Sulfasalazine (SSZ)
Definition: Sulfasalazine (Brand names: Azulfidine, Azulfidine EN-Tabs) is a medication used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease. It is often considered as a first-line treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. It is taken by mouth. It’s also available as a generic drug. Generic drugs usually cost less than the brand-name version. In some cases, they may not be available in all strengths or forms as the brand-name drug.
Sulfasalazine (Azulfidine) is in a class of medicines known as anti-inflammatories. It works by reducing inflammation in the body. The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) first approved sulfasalazine in 1950. The medicine is manufactured as Azulfidine by Pfizer.
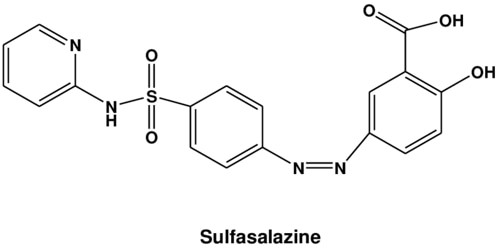
Sulfasalazine (SSZ) only comes as oral tablets, which come in immediate-release and extended-release forms. Sulfasalazine oral tablets are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis, juvenile rheumatoid arthritis, and ulcerative colitis.
Significant side effects occur in about 25% of people. Commonly these include loss of appetite, nausea, headache, and rash. Severe side effects include bone marrow suppression, liver problems, and kidney problems. It should not be used in people allergic to aspirin or sulfonamide. Use during pregnancy appears to be safe for the baby.
This medicine may cause very bad skin conditions such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome or toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Seek medical help right away if people experience symptoms such as:
- Red, swollen, blistered, or peeling skin
- Red or irritated eyes
- Sores in people’s mouth, throat, eyes, or nose
It is on the World Health Organization’s List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system. Continue to take sulfasalazine even if people feel well. Don’t stop taking the medicine without first talking to the doctor.
Uses and Dosages of Sulfasalazine (SSZ): Sulfasalazine is an anti-inflammatory drug. It isn’t fully understood how it works. It’s believed that it affects our immune system and decreases inflammation.
Sulfasalazine is used to treat a certain type of bowel disease called ulcerative colitis. This medication does not cure this condition, but it helps decrease symptoms such as fever, stomach pain, diarrhoea, and rectal bleeding. After an attack is treated, sulfasalazine is also used to increase the amount of time between attacks. This medication works by reducing irritation and swelling in the large intestines.
It is usually not given to children under 2 years of age.
Sulfasalazine isn’t likely to harm an unborn baby. However, tell the doctor if any women are pregnant or might become pregnant before taking this medicine. The drug can be found in breast milk. People shouldn’t breastfeed while taking sulfasalazine without first talking to the doctor.
Around 90% of a dose of sulfasalazine reaches the colon, where most of it is metabolized by bacteria into sulfapyridine and mesalazine (also known as 5-aminosalicylic acid or 5-ASA). Both metabolites are active; most of the sulfapyridine is absorbed and then further metabolized, but most mesalazine is not, and remains in the colon.
Sulfasalazine comes as a regular or delayed-release tablet. The regular tablets are usually taken four times a day. The doses should be evenly-spaced throughout the day, so they’re no more than eight hours apart. The delayed-release tablets may be taken less often throughout the day. Your doctor will tell you how often to take them.
Take this medicine after a meal or with a snack. Then drink a full glass of water (8 ounces). Swallow the tablets whole. Don’t chew or crush them.
Follow the doctor’s instructions carefully when taking sulfasalazine. Don’t take more or less of the drug that is prescribed. Be sure to drink plenty of fluids throughout the day while taking sulfasalazine.
Forms and strengths –
Generic: Sulfasalazine
- Form: oral tablet (immediate-release)
- Strength: 500 mg
- Form: oral tablet (extended-release)
- Strength: 500 mg
Brand: Azulfidine
- Form: oral tablet (immediate-release)
- Strength: 500 mg
Brand: Azulfidine EN-Tabs
- Form: oral tablet (extended-release)
- Strength: 500 mg
The mechanism of action is not clear, but it appears that sulfasalazine and its metabolites have immunosuppressive, antibacterial, and anti-inflammatory effects. It also appears to inhibit the cystine-glutamate antiporter.

Effects of Sulfasalazine (SSZ): Sulfasalazine metabolizes to sulfapyridine. Serum levels should be monitored every three months, and more frequently at the outset. Serum levels above 50 μg/l are associated with side effects. In rare cases, Sulfasalazine can cause severe depression in young males. It can also cause oligospermia and temporary infertility. Immune thrombocytopenia has been reported.
This medication may rarely cause very serious allergic reactions (e.g., Stevens-Johnson syndrome), blood disorders (e.g., agranulocytosis, aplastic anaemia), liver damage, nerve/muscle problems and infections. Get medical help right away if you have any very serious side effects, including: skin rash/blisters/peeling, mouth sores, itching/swelling (especially of the face/tongue/throat), severe dizziness, trouble breathing, chest pain, signs of infection (such as fever, chills, persistent sore throat, cough), swollen lymph nodes, easy bruising/bleeding, severe tiredness, muscle pain/weakness (especially with fever and unusual tiredness), pale or blue skin/lips/nails, new/worsening joint pain, confusion, persistent/severe headache, unexplained neck stiffness, seizures, signs of liver problems (e.g., persistent nausea/vomiting, severe stomach/abdominal pain, yellowing eyes/skin, dark urine).
If these effects are mild, they may go away within a few days or a couple of weeks. If they’re more severe or don’t go away, talk to the doctor or pharmacist.
Sulfasalazine may make people’s skin more sensitive to sunlight. Avoid any unnecessary sun exposure, and wear protective clothing and sunscreen while outdoors. The medicine may also cause drowsiness or dizziness. Be cautious when driving or performing any task that requires alertness.
Information Source: