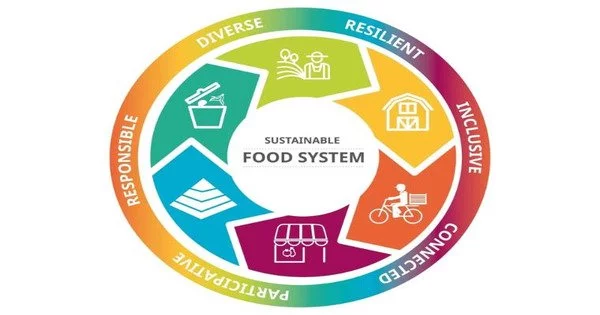
A sustainable food system is one that meets the needs of the present population without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This includes ensuring access to nutritious and culturally appropriate food for all, reducing the environmental impact of food production and distribution, and supporting the economic viability of farmers and other food system workers. Some strategies for achieving a sustainable food system include promoting local and organic agriculture, reducing food waste, and supporting fair trade and fair labor practices.
This is a system of food production, distribution, and consumption that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This includes environmentally sustainable practices, fair treatment of workers, and access to healthy and culturally appropriate food for all members of a community. It also involves reducing food waste and loss, and promoting biodiversity.
This involves a variety of practices and policies related to food production, distribution, and consumption, including reducing food waste, promoting organic and regenerative agriculture, and supporting local food systems. Additionally, a sustainable food system should also consider the social, economic, and environmental impacts of food production and distribution, and work to ensure that all members of society have access to healthy and nutritious food. This can include practices such as organic farming, local food production, and reducing food waste. It also involves creating a fair and just food system that promotes equity and access to healthy food for all people.
Moving to sustainable food systems, including shifting consumption to sustainable diets, is a critical component of addressing the causes and adapting to climate change. According to a 2020 review conducted for the European Union, the food system, including crop and livestock production, transportation, changing land use (including deforestation), and food loss and waste, could account for up to 37% of global greenhouse gas emissions. One major component of this change is the reduction of meat production, which accounts for 60% of GHG emissions and 75% of agriculturally used land.
The global food system is facing major interconnected challenges, such as mitigating food insecurity, the effects of climate change, biodiversity loss, malnutrition, inequity, soil degradation, pest outbreaks, water and energy scarcity, economic and political crises, natural resource depletion, and preventable ill-health. The concept of sustainable food systems is frequently at the heart of sustainability-focused policy programs, such as proposed Green New Deal programs.