Introduction:
After the end of Second World-war in fact to say the world is involved in another war called the trade war of achieving superiority over other countries through implementing the strategies of free market economy. The conference of GATT (General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade) to W.T.O. (World Trade Organization) with adopting new policies, the emergence of various region oriented economic organizations like NAFTA, SAFTA, ASEAN, APEC, G-8 etc. indicates that the 21st century will be the century of economic and business challenge.
Commercial Banks are one of the key contributors to the Bangladesh economy. The process of economic development requires the banking sector to operate efficiently and distribute the capital resources to the proper development agencies. People and the government itself are very much dependent on the services provided by these banks in the financial market. Commercial banks act as financial intermediaries by performing the function of mobilization the funds from one group and lending the same to another for the purpose of a reasonable amount of profit after meeting the cost of funding. So the objectives of a Bank can be looked at from three different perspectives of the key parties to the banking activities, these are the Bank owner, the Govt. and the bank customer.
Among other banks and as government owned bank Sonali Bank Limited is playing a good role in our economy through its various operations. Its general banking services, investment in several specified sectors and foreign exchange business is notable.
From the modest beginning, with an increase of responsibility and virtue of performance, Sonali Bank Limited, within a few years, emerged as the largest Nationalized Commercial Bank (NCB) in the country. The principal activities of the bank are providing all kinds of commercial banking services to the customers. It also performs Government Treasury functions as an agent of the Bangladesh Bank.
Primary Objective:
The primary objective of this report is to fulfill the requirement of MBA program and to apply the theoretical knowledge gained from the coursework of the MBA program in a specific field which will bring credit hours for getting MBA Degree.
Secondary objective:
- To understand and analyze the financial strength of the Sonali Bank Limited.
- To evaluate the existing financial performance of Sonali Bank Limited.
- To study the credit analysis of Sonali Bank Limited.
- To gain practical experiences and view the application of theoretical knowledge in real life.
Limitations of the study:
In spite of related peoples willingness I could not avail the full concentration as I supposed to have. The officers are extremely busy with their assigned jobs. And even I had to perform the internship while doing the job. On the way of my study, I have faced the following problems that may be termed as the limitations/shortcoming of the study. The main limitations encountered in producing this report are:
I have to work as a full-time employee of Sonali Bank Limited. It was difficult for me to allocate enough time to prepare the report. For an analytical purpose adequate time is required. Due to the time limit, the scope and dimension of the study has been curtailed.
I have used 3 years data in the financial analysis on which the Financial Statement 2009, so there are few information I could not include statutory reserve of year 2010.
At the time of preparing my report I tried to gather every details of process but the major limitation is lack of adequate information.
Definition of bank:
Generally bank is refers to an organization that deals with money. The definition of Bank may be as follows:
As per Bank companies act 1991:
Banking Company means any company which transacts the business of banking in Bangladesh and includes a new bank and specialized bank.
Banking means the accepting for the purpose of lending or institute of deposit of money from public repayable on demand or otherwise and withdraw able by draft, order or otherwise.
Provided by Banking Institutes:
A bank performs an essentially distributive task, service or acts as an intermediary between borrowers & lenders. In broader sense, however, a bank can be considered the heart of a complex financial structure.
– American Institute of Banking
Objective of a bank:
The objectives of a Bank can be looked at from 3 different perspectives of the 3 key parties to the banking activities- Bank owners, the Government and the Bank clients.
From the owner’s perspective:
i) Earning Profit: Just like any owner(s) of a commercial institution, a bank owner’s main objective is to earn profit, which is achieved mainly through monetary exchanges.
ii) Rendering Service: Banks provide different types of services to the government and people of the country.
iii) Good Will: In order to earn profit through rendering services, banks need to have a lot of good will, maybe a bit more than other commercial institutions.
iv) Raising Efficiency: To earn maximum profit, banks need to provide efficient service, for which they require expert workforce.
From the Government’s perspective:
i) Issue of Notes & Currencies: Since civilizations have moved along from the barter system, it has been the objective of the Government of different countries to provide its economy with a proper exchange media through issuance of notes & currencies through banks, which also take upon the duty of maintaining the system.
ii) Capital Formation: The government wants that bank assist in the macroeconomic objective of capital formation by encouraging people to participate in savings.
iii) Capital Investment & Industrialization: The government, as a part of their secondary macroeconomic objective, wants the bank to assist in capital investment & industrialization by lending out their accumulated capital.
iv) Money Market Control: Government tries to stabilize the money market through banks.
v) Employment: As part of their primary macroeconomic objectives, they expect banks to provide employment for its people.
vi) Advice on Financial Matters: Since banks hire a lot of financial experts and advisors, it often seeks advice from banks to help them develop policies.
From the bank clients’ perspective:
i) Deposit: One of the banks’ main objectives is to accept its clients’ deposits. Like bank clients also want to deposit money with a competitive rate of interest.
ii) Safety: Providing safekeeping of its clients’ monetary possessions and valuables is another one of banks’ essential objectives.
iii) Advisors & Consultants: Banks provide its clients with advisors and consultants to help them chalk out an appropriate savings plan.
iv) Representatives or Trustees: Both the clients and government rely on the bank to act as their representatives and trustees of monetary exchange activities.
v) Raising living standard: By providing interests against their deposits, banks help their clients to improve their living standards.
Business of banking companies (Bank company act 1991):
In addition to the business of banking a bank company may engage in any one or more of the following forms of business.
- The borrowing, collection or taking of money.
- The lending or advancing of money either upon on without security.
- The drawing, accepting, discounting, Bulling, selling, collecting and dealing in Bill of exchange bonds, promissory notes, coupons drafts, Bill of leading, Railway receipts, warrants, debentures certificate, term finance certificate Mudaraba certificate and such other instruments as may be approved by Bangladesh Bank and other instruments and security whether transferable of negotiable or not.
- The granting and issuing of letter of credit TC credit Card and circular notes.
- the buying, selling and dealing in gold silver and other hotel coin,
- The buying and selling of foreign exchange including foreign bank notes.
- The —– holding, issuing on commission, under writing and dealing in stock funds, share debentures stock bonds obligation, securities term certificate, Mudaraba certificate and such other instruments as may be approved by the Bangladesh Bank and Investment of all kinds.
- The purchasing and selling of bonds or other form of securities participating term certificate term finance certificate, Mudaraba certificate and such other instrument as may be approved by Bangladesh Bank on behalf of constitution or other negotiation of loans and advances.
- The receiving of all kinds of bonds, scripts of valuable on deposit for safe custody pr otherwise/
- The providing for safe deposit vaults.
- The collecting and transmuting of money as against a certificate of securities.
- Acting as agents for the Govt. on local authority or any other person or persons.
