes from realization of export Bill of Exchange. | |
Traveler’s Cheque (TC) | Issue of TC | TC is useful to traveler abroad. Customers can encash the TC in abroad from the drawer bank. TC is altemative to holding cash and it provides better security than holding cash in hand. |
Buying Of TC | If any unused leaf of TC is surrendered bank buys it from the customer. All payments are made in local currency. Banks generally by only those TC. | |
Telex Transfe | Outward TT | It remits fund by tested TT via its foreign correspondence bank in which it is maintaining its NOSTRO Account. |
Incoming TT | It also makes payment according to telegraphic message of its foreign correspondence bank from the corresponding VOSTRO Account. | |
Foreign Demand Draft | Bank issue demand draft in favor of purchaser or any other according to instruction of purchaser. The payee can collect it for the drawer bank in which the issuing bank of Demand Draft holds its NOSTRO Account. Bank also makes payment on DD drawn on this bank by its foreign correspondence bank through the VOSTRO Account. | |
In these processes of remittance, bank must have to make profit as a business institution. Profit is made in two ways:
- Commission charge
- Difference in the buying and selling rate.
Miscellaneous Services by this Department:
►Student File: Students who are desirous to study abroad can open file in the bank. By opening this file, bank assures the remittance of funds in abroad for study.
►F.C Accounts: Foreign Currency Account opened in the names of Bangladeshi nationals or persons of Bangladeshi origin working or self-employed abroad can now are maintained as long as the account holders desires.
►RFCD: stands for resident Foreign Currency Accounts. Persons ordinary resident in Bangladesh may maintain foreign currency accounts with foreign exchange brought in at abroad. Balance of such accounts is freely remittable abroad.
6.11 Formalities for opening foreign currency (FC) Account:
The AD may without prior approval of the Bangladesh bank open Foreign currency (FC) account in the name of:
- Bangladesh national residing abroad.
- Foreign nationals residing abroad/in Bangladesh and also foreign firms
- Registered abroad and operating in Bangladesh and abstract foreign missions and their expatriate employees.
- Resident of Bangladesh nationals working with the foreign/international organization operating in Bangladesh provided their salary in paid in foreign currency.
Foreign exchange earned through business done or service rendered in Bangladesh cannot be put into these accounts.
No payment in foreign currency (FC) may be made to any resident in Bangladesh out of the foreign currency (FC) account.
All citizens of Bangladesh and other persons are residing to Bangladesh who became the owner of any foreign currency (FC).
►Papers required:
·Application duty billed in and signed.
·Photograph (two copies).
·Passport photocopy.
·Work permit from board investment. (In case of foreign nationals).
►Rate of exchange:
It means the price of one currency expressed in terms of another currency. Rate of exchange is the rate by which the relation among different foreign currencies is established in terms of local currency of that country. Value at which one country currency can be converted into another country.
In exercise of the power conferred by section three of exchange regulation ACT 1947, Bangladesh has issued license to certain bank to deal in foreign exchange is called authorized dealer.
►Spot rate:
It is quoted for transaction where the foreign currency bought or sold is to be received or delivered immediately. The current rate of exchange quoted in the foreign exchange market.
►Forward rate:
When a rate is applied to a future date it is called forward rate at which foreign exchange can be sold or bought for delivery at a future time.
►Cross rate:
The rate of exchange quoted expressing the quotation for any two currencies in term of a third.
►SWAO:
Sport rate against forward purchased or a spot purchase against forward rate.
►Pence rate/direct quotation:
Rates are quoted in terms foreign currency per one unit of foreign currency.
►Currency rate/indirect quotation:
Rates are quoted in terms of foreign currency per one unit of home currency.
►Buying rate:
Authorized dealer applies this at the time of purchasing/negotiation of export document and payment against T.T.MT, check and drafts required from abroad.
►Selling rate:
Authorized dealer applies this at the time of lodgment of import documents, realization of LC margin from importer and other foreign exchanges transaction on overseas bank.
►Telquel rate:
This is the rate when rate of foreign currency is quoted according to the since of the bill.
►Forward rate at a discount:
When forward rate is higher than that of spot rate.
