Executive Summary
Management is an important organizational challenge today. Management process of a company is considered as one of the vital aspect for survival of a company. In an organization, the total activities are depending on the management system which includes the performance of the company. Thus managers are increasingly faced with the challenge of creating an environment that will be attractive to today’s workers. For this, we need to understand the basic elements of management functions and roles and responsibilities of different managers.
This report contains all the information related to the management process of different departments of a company. While writing this report, our intention was only to focus on the existing procedure of management system and to analyze the activities perform by the managers of different level of Anwar Group of Industries.
So far we know Anwar group is one of the largest industrial conglomerates in Bangladesh. For over a century Anwar Group has been contributing to different fields of development of the country. Through the nationwide network Anwar group is committed to serve its consumers & client from every corner of the country.
This report focuses basically three segments and each segment offers a different discussion. The segments are theoretical part, practical part and compare and contrast.
Phase – 1 covered theoretical part offers what are the requirements to manage a business and what are the roles and responsibilities of different managers according to the book.
Phase – 2 covered practical part offers what we have found in Anwar group.
Phase – 3 compare and contrast covered what are the similarities and differences between bookish knowledge and practical knowledge.
Methodology
We used both primary and secondary data and information to prepare our report.
• Primary Data:
We collected primary data through using well-structured questionnaire. We prepared a questionnaire for top-level managers of the Anwar Group. This questionnaire helped us to know the right information from the mangers.
• Secondary Data:
We searched books, journals, library books, and some web sites to collect secondary data and information about the topic.
Limitations
Prime limitation is the inadequate time and not having access to exclusive sites and articles. Our limited knowledge is also a constraint. Moreover, we could not collect all the information we needed because the organization that we selected did not disclose all the information we asked. Another major barrier was getting an appointment of the desired organization; we need to take attempt several times to get an appointment of Anwar Group.
An Introduction to Management
Traditionally, the term “management” refers to the activities (and often the group of people) involved in the four general functions: planning, organizing, leading and coordinating of resources. Note that the four functions recur throughout the organization and are highly integrated. Emerging trends in management include assertions that leading is different than managing, and that the nature of how the four functions are carried out must change to accommodate a “new paradigm” in management. Managers at different levels of the organizational hierarchy should thoroughly understand each of the basic functions planning; organizing, leading and controlling that comprise their jobs. They should also recognize that while each is important in its own right, effective managers are skilled in performing each function, must be capable of moving back and forth among the functions as circumstances warrant, and must often juggle multiple functions and activities simultaneously. Managers cannot afford to be effective in performing only some of the functions because all are important. Few managers have equally strong skills in all areas. However, it is very useful for managers to understand their own strength and weaknesses if they want to achieve the organizational goals successfully.
A form of work that involves coordinating an organization’s human, financial, physical and, information resources toward accomplishing organizational objectives.
Attainment of organizational goals in an effective and efficient manner through planning, organizing, leading and, controlling organizational resources.
Characteristics:
Goal-driven
Activity is effective and efficient
Uses the four managerial functions
Management is a set of activities including Planning and decision making, organizing, leading, and controlling directed at an organization’s resources human, financial, physical, and information with the aim of achieving organizational goals in an efficient and effective manner.
A Manager is someone whose primary responsibility is to carry out the management process. In particular, a manager is someone who plans and makes decisions, organizes, leads, and controls human, financial, physical, and information resources. A classic definition is that “Leaders do the right thing and managers do things right.” A more standard definition is usually something like “managers work toward the organization’s goals using its resources in an effective and efficient manner.” In a traditional sense, large organizations may have different levels of managers, including top managers, middle managers and first-line managers. Top (or executive) managers are responsible for overseeing the whole organization and typically engage in more strategic and conceptual matters, with less attention to day-to-day detail. Top managers have middle managers working for them and who are in charge of a major function or department. Middle managers may have first-line managers working for them and who are responsible to manage the day-to-day activities of a group of workers.
• Top Managers
– Relatively small group of executives who manage the organization’s overall goals, strategy, and operating policies. They represent the organization to the external environment by meeting with government officials and other top managers.
• Middle Managers
– Largest group of managers in organizations
Implement top management’s policies and plans.
Supervise and coordinate lower-level managers’ activities.
• First-Line Managers
Supervise and coordinate the activities of operating employees. In contrast to Top and Middle managers, First-Line managers spend the majority of there time supervising operating employees and the work of subordinates rather then determining strategy and operating plans.
Regardless of their level, managers work in different areas of the organization
1. Marketing Managers
These individuals are responsible for getting consumers and clients to buy the organization’s product or services. Their duties include new product development, promotion, and distribution.
2. Financial Managers
These individuals deal with the financial resources of the company
Their responsibilities include accounting, cash management, and investment management.
3. Operations Managers
These individuals create and manage the systems which allow for the production of the organizations product or service.
Their responsibilities include production control, inventory control, quality control, and plant layout and site selection
4. Human Resource Managers
These managers hire and develop the skills of employees.
They are involved in human resource planning, recruiting and selecting employees, training and development, designing compensation and benefit systems, formulating performance appraisal systems, and discharging low-performing and problem employees.
5. Administration Managers
These managers tend to be generalists, meaning they have limited knowledge of all the departments they manage, such as a hospital administrator
Planning
Setting an organization’s goals and selecting a course of action to achieve them. Planning produces fundamental decisions and actions that shape and guide what an organization is, what it does, and why it does it. It requires broad-scale information gathering, an exploration of alternatives, and an emphasis on the future implications of present decisions. Planning is the process of developing and analyzing the organization’s mission, overall goals, general strategies, and allocating resources.
Organizing
Determining how activities and resources are grouped. Organizing – includes designing the organizational structure, attracting people to the organization (staffing), and creating conditions and systems that ensure that everyone and everything works together to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization.
Leading
Getting organizational members to work together to advance the interests of the organization. Leading – is guiding and motivating others to work effectively to achieve the goals and objectives of the organization. An organization has the greatest chance of being successful when all of the employees work toward achieving its goals. Since leadership involves the exercise of influence by one person over others, the quality of leadership exhibited by supervisors is a critical determinant of organizational success.
Controlling
Monitoring organizational progress towards goals. Controlling – is directly related to planning. The controlling process ensures that plans are being implemented properly. In the functions of management cycle – planning, organizing, directing, and controlling – planning moves forward into all the other functions, and controlling reaches back. Controlling is the final link in the functional chain of management activities and brings the functions of management cycle full circle.
Planning
• Environmental scanning and analysis
• Developing a vision of the future
• Setting long-term organizational objectives
• Developing organizational and competitive strategies
Organizing
• Defining tasks and duties
• Grouping positions into effective structures (departments)
• Clarifying authority, responsibility, and reporting relationships
• Allocating scarce resources (financial, human, physical)
• Staffing positions with qualified personnel
Leading
• Effective communication
• Inspiring others to do their best
• Motivation and rewards
• Trust and assurance
Controlling
• Clear standards
• Monitoring progress and results
• Knowing when and how to intervene
• Correcting deviations successfully
Technical Skills
Skills necessary to accomplish or understand the specific kind of work being done in an organization. These skills are especially important for first-line managers.
Interpersonal Skills
The ability to communicate with, understand, and motivate both individuals and groups. As managers climb the organizational ladder, they must be able to get along with subordinates, peers, and those at higher levels of the organization
Conceptual Skills
The manager’s ability to think in the abstract and to see the “big picture. Managers must be able to visualize the organization as a whole and formulate strategies based on this understanding. This understanding will allow these managers to make broad decisions which affect all aspects of the organization and benefit the company or entity as a whole.
Diagnostic Skills
The manager’s ability to visualize the most appropriate response to a situation. After carefully analyzing all aspects of a situation, a successful manager will then be able to develop and implement a proper solution
Communication Skills
The manager’s abilities both to convey ideas and information effectively to others and to receive ideas and information effectively from others. Communication skills allow a manager to clearly indicate to subordinates his or her expectations of them as well as to facilitate an effective dialogue between different members of the organization.