- The carrying in of agency business of any description including the clearing and forwarding of goods giving of receipts and discharged and otherwise acting as an attorney on behalf of customers but excluding the business of a Managing Agent or treasure of a company.
- Constricting for public and private loans negotiating the same.
- Undertaking issue of share, stock debenture on debenture stock of any company, corporation on association and the lending of money for the purpose of any such issuance.
- Transacting in every kind of guarantee and indemnity business.
- Purchase of acquisition in the normal courses of its lending business of any property including patents, desires trademarks and copy rights with or without buying bock arrangement by the seller on for the sale by way of hire purchase on differed payment basis with marking for in leasing or licensing or for sharing of income on for any way financing.
- Managing selling and realizing any purposely which may come into the posses of the company is satisfaction or part satisfaction of any of its claim.
- Acquiring and holding and generally with any property or any right, title or in the rest in any such property which may be in form of security or part of the security for any loans and advances or which may be connected with any such security.
- Undertaking and exacting trust.
- Undertaking and administration of estates as executor trustee or otherwise
- Establishing and supplying or aiding in the establishment and support of associations, institutions, funds, trusts and advantage calculated to the benefit of employees or ex employees of the company or the dependents on connections of such persons graduating pensions and allowances and —- payments towards insurance.
- The acquisition, construction, maintenance and alternation of any building on works necessary or convenient for the purpose of the company. Selling, Improving, developing exchanging leasing, mortgaging disputing of on Turing into account or otherwise dealing with all on any part of the properties and rights of the company.
- Acquiring and undertaking the whole or any part of the business of any person, a company when such business is of a nature enumerated or described in this sub section.
- Doing all such other things as incidental on conducive to the promotion on advancement of the business of the company.
- Any other form of business which the Govt. may by notification in the official specify as a form of business which is legal for a banking company to be engaged in.
An overview of banking operation in Bangladesh:
The development process of a country largely depends upon its economic activities. Banking is a powerful medium among other spheres of modern socio-economic activities for bringing about socio-economic changes in a developing country like Bangladesh. Three different sectors like Agriculture, commerce, and industry provide the bulk of a country’s wealth. With the passage of time the functions of the bank has got a multi-dimensional configuration. Of all the functions of a modern bank, lending is by far the most important. They provide both short-term and long-term credit. The customers come from all walks of life, from a small business a multi-national corporation having its business activities all around the world. The banks have to satisfy the requirements of different customers belonging to different social groups. To regulate the activities of other banks, all the commercial private and/or nationalized, and specialized banks perform service related activities within the jurisdiction of the central bank. In our country, Bangladesh the role of the central bank is entitled to be executed by Bangladesh Bank.
The bank was responsible for regulating currency, controlling credit and monetary policy, and administering exchange control and the official foreign exchange reserves. The Bangladesh government initially nationalized the entire domestic banking system and proceeded to reorganize and rename the various banks. Foreign-owned banks were permitted to continue doing business in Bangladesh. The insurance business was also nationalized and became a source of potential investment funds. Cooperative credit systems and postal savings offices handled service to small individual and rural accounts. The new banking system succeeded in establishing reasonably efficient procedures for managing credit and foreign exchange. The primary function of the credit system throughout the 1970s was to finance trade and the public sector, which together absorbed 75 percent of total advances.
The government’s encouragement during the late 1970s and early 1980s of agricultural development and private industry brought changes in lending strategies. Managed by the Bangladesh Krishi Bank, a specialized agricultural banking institution, lending to farmers and fishermen dramatically expanded. The transformation of finance priorities has brought with it problems in administration. No sound project-appraisal system was in place to identify viable borrowers and projects. Lending institutions did not have adequate autonomy to choose borrowers and projects and were often instructed by the political authorities. In addition, the incentive system for the banks stressed disbursements rather than recoveries, and the accounting and debt collection systems were inadequate to deal with the problems of loan recovery. It became more common for borrowers to default on loans than to repay them; the lending system was simply disbursing grant assistance to private individuals who qualified for loans more for political than for economic reasons. The rate of recovery on agricultural loans was only 27 percent in FY 1986, and the rate on industrial loans was even worse.
As a result of this poor showing, major donors applied pressure to induce the government and banks to take firmer action to strengthen internal bank management and credit discipline.
List of scheduled Banks in Bangladesh:
Nationalized Banks-
National Commercial Bank | Web Link |
| Sonali Bank | http://www.sonalibank.com.bd/ |
| Janata Bank | http://www.janatabank-bd.com/ |
| Agrani Bank | http://www.agranibank.org/ |
| Rupali Bank Limited | http://www.rupali-bank.com/ |
Specialized Commercial Banks-
|
|
| Bangladesh Krishi Bank | http://www.krishibank.org.bd/ |
| Bangladesh Shilpa Bank | http://www.shilpabank.gov.bd/ |
| Rajshahi Krishi Unnayan Bank | http://www.rakub.org.bd/ |
| Bangladesh Shilpa Rin Sangstha | http://www.bsrs.org.bd/ |
| BASIC Bank Limited | http://www.basicbanklimited.com/ |
Private Commercial Banks-
Private Banks | Web Link |
| Pubali Bank Limited | http://www.pubalibangla.com/ |
| Uttara Bank Limited | http://www.uttarabank-bd.com/ |
| AB Bank Limited | http://www.abbank.com.bd/ |
| IFIC Bank Limited | http://www.ificbankbd.com/ |
| Islami Bank Bangladesh Ltd | http://www.islamibankbd.com/ |
| National Bank Limited | http://www.nblbd.com/ |
| The City Bank Ltd. | http://www.thecitybank.com/ |
| United Commercial Bank Limited | http://www.ucbl.com/ |
| ICB Islamic Bank Ltd. | http://www.oriental-bank.com/ |
| Eastern Bank Limited | http://www.ebl-bd.com/ |
| National Credit & Commerce Bank Ltd | http://www.nccbank-bd.com/ |