►Forward rate at a premium:
When for ward rate is lower than that of spot rate .
7.1 SWOT Analysis:
SWOT analysis is the detailed study of an organizations exposure and potential in perspective of its strength, weakness, opportunity and threat. This facilitates the organization to make their existing line of performance and also foresee the future to improve their performance in comparison to their competitors. As though this tool, an organization can also study its current position, it can also be considered as an important tool for making changes in the strategic management of the organization.
Strengths:
►Exim Bank Limited has already established a favorable reputation in the banking industry of the country. It is one of the lading private sector commercial banks in Bangladesh. The bank has already shown a tremendous growth in the profits and deposits sector.
►Exim Bank has provided its banking service with a top leadership and management position. The Board of Directors headed by its Chairman Mr. Md. Nazrul Islam is a skilled person in business world. Alamgir kabir, the advisor of the bank is a reputed senior chartered accountant having 30 years vast experience in accounts, audit, finance and banking at home and abroad. Mr. Mohammed Lakiotullah as the Managing Director of the bank management team. The top management officials have all worked in reputed banks and their years of banking expansion of the bank.
►Exim Bank Limited has already achieved a higher growth rate accompanied by an impressive profit growth rate in 2001. the number of deposits and the loans and advances are also increasing rapidly.
►Exim Bank has an interactive corporate culture. The working environment is very friendly, interactive and informal. And, there are no hidden barriers or boundaries while communicate between the superior and the employees. This corporate culture provides as a great motivation factor among the employees.
► Exim Bank has the reputation of being the provider of goods quality service too its, potential customers
Weakness:
►The main important thing is that the bank has no clear mission statement and strategic plan. The banks not have any long-term strategies of weather it wants to focus on retail banking or become a corporate bank. The path of the future should be determined now with a strong feasible strategic plan.
►The bank failed to provide a strong quality-recruitment policy in the lower and some mid level position. As a result the services of the bank seem to be Deus in the present days.
►The poor service quality has become a major problem for the bank. The quality of the service at Exim Bank is higher than the Dhaka Bank, prime bank or Dutch Bangla bank etc. but the bank has to compete with the Multinational bank located here.
►Some of the job in Exim Bank has no growth or advancement path. So lack of motivation exists in persons filling those positions. This is a weakness of Exim Bank that it is having a group of unsatisfied employees.
►In terms of promotional sector, Exim Bank has to more emphasize on that. They have to follow aggressive marketing campaign.
Opportunity:
►In order to reduce the business risk, Exim Bank has to expand their business portfolio. The management can consider options of starting merchant banking or diversify into leasing and insurance sector.
►The activity in the secondary financial market has direct impact on the primary financial market. Banks operate in the primary financial market. Investment in the secondary market governs the national economic activity. Activity in the national economy controls the business of the bank.
►Opportunity in retails banking lies in the fact that the country’s increased population is gradually learning to adopt consumer finance. The bulk of our population is middle class. Different types of retail lending products have great appeal to this class. So a wide variety of retail lending products has a very large and easily pregnable market.
►A large number of private banks coming into the market in the recent time. In this competitive environment Exim Bank must expand its product line to enhance its sustainable competitive advantage. In that product line, they can introduce the ATM to compete with the local and the foreign bank. They can introduce credit card and debit card system for their potential customer.
►In addition of those things, Exim Bank can introduce special corporate Scheme for corporate customer or officer who have an income level higher from the service holder. At the same time, they can introduce scheme or loan for various service holders. And the scheme should be separate according to the professions, such as engineers, lawyers, doctors’ etc.
Threats:
►The default risks of all terms of loan have to be minimizing in order to sustain in the financial market. Because default risk leads the organization towards to bankrupt. Exim Bank has to remain vigilant about this problem so that proactive strategies are taken to minimize this problem if not elimination.
►The low compensation package of the employees from mid level to lower level position threats the employee motivation. As a result, good quality employees level the organization and it effects the organization as a whole.
7.2 Problems of EXIM Bank:
Ä General Banking Department:
In general banking department they follow the traditional banking system. The entire general banking procedure is not fully computerized.
