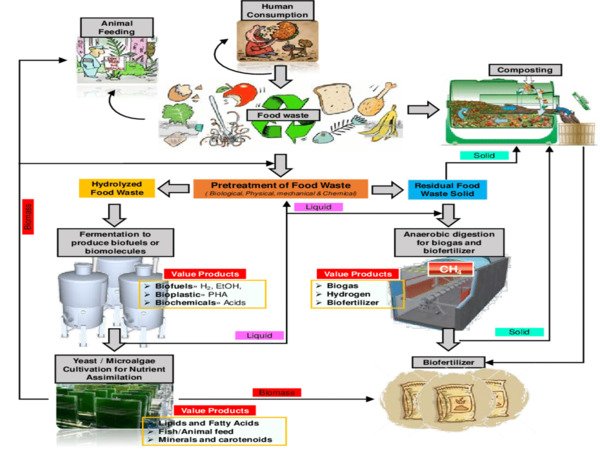
Using biological waste to recover valuable fertilizer components is a solution. It is suggested that nutrients be recycled in accordance with the circular economy assumption. Bio-waste management can improve the recovery of valuable materials. Chemical fertilizers could be replaced with bio-based products. Practical solutions are required for the conversion of biomass to fertilizer.
Researchers from the Università Cattolica di Piacenza have developed a new fertilizer from food chain waste, specifically waste from lactic acid bacteria productions, which are currently eliminated through purification processes.
This is the result of a study published in the journal Land and coordinated by Pier Sandro Cocconcelli, professor of Food Microbiology at Cattolica University’s Faculty of Agricultural, Food, and Environmental Sciences, and Edoardo Puglisi of the Department of Food Science and Technology for a Sustainable Food Supply Chain—DiSTAS.
The study was carried out in collaboration with the company Sacco srl of Cadorago (CO) and the agronomic assay center LandLab srl of quinto Vicentino (VI); Gabriele Bellotti, a Ph.D. student at the Agrisystem School of the Università Cattolica, is the first author.
Lactic acid bacteria are produced for food and nutraceutical use, to produce foods, beverages and probiotics. Normally the waste from the culture substrate used in the production of lactic acid bacteria is cleared off by using purification plants; this is several thousand tons of waste produced each year in Italy.
Professor Cocconcelli
Lactic acid bacteria
Lactic acid bacteria are a group of microorganisms capable of fermenting various substrates, giving rise to numerous products of interest to the agri-food and industrial sectors. Lactic acid bacteria are involved in the production of cheeses, fermented milks, and sausages.
“Lactic acid bacteria,” Professor Cocconcelli says, “are produced for food and nutraceutical use, to produce foods, beverages, and probiotics. Normally the waste from the culture substrate used in the production of lactic acid bacteria is cleared off by using purification plants; this is several thousand tons of waste produced each year in Italy.”
The high environmental impact of chemical fertilizers
“The agricultural plant production sector is subject to new and complex challenges determined also by international economic and geopolitical conjunctures,” Professor Pier Sandro Cocconcelli says, “as well as by an increasing attention of citizens and consumers towards environmental protection. “
The European Commission has committed, accordingly to the Farm to Fork strategy, to reduce by 2030 the use of fertilizers by 20%, nutrient losses from the soil by 50%, and the use of chemical pesticides by 50%.
Moreover, the geopolitical situation and especially the conflict in Ukraine have sharply raised prices of raw materials used in agriculture, starting with chemical fertilizers. “In this scenario, circular economy approaches, aimed at enhancing industrial waste by minimizing waste and reducing dependence on external inputs,” Professor Cocconcelli says.
The study
The Italian researchers showed how it is possible to recycle waste from the industrial production of lactic acid bacteria as fertilizers and biostimulants in agriculture.
Specifically, the trials focused on the greenhouse cultivation of tomatoes and lettuce and demonstrated how the use of these industrial wastes makes it possible to reduce the amount of chemical nitrogen fertilizers by 30%, without reducing production at all and also improving some physiological characteristics of the plant.
In addition, they estimated that this approach could reduce 40% of greenhouse gas emissions associated with chemical fertilizer production.
“Extensive chemical, microbiological and ecotoxicological analyses have ruled out any negative impact on the environment and soil, indeed showing effects of promoting microorganisms useful for plant growth and defense,” Professor Edoardo Puglisi explains.
The advantage of using this fertilizer would be that it would simultaneously nourish the plant (with direct and indirect nutrients), the soil bacteria that have positive effects on the plant, and the soil itself (enriching the humification rate of the soil). “It would thus be an ecological fertilizer in the broadest possible meaning, able to stimulate the whole system and not just one organism at the expense of others,” Professor Cocconcelli points out.
“This study shows the ability of research in the agricultural sector to quickly provide solutions to contingent emergencies in the sector,” Professor Puglisi concludes; it is also a virtuous example of technology transfer, demonstrated by the fact that the company Sacco srl involved in the project is now recycling more than 700 tons per year of residues from their production process with this approach.