| Prime Bank Ltd | http://www.prime-bank.com/ |
| Southeast Bank Limited | http://www.sebankbd.com/ |
| Dhaka Bank Limited | http://www.dhakabank.com.bd/ |
| Al-Arafa Islami Bank Limited | http://www.al-arafahbank.com/ |
| Social Investment Bank Ltd. | http://www.siblbd.com/ |
| Dutch-Bangla Bank Limited | http://www.dutchbanglabank.com/ |
| Mercantile Bank Limited | http://www.mblbd.com/ |
| One Bank Limited | http://www.onebankbd.com |
| EXIM Bank Limited | http://www.eximbankbd.com/ |
| Premier Bank Limited | http://www.premierbankltd.com/ |
| First Security Bank Limited | http://www.fsiblbd.com/ |
| Standard Bank Limited | http://www.standardbankbd.com/ |
| The Trust Bank Limited | http://www.trustbankbd.com |
| Mutual Trust Bank Limited | http://www.mutualtrustbank.com/ |
| Bank Asia Limited | http://www.bankasia-bd.com/ |
| Bangladesh Commerce Bank Limited | http://www.bcbl-bd.com/ |
| Jamuna Bank Ltd | http://www.jamunabankbd.com/ |
| Shahjalal Bank Limited | http://www.shahjalalbank.com.bd/ |
| BRAC Bank Limited | http://www.bracbank.com/ |
Foreign Banks-
Foreign Bank | Web Link |
| Commercial Bank of Ceylon Limited | http://www.combank.net/ |
| Standard Chartered Bank Ltd. | http://www.standardchartered.com/bd/ |
| Habib Bank Ltd. | http://www.habibbankltd.com/ |
| State Bank of India | http://www.statebankofindia.com/ |
| National Bank of Pakistan | http://www.nbp.com.pk/ |
| Citibank N.A | http://www.citi.com/domain/index.htm |
| Woori Bank | http://www.wooribank.com |
| Bank Al-Falah Limited | http://www.bankalfalah.com |
| The Hong Kong and Shanghai Banking Corporation. Ltd. | http://www.hsbc.com/ |
A brief overview of Sonali bank limited:
Sonali Bank is a state-owned commercial bank in Bangladesh. It is the largest bank of the country. A fully state-owned enterprise, the bank has been discharging its nation-building responsibilities by undertaking government entrusted different socio-economic schemes as well as money market activities of its own volition, covering all spheres of the economy. Sonali Bank Limited singularly enjoys the prestige of being the agent of the Central Bank of Bangladesh in such places where the guardian of the money market has chosen not to act by itself. Sonali Bank was established in 1972 under the Bangladesh Banks (Nationalization) Order, through the amalgamation and nationalization of the branches of National Bank of Pakistan, Bank of Bahawalpur and Premier Bank branches located in East Pakistan until the 1971 Bangladesh Liberation War. When it was established, Sonali Bank had a paid up capital of 30 million taka. In 2009, it’s authorized and paid up capital were Taka 10.00 billion and Taka 9.00 billion respectively. The bank’s reserve funds were Tk 4000 million in Bangladesh Bank.
The management of Sonali Bank has appointed 7-member board of directors appointed by the government. The managing director is the chief executive. He is assisted by a deputy managing director, six general managers, and other senior executives. The general managers are in charge of the bank’s branches in the headquarters of the six administrative divisions of the country namely, Dhaka, Chittagong, Rajshahi, Khulna, Sylhet and Barisal. The bank has 32 departments at its head office including a training institute in Dhaka. On 31 December 2008, the total number of employees of the bank was 26,085.
Role of Sonali bank limited in the national economy:
Economy and banking Industry go together and are inseparable. Sonali Bank has been playing an important role in the economic development of the country. As many as 26,085 people are in the employment of the Bank as on December 31, 2008. Besides, Sonali Bank has generated employments for hundreds of people in the projects and industries established under finance. The Bank has been financing the trade and commerce of the country since inception of the Bank in 1997. We have handled a big volume of countries exports and imports. The deposits our Bank mobilized through the outlets of branches helped in the formation of capital in the country. Our lending to borrowers reached Tk. 23163.18 million as on June 30, 2009. It has contributed to the industrialization and improvement of trade and commerce of the country which ultimately accelerated economic growth and national welfare through multiplying effect. We have collected VAT and tax on interest / profit earnings of customers of the Bank. For relief and rehabilitation of natural calamity-hit people of the country in 2007 the bank has donated a denotable amount of money.
Foreign Remittance:
To develop national infra-structure and economy of Bangladesh Sonali Bank Limited has been playing dominant role to bring hard earnings of Bangladeshi expatriates working / living abroad through banking channels. For this purpose, Sonali bank Limited has established a bank named Sonali Bank (U.K) Ltd., U.K and an exchange house named Sonali Exchange Company Inc (SECI), U.S.A. Our bank has also established drawing arrangement with various exchange houses / banks in Middle East, Canada and Malaysia. Under this arrangement, remitters can easily send their hard earnings to the beneficiaries in Bangladesh through 1191 Sonali Bank Limited Branches across the country. They can remit their money through Demand Drafts (DDs), Telegraphic Transfers (TTs), SWIFT and / or Computerized Payment Instructions (PC to PC via dial up modem) on Sonali Bank Limited selective branches.
Trade Financing:
Sonali Bank Limited extends multiple credit facilities to boost up trade, commerce and industry. The credit packages and interest rates are as under:
| Credit Packages | Interest Rates (Floating) |
| 1.Credit to Tread and Commerce | 14% |
| 2. Credit for Power Driven Vehicle/Water Transport | 14% |
| 3.Overdraft against: | |
| Fixed deposits | 13% |
| SDPS Accounts | |
| Five years period | 12% |
| Ten years period | 14% |
| Insurance Policy/Shares and Debenture of Public Ltd. Co. | 14% |
| Work order of Govt. Semi Govt./Corp | 14% |
| Wage Earners Dev. Bond | 13% |
| 4. Housing Loan | |
| Residential | 13.5% |
| Commercial | 14% |
| 5. Small Loan | 14% |
| 6. Consumers credit | 14% |
| 7. Loans to Public Sector Enterprises | 14% |
| 8. Cash credit facilities for Small Business enterprises | 14% |
| 9. Cash Credit facilities against Bricks Manufacturing | 14% |
Investment Banking
Central Accounts & Fund Management Division at Head Office maintains Investment Portfolio of the Bank. With a view to implementing Government policies & decisions and accelerating the growth of the Capital Market of the country, surplus funds of Sonali Bank are utilized in the following areas:
a) Short Term:
1. Call Loans: An overnight investment to other Banks & Financial Institutions.
2. Treasury Bills: Investment made to the Government through Treasury Bills.
b) Long Term:
1. Government / Public Bonds: Sonali Bank Limited purchases bonds issued by the Govt. of Bangladesh and other Public Bodies.
2. Shares / Equity Participation: Sonali Bank Limited participates in the IPO and extends bridge finance to the equity of Public Ltd. Companies, Institutions and Public Bodies.
3. Debentures: Sonali Bank Limited purchases debentures issued by the Public Bodies and Financial Institutions under Government.