The cash counter I think is congested and the procedure is also traditional
Lack of variety of services is also a back of the general banking department. The bank provides only some traditional limited service to its clients.
They are not using database networking in the information Technology (IT) Department.
According to some clients opinion introducer is one of the problems to open an account. If a person, who is new in the city, wants to open account, it is a problem for her/his to arrange an introducer of SB or CD account holder.
Ä Loans and Advances department
►Political influence is one of the major problems in Bangladesh. Due to political intervention the bank becomes obligated to provide loans in most of the cases, which are rarely recovered. Bank has to face this in convenience situation almost every year.
►The loans and advances department takes a long time to process a loan because the process of sanctioning loans is done manually.
►Sometimes the employees to unlawfully help the client deliberately overrule the securities taken against the loan. As a result if the clients fail to repay the bank authority cannot collect even the principle money invested by the selling those assets. It is also a very important factor that leads to loan default.
►CIB report is not readily available from Bangladesh bank.
Ä Foreign Exchange Department
►In Foreign Exchange Department it is required to communicate with foreign banks frequently and quickly. To make the process easily modern communication media for example e-mail, fax,internate etc.should be used. But the bank has not so much practice of using these media.
►Modern technical equipment such as computer is not sufficient in foreign Exchange department. As a result the exchange process makes delay and it is also complicated.
Ä Other problem:
►Exim Bank doesn’t give their attention on advertisement. As a competition market it is too much important for any organization to increasing their advertisements procedure.
8.1 Conclusions:
As an internee of Exim Bank Ltd. I have truly enjoying my internship from the learning and experience viewpoint. I am confident that this three months internship program at Exim Bank will definitely help me to realize my future carrier in the job market. Exim Bank has converted all of their system and policy of traditional banking to Islamic Banking. I think which a very practical and bold decision is. As there are lots of local and foreign Banks in Bangladesh the Exim Bank Ltd. Is promising commercial bank among them. In this competitive market Exim Bank has to compete not only the others commercial banks but also the public bank. Exim Bank Ltd. Is more capable of contributing towards economic development as compared with other bank. Exim Bank Ltd. Invested more funds in export and import business. It is obvious that the right thinking of this bank including establishing a successful network. Over the country and increasing resources will be able to play a considerable role in the portfolio of development. Success in the banking business largely depends on effective lending. Less the amount of loan losses, the more the income will be from credit operations the more will be the profit of the Exim Bank Ltd. and here lays the success of credit Financing.
During the course of my practical Orientation I have tried to learn the practical banking activities to realize it with my theoretical knowledge, which I have greathearted and going to acquire from various courses of my MBA Program.
8.2 Recommendations:
- The entire department should be well informed regarding their goals and objectives. It is essential to execute company objectives into individual target.
- There must be a clear allocation of responsibility authority and accountability.
- One of the most import limitations is that it has no that much of advertisement of its Exim Bank operations. It can gain dual benefit of attracting deposit and credit.
- The bank should take the initiative to develop an effective research and development center to get innovative ideas to capture the competitive market.
- Job description should be clarified and proper training should be imparted to improve the performance of bottom level management.
- Selection and training must be focused to develop and exploit leadership and entrepreneurial qualities within the work place.
- While the other banks are launching “Customer Credit Scheme” Exim Bank is failing to launch this kind of scheme. The management can undertake such sort of schemes and earn profit.
- To meet today urging of the customer, the bank should introduce automated Teller machine (ATM).
- The bank should provide total investment money at once to the clients so that they can exploit money properly.
- Exim Bank should provides facilities to the internees through monthly allowance, proper placement and practical operations as well as jobs certainly to those who have better performance in doing their particulars. Because this internship program may act as promotional program.
- To fulfill the vision of “mass banking” this bank should grants investment portfolio to new entrepreneurs, young businessman and also to new small companies.
- The bank has to open new branch in the rural but profitable areas so that it can attract new source of deposit and credit. By opening Rajuk Avenue Branch it shoes great success so taking this branch as a sample the bank should consider it as a model.
- The human resource management of the bank is done as the conventional banks do it. The banks should made a collaborate effort to improve the ways of human resource management.