Decision-Making Skills
The manager’s ability to recognize and define problems and opportunities correctly and then to select an appropriate course of action to solve the problems and capitalize on opportunities.
Time-Management Skills
The manager’s ability to prioritize work, to work efficiently, and to delegate appropriately. Unless a manager’s time is effectively managed, crucial takes will often be neglected or totally overlooked
Management Skill at Different Organizational Levels
The three interpersonal roles are primarily concerned with interpersonal relationships.
In the figurehead role, the manager represents the organization in all matters of formality. The top level manager represents the company legally and socially to those outside of the organization.
The leader role defines the relationships between the manger and employees.
In the liaison role, the manger interacts with peers and people outside the organization. The top level manager uses the liaison role to gain favors and information, while the supervisor uses it to maintain the routine flow of work.
The direct relationships with people in the interpersonal roles place the manager in a unique position to get information. Thus, the three informational roles are primarily concerned with the information aspects of managerial work.
In the monitor role, the manager receives and collects information.
In the role of disseminator, the manager transmits special information into the organization. The top level manager receives and transmits more information from people outside the organization than the supervisor
In the role of spokesperson, the manager disseminates the organization’s information into its environment. Thus, the top level manager is seen as an industry expert, while the supervisor is seen as a unit or departmental expert.
The unique access to information places the manager at the center of organizational decision making. There are four decisional roles.
In the entrepreneur role, the manager initiates change.
In the disturbance handler role, the manger deals with threats to the organization.
In the resource allocate role, the manager chooses where the organization will expend its efforts.
In the negotiator role, the manager negotiates on behalf of the organization.
Introduction to Anwar Group
Anwar group is one of the largest industrial conglomerates in Bangladesh. For over a century Anwar Group has been contributing to different fields of development of the country. Through the nationwide network Anwar group is committed to serve its consumers & client from every corner of the country.
Anwar Group is also proud to be one of the pioneer exporters of the country. Not only did Anwar Group present at least 5 different product to the Bangladeshi market, but also proudly present Bangladesh in the world market with many world class products namely Galvanized corrugated/plain sheet, Textile synthetic fabric, Jute yarns and Electrical cables.
Anwar Group has built its strength on more than a century of experience. The cornerstone of our success is sharing knowledge to create relevant solutions – shaping the best thinking to reflect the ideas of a new age.
Our corporate strategy emphasizes speed, efficiency, flexibility and innovation in every facet of the Company’s operations-from product development and manufacturing to marketing – Anwar Group strives to achieve the ultimate goal of satisfying its customers. Honesty, integrity and respect for people are our core values and are the basis on which we do business.
Through a nation-wide commitment to advancing this objective, Anwar Group – and its many partners who share this commitment – has succeeded in creating a national network that comprises many subsidiaries and affiliates. We are paving the way for our journey into a new century – for the generation.
Vision
21st Century – The New Frontier
Anwar Group of Industries has been working as a development associate in building up the homeland for almost two centuries. Now at the outset of the twenty-first century, the Group is ever more prepared for heeding the challenging demands of the new millennium. Highly qualified management team, modern management techniques and R&D have empowered the Group to be the forerunner in economic progress of the country. As part of its ‘Vision 20-20’ the Group envisions to make at least one product of Anwar Group available at every home in Bangladesh. The Group shall be at the forefront to herald the millennium on the horizon.
SISTER CONCERN OF ANWAR GROUP
TEXTILE
Anwar Silk Mills Ltd.
Mehmud Industries Ltd.
Hossain Dyeing & Printing Mills Ltd.
FINANCE
The City General Insurance Co. Ltd.
The City Bank Ltd.
Bangladesh Finance & Investment Co. Ltd.
Bangladesh Commerce Bank Ltd.
STEEL
Anwar Galvanizing Ltd.
Anwar Ispat Ltd.
Khaled Iron & Steels Ltd.
TRADING
Anwar Export Import Ltd.
AG Automobiles Ltd.
Mala Corporation.
JUTE
Anwar Jute Spinning Mills.
Anwar Jute Specialized Jute Goods Ltd.
AGRO & FOODS
Anwar Fisheries & Poultry Ltd.
Anwar Green Ltd.
Jamilabad Agro Estate Ltd.
ENGINEERING
Anwar Cement Ltd.
Sunshine Cables & Rubber Works Ltd.
ICT
In2it Interactive Ltd.
REAL ESTATE
Anwar Land Mark Ltd.
Anwar Landmark Limited
In the emerging shape of Dhaka’s urban outlook & life style, Anwar Landmark Limited is a promising name that has already marked its success as one of the distinct Real Estate Companies. Established in 2001, the company has steered successfully through meticulous management & effective satisfaction of its client up to the present. Keeping unwavering standard with careful attention to greatest comfort and impeccable service, Anwar Landmark Limited has initiated and already handed over projects in different locations of Dhaka city.
In recognition of commitment to quality and management efficiency, Anwar Landmark Limited has been awarded with internationally renowned ISO 9001: 2000 certificate. With the pledge to fulfill the rigorous demands and elucidate satisfaction of its various clients, Anwar Landmark Limited is working with its efficient team of architects, engineers and management body. The success in their past achievements and their trend of involving better comprehension in configuring the needs and aspiration of urban home dwellers is leading the company towards a path of continuing success and excellence.
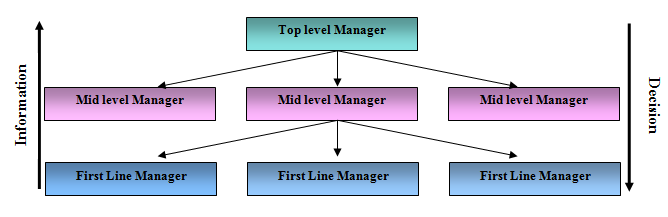
Managerial Hierarchy of Anwar Group (Anwar Landmark Limited)
What is “Management”?
| M |
anagement needs to focus more on leadership skills, establishing vision and goals, communicating the vision and goals, and guiding others to accomplish them. Leadership must be more facilitative, participative and empowering in how visions and goals are established and carried out. This really isn’t a change in the management functions; rather it’s re-emphasizing certain aspects of management.
The above interpretations acknowledge the major functions of planning, organizing, leading and coordinating activities — they put different emphasis and suggest different natures of activities in the following four major functions.
What Do Managers Do?
1. Planning
Including identifying goals, objectives, methods, and resources needed to carry out methods, responsibilities and dates for completion of tasks. Examples of planning are strategic planning, business planning, project planning, staffing planning, advertising and promotions planning, etc.
Guidelines to Ensure Successful Planning and Implementation
1. Involve the right people in the planning process
2. Write down the planning information and communicate it widely
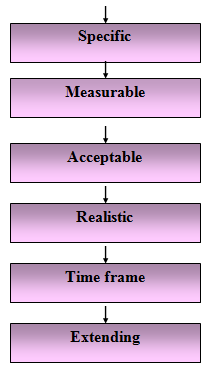
3. Goals and objectives should be Smarter
4. Build in accountability (Regularly Review Who’s Doing What and By When?)
6. Evaluate planning Process and the Plan
7. Recurring planning process is at least as important as plan document
8. Nature of the process should be compatible to nature of planners
9. Critical — but frequently missing step — acknowledgement and celebration of results.
Decision Making Tips
- Do not make decisions that are not yours to make.
- When making a decision, simply choosing from among alternatives. Should not make a choice between right and wrong.
- Avoid snap decisions. Move fast on the reversible ones and slowly on the non-reversible.
- Choosing the right alternative at the wrong time is not any better than the wrong alternative at the right time, so make the decision while you still have time.
- Do decision making on paper. Make notes and keep ideas visible that consider all the relevant information in making this decision.
- Be sure to choose based on what is right, not who is right
- Don’t waste time making decisions that do not have to be made.
- Determine alternative courses of action before gathering data.
- Once the decision has been made, don’t look back.
- Once the decision have been made and have started what you are going to do, put the “what it’s” aside and do it with commitment.
Decision flow and authority delegation
2. Organizing resources
To achieve the goals in an optimum fashion. Examples are organizing new departments, human resources, office and file systems, re-organizing businesses, etc.
3. Leading
Setting direction for the organization, groups and individuals and also influencing people to follow that direction. Examples are establishing strategic direction (vision, values, mission and / or goals) and championing methods of organizational performance management to pursue that direction.
4. Controlling, or Coordinating
This occurs with the organization’s systems, processes and structures to effectively and efficiently reach goals and objectives. This includes ongoing collection of feedback, and monitoring and adjustment of systems, processes and structures accordingly. Examples include use of financial controls, policies and procedures, performance management processes, measures to avoid risks etc.
1. Determine Anwar group’s Mission and Purpose.
2. Ensure effective organizational planning
3. Provide continuity for Anwar group by setting up a corporation or legal existence, and to represent the Anwar group’s point of view through interpretation of its products and services, and advocacy for them
4. Select and appoint a chief executive to whom responsibility for the administration of the Anwar group is delegated, including:
5. To review and evaluate CEO’s performance regularly on the basis of a specific job description, including executive relations with the board, leadership in the Anwar group,
6. In program planning and implementation, and in management of the Anwar group and its personnel
7. To offer administrative guidance and determine whether to retain or dismiss the executive
8. Govern Anwar group by broad policies and objectives, formulated and agreed upon by the chief executive and employees
9. Acquire sufficient resources for the Anwar group’s operations and to finance the products and services adequately
10. Determine and Monitor the Anwar group’s Programs and Services
11. Enhance Anwar group’s Public Image
Under the authority of the association’s by-laws and the policies of the board of directors, the CEO has two major functions:
• direct and execute all activities of the association either directly or through delegated authority;
• provide leadership in these and other areas: the creation of strategic, tactical, and financial plans; developing goals and measuring performance to the approved goals; organizational development; liaison to the public, government, affiliated organizations, and other stakeholders; develop member services and member development; the development of the association’s staff.
The typical roles and general responsibilities of a non-profit association CEO are:
Leader
• Advises the Board
• Supports motivation of employees in organization products/programs and operations
Information Bearer
• Ensures staff and Board have sufficient and up-to-date information
• Looks to the future for change opportunities
• Interfaces between Board and employees
• Interfaces between organization and community
Decision Maker
• Formulates policies and planning recommendations to the Board
• Decides or guides courses of action in operations by staff
Manager
• Oversees operations of organization
• Implements plans
• Manages human resources of organization
• Manages financial and physical resources
Board Developer
• Assists in the selection and evaluation of board members
• Makes recommendations, supports Board during orientation and self-evaluation
• Supports Board’s evaluation of Chief Executive
1. Provide leadership in the development of the association’s statement of vision, mission, and goals, and the corresponding strategies, plans, and budgets to achieve them;
2. Ensure the development of priority plans, performance measurements, management controls, and critical success factors;
3. Review approved plans and budgets as part of the annual planning and budgeting cycle and present recommendations to the board of directors and/or the appropriate committee;
4. Develop and provide appropriate policy recommendations for consideration by the board;
5. Ensure that an annual plan and budget are prepared for and presented to the board of directors;
6. Propose agendas for the board of directors reflecting issues, opportunities, and priorities;
7. Hire, reward, discipline, terminate, and set the remuneration of, all association
employees except for him/her, in accordance with policy and/or approved budgets;
8. Maintain the necessary contacts to keep abreast of emerging issues of significance to the association management profession;
9. Develop project planning and operation (construction of planning, drawing etc.)
10. Act as the spokesperson for the association;
1. Conducting basic management skills (decision making, problem solving, planning, delegation and meeting management)
2. Organizing their department and teams
3. Noticing the need for and designing new job roles in the group
4. Hiring new employees
5. Training new employees
6. Employee performance management (observing and giving feedback, addressing performance issues, giving information to middle and top level, etc.)