Corporate profile of Sonali bank limited:
| Name of the Company | Sonali Bank Limited |
| Chairman | Quazi Baharul Islam |
| Managing Director and CEO | Md. Humayun Kabir (Current Charge) |
| Company Secretary | Zaheed Hossain |
| Legal Status | Public Limited Company |
| Genesis | Emarged as Nationalised Commercial Bank in 1972, following the Bangladesh Bank (Nationalization) Order No. 1972(PO No.26 of 1972) |
| Date of Incorporation | 03 June, 2007 |
| Date of Vendor’s Agreement | 15 November, 2007 |
| Registered Office | 35-42, 44 Motijheel Commercial Area, Dhaka, Bangladesh |
| Authorized Capital | Taka 10.00 billion |
| Paid-up Capital | Taka 9.00 billion |
| Number of Employee | 26,085 |
| Number of Branches | 1191 |
| Dialogue | Your Trusted Partner in Innovative Banking. |
| Phone-PABX | 9550426-31, 33, 34, 9552924 |
| FAX | 88-02-9561410, 9552007 |
| SWIFT | BSONBDDH |
| Web-site | www.sonalibank.com.bd |
| sbhoid@bdmail.net sbhoitd@btcl.net.bd | |
| Logo |
Mission statement:
Dedicated to extend a whole range of quality products that support divergent needs of people aiming at enriching their lives, creating value for the stakeholders and contributing towards socio-economic development of the country.
Vision statement:
Socially committed leading banking institution with global presence.
Nature of business:
The principle activities of the bank include providing of all kinds of commercial banking services to its customers. The activities can be classified in the following ways:
- Corporate Banking
- Project Financing
- SME Financing
- Consumer Credit
- International Trade
- Trade Finance
- Loan Syndication
- Foreign Exchange Dealing
- Rural and Micro credit
- Investment
- Government Treasury Function
- Remittance
Organogram of Sonali bank:
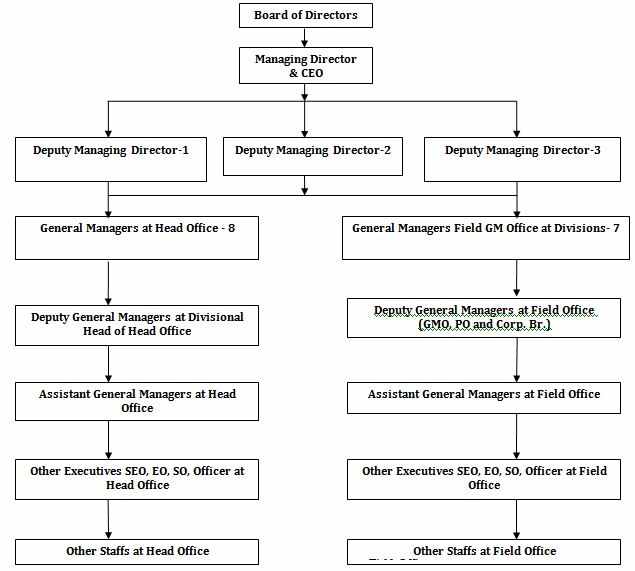
Organogram of Sonali Bank as follows-Objectives of Sonali Bank Limited:
Sonali Bank is one of the government own banks in Bangladesh. It was established to provide more banking facilities to the Bangladeshis. For this, from the very beginning of the bank, it had defined its objectives properly. These objectives are discussed in the below:
Earning profit: Earning profit is one of the main objectives of Sonali Bank Limited in order to survive in the competitive banking world. Without making profit, no bank can work properly. As a result, it will have to face many problems and will not be able to run in a proper way. To make profit, it provides advances to the deficit units, invests shares and bonds and purchases Treasury Bills and tries to minimize its operational costs.
Collecting savings: Sonali Bank Limited always tries to collect savings from the surplus units through different accounts, special schemes, and provident fund facilities and in many other ways. It gives opportunity to people to open current account, saving account, and fixed deposit accounts. To encourage people, it offers different profitable investment opportunities like double benefit schemes. Hence, it has been able to increase its deposit amounts over the years.
Creating capital: By collecting savings from the surplus units through different accounts, it creates capital for the deficit units and uses the accumulated capital for the development of the country as well as acquiring its assets.
Creating the medium of exchange: Sonali Bank Limited creates medium of exchange through its branches very easily. It issues check, bank draft, bills, demand draft, pay order and provides telegraphic transfer, mail service for creating medium of exchange.
Supplying money: To supply the money created by Bangladesh Bank to the people of Bangladesh is another objective of Sonali Bank Limited. It helps Central Bank to manage money supply and money management.
2.9.6-Granting loans and investment: By providing loans to the people of Bangladesh, who are in need to run their own work efficiently, promotes the economic development of the country. Thus, it is considered as one of the objectives of Sonali Bank Limited.
Maintaining security of money: To provide safeguard of people’s money is the main objective of Sonali Bank Limited. In order to do this, it collects their money, provides locker facilities, and creates medium of exchange for transferring money from one place to another. Besides, it encourages people to keep their money to bank by offering different profitable offers.
Regional development: Bangladesh is not a big country but it has sixty four districts. Each district is not equally developed. Some districts are enjoying the benefit of modern facilities of bank services. Some are suffering from banking services. But as a largest bank of Bangladesh Sonali Bank Limited are cooperating to regional development.
Removing poverty: Poverty is a curse for the newly born Bangladesh. It has grasped most of the people’s life particularly in the rural areas. The people of the rural areas are suffering from malnutrition, hunger and epidemic diseases. To minimize their suffering, Sonali Bank Limited Bank is playing an important role. It provides credits them at lower rates and encourages to work like as micro credit services.
Creating employment: Bangladesh is suffering from the curse of unemployment. The rate of unemployment is increasing day by day. To minimize that rate is another objective of Sonali Bank Limited. For this reason Sonali Bank’s Board of Directors has declared at least 250 people will be hired each year.
Economic development: Although Sonali Bank Limited is making profit, it always tries to increase the economic development of the country. For this purpose, it provides advances, creates capital, medium of exchange, supplies money, and provides security and creating employment opportunities. But some times it has to work without seeking profit as because of government owned bank. From the above discussion, it is clear that the objectives of Sonali Bank Limited are very clear and well defined. Its objectives are made for the best interest of its valuable customers and for the country.
Sources of fund:
- Authorized Capital
- Issued Capital
- Subscribed Capital
- Called up Capital
- Paid up Capital
- Reserve fund and other reserves
- Deposits and other accounts
- Borrowing from Banking companies, Agency.
- Loan from Central Bank.
Uses of fund:
- Cash in Hand
- Balances in Current Account with other banks
- Balance to the Central Bank
- Call Loan
- Short Loan
- Purchase of Govt. Credit Instrument, Share, Security
- Bills Discounting and Treasury Bill
- Loans And Advances
Ethical principles of Sonali bank limited:
Sonali Bank believes that it will become a leading bank in the government sector. They believe that their aims and objectives can only be realized fully and sustained overtime by faithfulness to ethics that cannot always be built into sets of rules and regulations. In this belief in ethics that motivates the bank in its dealings with customer, regulators & employees.
