Sustainable design strives to reduce the negative environmental impact of buildings by improving efficiency and moderation in the use of materials, energy, development space, and the ecosystem as a whole. It is also known as green or eco-friendly architecture, and it is a method of planning and constructing buildings that prioritizes environmental and social responsibility, resource efficiency, and long-term sustainability.
In the design of the built environment, sustainable architecture takes a mindful approach to energy and environmental conservation. The primary purpose of sustainable design is to reduce the negative influence on the environment while building healthy and efficient spaces for people to live and work in. This field examines a building’s whole life cycle, from design and construction to operation and eventual demolition or reuse.
Sustainable architecture is a broad phrase that refers to buildings that are designed to reduce humanity’s environmental effect. The goal of sustainability, or ecological design, is to ensure that the use of currently accessible resources does not have a negative impact on the well-being of future societies or make it difficult to get resources for other purposes in the long run.
Key principles and features of sustainable architecture include:
- Energy efficiency: Buildings are designed to use energy efficiently and reduce energy consumption. This involves incorporating energy-efficient lighting, insulation, windows, and HVAC systems.
- Renewable energy sources: Utilizing renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, or geothermal power, to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and decrease carbon emissions.
- Sustainable materials: Selecting eco-friendly and recyclable materials with low embodied energy and minimal environmental impact during their production and disposal.
- Water efficiency: Implementing water-saving measures like rainwater harvesting, greywater recycling, and water-efficient fixtures to reduce water consumption.
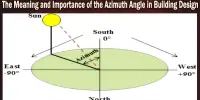
- Passive design: Employing passive design strategies that use the building’s orientation, materials, and landscaping to maximize natural light, ventilation, and temperature control, reducing the need for mechanical systems.
- Waste reduction: Reducing construction waste through efficient design and recycling construction materials whenever possible.
- Adaptive reuse: Preserving and adapting existing structures for new purposes rather than demolishing and rebuilding, thus reducing resource consumption.
Sustainable architecture is an essential component of the larger notion of sustainable development, which seeks to achieve a balance of economic, environmental, and social issues. It is critical in limiting the effects of climate change, conserving natural resources, and building healthier, more resilient communities. As public knowledge of environmental issues grows, so does the need for sustainable architecture, resulting to more inventive and efficient ways in the building sector.