7. Conforming to personnel policies and other internal regulations
Anwar group has seven departments as follows:
Accounts
Construction
Sales
Finance
Marketing
Human Resource
Logistic
Maintaining cash funds
Maintain the accounts
Prepare the balance sheet in every financial year
Prepare other financial statements
Payment of all supplier
Payment of all creditor
Ensure smooth payment
Constructor payment
Bill payment
Schedule implement
Consult constructor
Determine what are needs and how to be done
What are the requirement of the job
Material supply
Report to managing director if any problem occur
Manage constructors and labor
Build effective business relationship with key customers
Lead and manage a sales team
Execute individual and group sales plan for the team
Product price determine
Distribute the products
Product promotion
Client handle
Leads strategic financial analysis and planning
Identify new revenue and efficiency opportunities
Assemble loans and grants through bank, donors
Cash management
Provide the salary to the employees.
Prepare the annual budge for the company
Collection of funds
Meet financial needs of other departments
Develop human resource policy
Human Resource planning
Recruit and select employees
Design career planning including training, placement, promotion
Design compensation and benefit system
Discharging low performing employees
Maintain the individual records of employees
Managing employee relation issues for the relevant business units
Assist the marketing team in preparing realistic marketing plan
Coordinate with sales team and get their requirement
New product development
Identifying new market
Identifying consumers needs and demands
Market research
Promotion and distribution
Specifies and procure the process of electrical and electronic office equipment
Planning, monitoring, supervise, and quality control of individual electrical and electronic projects
Maintain and supervise of air conditioners
Ensure smooth connection of water, telephone, gas, electricity
Bill payment
Decision flow and authority delegation
Anwar Group maintains a well structured decision flow. All the decision make and given by the top management, for the middle and lower management. And all the information is given by the first line managers to top, middle managers. They maintain the upward downward decision flow. In authority delegation, Anwar group is 60% decentralized and 40% centralized.
Corporate Social Responsibility
Anwar Group of Industries is committed to proper business ethics and is operated following stringent code of honor. The multitude of initiatives that the Group has been nurturing under the able leadership of the Chairman is voluntary performed with the objective to enhance the quality of life of the mass in general.
In this regards the Group is operating a maternity center, orphanage, eye-hospital, charitable dispensary, vocational training for the poor & challenged, general culture & educational activities, stipend for the poor & meritorious students, financial aid for poor women, small savings & cooperative activities, tree plantation, etc.
• Anwar Hossain Foundation
• Alhaz Anwar Hossain Shohid Nagar Primary School
• Azad Muslim Welfare Complex, Bangladesh
• Azad Muslim Mohila Porishad
• Azad Muslim Children Art Center
• Rohim Buksh Memorial Charitable Dispensary
• Jamila Khatun Red Cresent Maternity Center
• Jamila Khatun Lalbagh Girls High School
Conclusion
Management is very complex process that carries out all managers of the particular organization with the managerial skills, function, roles and responsibilities. They take their jobs seriously and perform the roles and responsibilities from different managerial hierarchy on the perspective of organization.
After comparison we found that Anwar group is closely related to the theoretical concept that we learned in our book. Anowar Uz Zaman (HR manager of Anwar Group) said that “In reality theory and practical knowledge or experience both are important to all managers today”. In any organization, managers are responsible for carrying out the managerial functions and to run a business. Thus, a manager should perform their responsibilities carefully and to do so they must have the basic managerial skills. To be a successful manager, a manager must combine theoretical and practical experience. One who has theoretical knowledge he or she can implement the theoretical concept in practical life effectively and efficiently. Management theories are not fully exploited in any organization. It varies from one to another. Therefore, managers has to refine and develop their own theories of how should they run their organization.


![Report on Overall Banking Practice of National credit and commerce bank [Part-2]](https://assignmentpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/05/images-11-200x79.jpg)