Commitment to clients of Sonali bank limited:
Sonali bank limited has trying to concentrate on modern banking through continuous using modern technology. We also trying to help more to customer by providing various savings schemes like as EDS, MES, and DBS etc. Our Commitments to the clients are the following:
- Provide service with high degree of professionalism & continuous use of modern technology through proper use of young generation officers.
- Create long-term relationship based on mutual trust with customers.
- Share customer’s values & beliefs.
- Provide product and service at competitive pricing.
- Ensure safety and security of customers’ valuables in trust with us.
Products include-
Personal banking:
Sonali Bank Limited extends all the major personal banking facilities and services to its customers with its skilled manpower and largest network of around 1191 branches covering all the urban and remote rural areas of Bangladesh. Sonali Bank Limited provides Local & Foreign Remittance in quickest possible time. Foreign remittance is available in both Taka cash. & Taka draft.
1. Transfer of fund from one branch to another by – Demand Draft Savings A/C – Mail Transfer Daily Profit A/C – Telegraphic Transfer FDR A/C.
2. Transfer of fund on Standing Instruction Arrangement (Trade Finance).
3. Collection of cheques through clearing house/beyond Clearing House.
4. Issuance of Payment Order / Call Deposit.
5. Locker facilities for safe keeping of valuables.
6. Corporate Client Services with computerized system at selective branches.
Rural credit:
Rural Credit Bangladesh is an agricultural country. A major portion of its population (about 85%) lives in the rural areas. About 75% of the active rural population depends on agriculture as the main source of their livelihood. Agriculture contributes about 22% to the GDP. Majority of the farmers are either small or marginal. So Credit plays a paramount role to augment the capital base to support agriculture production. Sonali Bank Limited the largest state owned commercial bank has been playing a vital role in the socio-economic development & poverty alleviation since 1973. Keeping in view that Credit is one of the many inputs that complete the cycle of agricultural production .Sonali Bank extending rural credit through 1191 branches over the country. Sonali Bank Limited introduced indirect rural credit in 1973 through the then IRDP (Now BRDB) there after continuing lending in the following programs
1. Crop Loan (Special Agricultural Credit Program): This program was introduced in 1977 to increase crop production and is continuing through 707 branches. Recently Sonali Bank Limited introduced Revolving Crop Credit Limit System from one branch of each district.
2. Special Investment Program: This program was introduced in 1993 for creating self employment by establishing small & medium farms (Poultry, Dairy & Fishery) through bank finance and is extended through 236 selected branches over the country. Maximum ceiling of loan is Tk. 5.00 Lac.
3. Farming & off farming program: This program was introduced in 1994 to involve unemployed rural people in income generating activities (Poultry, Dairy, Fishery, Horticulture, Nursery, Beef fattening) by establishing small & medium farms through bank finance and is extended through all branches over the country. Maximum ceiling of loan is Tk.15.00 Lac.
4. Krishi Khamar Rin Karmasuchi (Project):This program was introduced is 1993 for creating new employment, increase national income & Socio economic development by establishing medium & big project (Poultry, Dairy & Fishery) through bank finance.
5. Pond Fisheries credit Program: This program was designed to extend bank credit for pisiculture in derelict ponds/Tanks/water bodies in 1977 Credit is extended through 200 branches over the country. Maximum ceiling of loan is Tk.5.00 Lac.
6. Fertilizer Dealers Credit Program: This program was introduced to extend bank credit among the approved fertilizer dealers operating at primary distribution point of BADC for lifting their quota of Fertilizer from BADC for ultimate distribution among the farmers in 1981.
7. Sugarcane production loan program in mill Zone area: This program was introduced in 1975 to increase sugar production. Under this program credit is extended to 11 (eleven) sugar mills for ultimate disbursement among their affiliated farmers.
8. Social A forestation Program: This program was introduced in 2004 to increase forestation and to reduce greenhouse and is intended through all branches over the country. Maximum ceiling of this program is Taka 5.00 lac.
Micro credit :
Poverty mitigation has appeared to be the focal point of all policy formulation and development issues of the nation. As such, it has been globally accepted as an effective strategy for poverty alleviation in one hand and generating employment opportunities on the other. In commitment to reduce poverty in urban, semi-urban and rural areas, Sonali Bank Limited has started functioning in Micro Credit through a full pledged micro credit division in its Head Office in the year 2003. Presently, 32 projects are being run under the control and supervision of this Division.
Sonali Bank Limited jointly with Swanirvar Bangladesh, BRDB and ADB has been providing huge investible funds into the different Upazillas within the country. 152 Upazillas have been covered by the Rural Livelihood Programme (RLP). Further, this Division has provided taka 179.09 crore to 68 NGO’s under its widely accepted Bank-NGO Linkage Programme on whole sale basis and whose recovery rate is 100%. Specially, for the disable people Disable Loan Programme has been undertaken to bring the disable section of the people under the micro credit facilities. Further, in order to create employment opportunities and to generate income of the rural people two loan schemes under the name and style “Rural Small Farming Loans scheme” and “Rural Small business loan” scheme have been introduced in-2004. In both the programs there is a provision of collateral free loan up to Tk. 50,000/- . In 2006 a new program has been introduced named ‘‘ Daridra Bimochane Sahayta Karmasuchi’’for the extremely ‘Monga’ affected rural people. Moreover, in 2007 a special program has been introduced for SIDR affected 12 areas in which there is a provision of collateral free loan up to TK.20,000/-. Upto December 2008, Tk. 3299.47 crore has been disbursed under various project/ programs of this Division where as this disbursement figure was Tk. 3056.63 crore upto December 2007. The key features of some running projects/Programs of Micro Credits given as follows:-
Features:
SL. | Project/Programs | Target group | Loan size in Tk. |
1 | Swanirvar Credit Program | Poor Landless people | 1,000-15,000 |
2 | Crop Godown Credit Project | Small & Medium Farmers | Highest 10,000 |
3 | Sonai Bank -BARD, Comilla Priogik Gabesana Rin Prokalpa | Bittahin rural male & female | Highest 10,000 |
4 | Sonai Bank- RDA, Bogra Priogik Gabesana Rin Prokalpa | Bittahin rural male & female | Highest 10,000 |
5 | Marginal and Small Farms System Crop Intensification program(MSFSCIP) | Marginal, Poor & Small Farmers | Highest 10,000 |
6 | Herbal & Forestry, Medicinal Plant & Nursery Development Credit program | Bittahin, Poor Energetic Youth | 5,000-25,000 |
7 | Grameen Khudra Babsa Rin Karmasuchi | Poor People | Highest 50,000 |
8 | Daridra Bimochane Sahayta Rin Karmasuchi | Hard Core Poor People | 5,000-10,000 |
9 | Loans to Disable People | Disabled People | 25,000-50,000 |
10 | Unmesh Credit Program | Micro Entrepreneurs | 50,000-2,00,000 |
11 | Goat Rearing Credit Program | Small &Medium Entrepreneurs | Highest 50,000 |
12 | Credit for Urban Women Micro Enterprise Development (CUMED) | Urban Women Entrepreneurs | Highest 5,00,000 |
13 | Bank-NGO linkage Credit Program | Poor People | Highest 5000-50,000(Loan Wholesaling to NGOs) |
14 | Khudra Khamar Rin Karmasuchi | Small Entrepreneurs | Highest 50,000 |
15 | Salt Production Credit Program | Actual Salt Producer | 5,000-12,500 |
16 | Individual Irrigation / Agriculcural Equipment Credit Program | Small, Marginal & Medium Farmers | 10,000-16,500 |
17 | BRDB Crop Credit Program | Small, Marginal & Medium Farmers | 8,000-15,000 |
18 | BRDB Integrated Rural Development Program | Co operative Poor Male & Female Member | 1,500-20,000 |
19 | BRDB Rural Livelihood Program | Small, Marginal & Medium Farmers | 5,000-20,000 |
20 | BRDB -Shrimp Culture Credit Program | Small, Marginal & Medium Farmers | 2,333-28,000 |
21 | Special Loan for SIDR affected Area | SIDR affected People | Highest 20,00 |
International banking:
Sonali Bank Limited expertise in International Banking has a record of in-house growth over more than half a century. Its pioneer role in handling foreign trade and foreign exchange transactions ever before independence of the country still remains unchallenged. With wide network of branches at home and also a large number of correspondent banks world-wide it is singularly handling the largest volume of export-import business including home-bound remittances.
