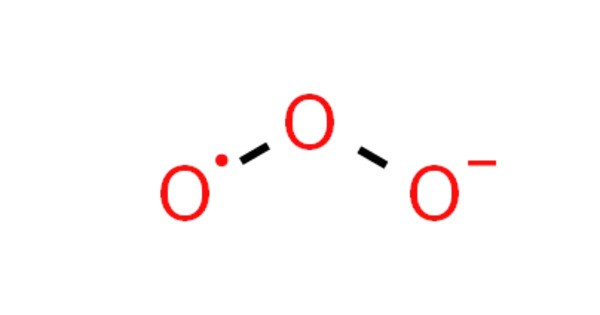
Sodium ozonide (NaO3) is an oxygen-rich compound of sodium. As an ozonide, it contains the ozonide anion (O3−). It’s a highly reactive substance that forms when sodium reacts with ozone gas, typically in a controlled environment. It is used in various chemical processes and has applications in organic synthesis, as well as in the study of ozone-based reactions.
Some experiments report creating sodium ozonide by applying ozone to sodium hydroxide, but the substance was not pure, and the claimed stability at room temperature was contradicted by other reports. This is in contrast to potassium ozonide, rubidium ozonide, and caesium ozonide, which can be synthesized applying ozone directly to the metal. Instead, it is made in ammonia solution using ion exchange and cryptands.
The compound is unstable at room temperature and decomposes at -10 °C to sodium superoxide and oxygen.
2 NaO3 → 2 NaO2 + O2
However, the compound can be stored for months at -18 °C.
Properties
- Chemical formula: NaO3
- Appearance: Intensely red solid
- Stability: It is relatively unstable and sensitive to heat and moisture. It decomposes in water, releasing oxygen and forming sodium hydroxide (NaOH).
- Solubility: It is soluble in water, but as it dissolves, it breaks down and releases oxygen.
- Reactivity: It is a strong oxidizer and can react violently under certain conditions, especially in the presence of organic materials or reducing agents.
- Formation: It can be synthesized by reacting sodium metal with ozone (O₃) under controlled conditions.
Occurrences
- Laboratory: Sodium ozonide is not commonly found in nature but can be synthesized in the lab.
- Synthetic Reactions: It can be formed in ozone-rich environments or used in some industrial processes where ozone is involved.
Applications
Sodium ozonide’s most common use is as a strong oxidizing agent in chemical synthesis, particularly in reactions that require the presence of ozone. It may also be used in ozone production processes or in some types of cleaning agents that utilize ozonides for disinfection.