- Export Credit (Pre-shipment & Post shipment)
- Facilitating Supplier’s Credit
- LCs (Letters of Credit)
- Guarantees in Foreign Currency-
- – Bid Bond
- – Performance Guarantee
- – Advance Payment Guarantee.
- Bill Purchasing/Discounting
- Remittance, collection, purchases & sales of Foreign Currency & Traveller’s Cheques.
- NRAT (Non-Resident Account in Taka)
- NFCD A/c (Non-Resident Foreign Currency Deposit)
- RFCD A/c (Resident Foreign Currency Deposit)
- Convertible and Non-convertible Taka Account
- Forward contracts
- Correspondent Banking Relations
Import Finance: Sonali Bank Limited supports its customers by providing facilities throughout the import process to ensure smooth running of their business. The facilities are:
- Import Letter of Credit.
- Post Import Financing (LIM, LTR etc).
- Import collection services & Shipping Guarantees.
Interest rate: 12.00% to 14.00%
Export Finance: Sonali Bank Limited offers extra cover to its customers for whole export process to speed up receipt of proceeds. The facilities are:
- Export Letters of Credit advising.
- Pre-shipment Export Financing.
- Export documents negotiation.
- Letter of Credit confirmation.
Interest rate: 7.00% + 1.00% Service Charge
Industrial Financing:
Industrial Finance Credit Schemes : Long term loan for setting up new industrial units and BMRE of existing units including working capital finance are extended by Sonali Bank Limited to cottage industries, small-medium-large scale industries and also to self-employed persons with a view to creating employment opportunities, deployment of resources, increasing GDP and over-all industrial development of the country.
Designated Branches: About 100 branches including all the corporate and district headquarters branches are designated to handle industrial credit. Sonali Bank Limited has also come up with very low rate of interest to finance the following thrust sectors of the economy as identified by the Government:
- Software development and data processing.
- Agro-based industries (excepting cold storage for preservation of potatoes).
- Manufacture of artificial flowers.
- Gift items (preferably export oriented).
- 100% export oriented finished leather goods.
- Oil and Gas.
- Sericulture and silk industries.
- 100% export oriented textile industry (excepting garments manufacturing industries).
Other Viable Industrial Sectors:
- Composite textile (woven & knit fabrics).
- Sweater Industry.
- Garments Accessories & Washing Plant.
- Hospital & Clinics.
- Other Export linkage industries.
- LPG, CNG Filling & Conversion plant.
- Pharmaceutical Ind.
- Plastic Ind.
Interest Rates:
- Project/Term Loan : 12.00% to 13.00%
- Working Capital : 13.00%
Ancillary services:
Sonali Bank Limited offers multiple special services with its network of branches throughout the country in addition to its normal banking operations.
Collection:
- Gas bills.
- Electricity bills.
- Telephone bills.
- Water/Sewerage bills.
- Municipal holding Tax.
- Passport fees, visa fees and Travel tax.
- Customs & Excise duties.
- Source tax and VAT.
- Jakat fund.
- Hajj deposit.
- Land development tax.
Payment:
- Pension of employees of Government and other Corporate Bodies.
- Bangladesh Bank employee’s pension.
- Army pension.
- British pension.
- Students’ stipend/scholarship.
- Govt. & Non-Govt. Teachers’ salary.
- Food procurement bill on behalf of the Govt.
Social Services:
- Old age allowances.
- Widows, divorcees and destitute women allowances.
- Freedom Fighters’ allowances.
- Rehabilitation allowances for acid survival women.
Sale & Encashment/Purchase:
- Savings Certificates.
- ICB Unit Certificates.
- Prize Bonds.
- Wage Earner’s Development Bonds.
- US Dollar Premium & Investment Bond.
- Lottery tickets of different Semi-Govt. and Autonomous Bodies.
- Sanchaypatra.
- Public Service Commission’s application form.
- Judicial Service Commission’s application form.
- Exchange of soiled / torn notes.
Miscellaneous services:
Bank a/c information of tax payee client according to demand of NBR.
Local Governance Support Project.
Enlist of Non-government insurance company.
Locker Service Secured Locker Service is provided in some branches of Sonali Bank Limited. Customers may avail this service and secure their valuables.
Locker size | Yearly Charge (Tk.) | Security Deposit (Tk.) |
Small | 1,200.00 | 2,000.00 (refundable) |
Medium | 1,500.00 | |
Large | 2,000.00 |
Under special schemes the following products are generally offered by Sonali Bank Limited-
Rural Deposit Scheme (RDS):
A deposit scheme for the rural or people live under middle-class. Monthly deposits- 100, 200, 300, 400, 500 and 1000Tk.
Duration of the deposit- 7 years & rate of interest- 9%
Loan against account– When any particular account duration reaches to 1 year and on that account if there is 5000 Tk. Balance money then the account-holder can get maximum 80% overdraft opportunity. RDS can be opened in those branches of Sonali bank which are located in the rural area.
Procedure of Rural Deposit scheme | ||||
Deposit amounts types | Total Money After 7 Years | Given Interest | Bonus Amount | Total Money including Interest and Bonus |
100 | 8400 | 2677 | 1000 | 12077 |
200 | 16800 | 5355 | 1100 | 23255 |
300 | 25200 | 8032 | 1200 | 34432 |
400 | 33600 | 10710 | 1300 | 45610 |
500 | 42000 | 13387 | 1400 | 56787 |
1000 | 84000 | 26775 | 1900 | 112675 |
Marriage Savings Scheme (MSS):
Duration of the deposit- 10 years & rate of interest- 8.5%
Loan opportunity against account- When any particular account duration reaches to 1 year and on that account if there are 10000 Tk. balance money then the account-holder can get maximum 80% overdraft opportunity. MSS can be opened in all branches of Sonali bank. Bonus only be given after the
Procedure of Rural Deposit scheme | ||||
Deposit amounts types | Deposit amounts types | Deposit amounts types | Deposit amounts types | Deposit amounts types |
100 | 1200 | 6622 | 300 | 18922 |
200 | 2400 | 13244 | 600 | 37844 |
300 | 3600 | 19866 | 900 | 56766 |
400 | 4800 | 26488 | 1200 | 75688 |
500 | 6000 | 33110 | 1500 | 94610 |
1000 | 120000 | 66220 | 2000 | 188220 |
2000 | 240000 | 132440 | 3000 | 375440 |
3000 | 360000 | 198660 | 4000 | 562660 |
4000 | 480000 | 264880 | 5000 | 749880 |
5000 | 600000 | 331100 | 6000 | 937100 |
6000 | 720000 | 397320 | 7000 | 1124320 |
7000 | 840000 | 463540 | 8000 | 1311540 |
8000 | 960000 | 529760 | 9000 | 1498760 |
9000 | 1080000 | 595980 | 10000 | 1685980 |
10000 | 1200000 | 662200 | 11000 | 1873200 |
Monthly Earning Scheme (MES):
Duration of the deposit- 3 and 5 years. Amount of deposits-50000 or 100000.
Rate of interest- For 3 years 9% and for 5 years 10% Loan opportunity against account- When 80% overdraft opportunity on a particular account. MES can be opened in all branches of Sonali bank. Bonus amount can be taken monthly wise.
Procedure Of Payment Of Monthly Interest | ||
Deposit | 3 years | 5 years |
50000 | 375 | 420 |
100000 | 750 | 835 |
Double Benefit Scheme (DBS):
Duration of the deposit- 8 years. Amount of deposits-50000 minimum.
Rate of interest given yearly basis as following:
Duration | Interest rate | Interest | Total Amount |
Upto 6 Month | 4% | 1000 | 51000 |
Upto 1 Year but more than 6 Months | 5% | 2500 | 52500 |
Upto 2 Year but more than 1 Year | 6% | 6000 | 56000 |
Upto 3 Year but more than 2 Year | 7% | 10500 | 60500 |
Upto 4 Year but more than 3 Year | 8% | 16000 | 66000 |
Upto 5 Year but more than 4 Year | 8.5% | 21250 | 71250 |
Upto 6 Year but more than 5 Year | 8.5% | 31537 | 81573 |
Upto 7 Year but more than 6 Year | 8.75% | 39945 | 89945 |
Upto 8 Year but more than 7 Year | 9% | 49628 | 99628 |
Including Bonus 372 Tk. | 100000 |
All types of vat according to government rule will be deducted from the account.
Rules for Double Benefit Scheme-
This account can be open in all the branches of Sonali Bank Limited. But account holder must be age of 18 or above.
An account holder can get up to 80% loan against his deposit in the account.
In case of closing account customer can any time apply to the Manager (Where account was opened), but a charge of 250 Tk. will be applicable.
Medicare Deposit Scheme (MDS):
Duration-10 years
Amount of monthly savings-500-10000 Tk. & rate of interest is yearly 8%.
Date of payment- 10 -20 of every month.
Duration-5 years
Amount of monthly savings-500-10000 Tk. & rate of interest is yearly 8.5%.
Date of payment- 16-25 of every month.
Cumulative total after end of duration | ||
Monthly Payment amount | Bonus | Bonus + Interest after end of duration |
500 | 1500 | 38689 |
1000 | 2000 | 76378 |
2000 | 3000 | 151756 |
3000 | 4000 | 227134 |
4000 | 5000 | 302512 |
5000 | 6000 | 377891 |
6000 | 7000 | 453269 |
7000 | 8000 | 528647 |
8000 | 9000 | 604025 |
9000 | 10000 | 679404 |
10000 | 11000 | 754782 |
Education Deposit Scheme (EDS):
Duration-10 years
Amount of monthly savings-500-10000 Tk. & rate of interest is yearly 8 %.
Date of payment- 10-15 of every month.
Cumulative total after end of duration | ||
Monthly Payment amount | Bonus | Bonus + Interest after end of duration |
500 | 1500 | 92185 |
1000 | 2000 | 183371 |
2000 | 3000 | 365473 |
3000 | 4000 | 548115 |
4000 | 5000 | 730487 |
5000 | 6000 | 912885 |
6000 | 7000 | 1095230 |
7000 | 8000 | 1277602 |
8000 | 9000 | 1459974 |
9000 | 10000 | 1642345 |
10000 | 11000 | 1824717 |
Requirements for the special schemes-
- Photocopy of national ID of both nominee and client, 2 copy of passport size photograph which is attached by introducer and one copy of photograph of nominee which is attached by the client.
- Valid introducer of particular branch.
- Clients must be 18.
Bank for International Settlements (BIS):
BIS is an international organization promoting the cooperation of central banks and international monetary policy makers. BIS established in 1930, the oldest international financial organization, and was created to administer the transaction of monies according to the Treaty of Versailles. Among others, its main goals are to promote information sharing and to be a key center for economic research. Essentially, the BIS is a central bank for central banks; it does not provide financial services to individuals or corporations. The BIS is located in Basel, Switzerland, and has representative offices in Mexico City and Hong Kong. Member banks include the Bank of Canada, the Federal Reserve Bank and the European Central Bank. BIS’s main frame work is-
A brief history of BASEL-II:
BASEL-II:
Basel II is the second of the Basel Accords, which are recommendations on banking laws and regulations issued by the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision. The purpose of Basel II, which was initially published in June 2004, is to create an international standard that banking regulators can use when creating regulations about how much capital banks need to put aside to guard against the types of financial and operational risks banks face.Operational risk is included credit risk and market risk in BASEL-II. Operational risk is the risk of loss arising from human error or management failure. Basel II Capital Accord will be implemented from 2007 on. Its goal is to better align the required regulatory capital with actual bank risk.
Basel II is Three Pillars:
Basel II has three pillars which are known as- minimum capital, supervisor review and market discipline
1st Pillar: Minimum capital is the technical, quantitative heart of the accord. Banks must hold capital against 8% of their assets, after adjusting their assets for risk. It refers to maintenance of regulatory capital through credit risk, market risk and operational risk.
2nd Pillar: It refers the first pillar plus the following risk-
- Systematic risk
- Liquidity risk
- Concentration risk
- Legal risk
- Strategic risk
- Reputation risk
3rd Pillar: Market discipline is based on enhanced disclosure of risk. This may be an important pillar due to the complexity of Basel. Under Basel II, banks may use their own internal models (and gain lower capital requirements) but the price of this is transparency.
Basel II Charges for Three Risks
This accord recognizes three big risk buckets: credit risk, market risk and operational risk. In other words, a bank must hold capital against all three types of risks.
The Basel II Accord attempts to fix the glaring problems with the original accord. It does this by more accurately defining risk, but at the cost of considerable rule complexity. The technical rules will be importantly supported by supervisor review (Pillar 2) and market discipline (Pillar 3).
Generally speaking, these rules mean that the greater risk to which the bank is exposed, the greater the amount of capital the bank needs to hold to safeguard its solvency and overall economic stability.
Capital and Reserves:
The Authorized Capital of the Bank is Tk. 10.00 billion and the paid up Capital is TK. 9.00 billion as of June 31, 2010. The bank reserve is 311.65 million which more than previous year of 299.47 million.
Capital Adequacy Ratio: The Bank maintained a capital adequacy ratio of 11.12% of the risk-weighted assets as on June 31, 2010 as against regulatory requirement of 10% as per Bangladesh Bank.
Deposits:
The Bank’s deposit stood Tk. 396.25 billion as on June 31, 2010 and which is compared to Tk. 364.37 billion in 2008. Competitive interest rates, attractive deposit products, deposit mobilization efforts of the Bank and self-reliance reposed by the customers in the Bank contributed to the notable growth in deposits. The Bank develops a number of attractive Deposit Schemes to cater to the requirement of small medium savers. This improved not only the quantity of deposits but also brought about qualitative changes in deposits structure.
The deposit-mix of the Bank as on June 31, 2010 is in following:
|
Particulars |
Taka in Billion |
Share in Total Deposits |
| a) | Current and Other Deposit | 96.61 | 24.38% |
| b) | Savings Bank Deposits | 124.99 | 31.55% |
| c) | Fixed Deposits or Term Deposits | 167.39 | 42.24% |
| d) | Bills Payable Accounts | 7.26 | 1.83% |
| Total | 396.25 | 100% |
Loans and Advances:
Sonali Bank Limited provides various types of loans to the customer for economic development of the country. The loan scenario of last 3 years is as following-
Year | Amount of Loan (Tk. In Billion) |
2008 | 206.35 |
2009 | 231.17 |
2010 | 231.63 |
The increasing rate of loan is 12.03% in 2009& 0.20% in 2010 compared with previous year.
Investment:
The investment portfolio of Sonali Bank Limited is as follows for the last 3 years-
Year | Amount of Investments (Tk. In Billion) |
2008 | 88.89 |
2009 | 95.09 |
2010 | 104.79 |
The portfolio of investment includes Government Treasury Bills, Prize Bonds, Shares of Publicly Listed Companies, etc.
SWIFT:
Sonali Bank is an active member of SWIFT user Group in Bangladesh .At present all of our Authorized Dealer Branches are connected to SWIFT. Bank SWIFT team has been putting relentless efforts for continuous upgrading of SWIFT as and when any new features are introduced globally. The Bank’s SWIFT code is BSONBDDH.
Operating Income and Profit:
The Bank’s operating profit is as follows-
Year | Total Operating Income | Total Operating Expenses | Operating Profit |
2008 | 7.66 Billion | 3.42Billion | 4.24 Billion |
2009 | 12.66 Billion | 11.03 Billion | 1.63 Billion |
2010 | 7.07 Billion | 3.31 Billion | 3.76 Billion |
Interest Income:
During the year 2010, interest income of Sonali Bank was Tk. 8.96 billion as against of Tk. 13.10billion of the previous year. The interest income scenario is as follows-
Year | Interest Income |
2008 | 8.96 Billion |
2009 | 13.10 Billion |
2010 | 8.36 Billion |
Net Interest Income:
The net interest income scenario of the last 3 years of Sonali Bank Limited is as follows-
Year | Net Interest Income |
2008 | 2.33 Billion |
2009 | 8.64Billion |
2010 | 9.34 Billion |
Investment Income:
The investment income scenario of Sonali bank Limited is as follows-
Year | Investment Income |
2008 | 2.37 Billion |
2009 | 6.68 Billion |
2010 | 3.40 Billion |
Other Income:
The other income scenario of Sonali Bank Limited is as follows-
Year | Other Operating Income |
2008 | 1.29 Billion |
2009 | 2.06 Billion |
2010 | 2.29 Billion |
Net Profit after Tax:
The profit of Sonali Bank Limited is upward slopping.
Year | Net Profit After Taxation |
2008 | 0.97 Billion |
2009 | 2.31 Billion |
2010 | 3.76 Billion |
Statutory Reserve:
Statutory Reserves are those liabilities an insurance company is legally required to maintain on its balance sheet with respect to the un-matured obligations (i.e., expected future claims) of the company. The Statutory reserve scenario of Sonali Bank Limited is as follows-
Year | Statutory Reserve |
2008 | 2.99 Billion |
2009 | 3.12 Billion |
2010 | – |
Ratios under financial analysis:
Net Working Capital:
Net working capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
= 3992473379799 – 396321463480
= 3596151916319
Comment: Sonali Bank has 3596.15 billion Tk. as Net Working Capital.
Cash Ratio:
Cash Ratio = (Cash + Marketable Securities)/Current Liabilities
= (53209336915 + 0)/ 396321463480
= 0.1342 or 13.42%
Comment: Cash is the most liquid asset. Here, Sonali Bank carries 13.42% of cash. There is nothing to be worried if Sonali Bank has reserve borrowing power which allows cash draw from banks.
Return on Investment (ROI):
ROI = Net profit after tax / Total Assets
= 3761530336/ 532560805129
= 0.0071 or 0.71%
Comment: The ROI 0.124 means that Sonali Bank earned 0.71% percent return on owners’ investment.
Return on Equity (ROE):
ROE = Net profit after tax / Shareholders Equity
= 3761530336/ 30438890224
= 0.124 or 12.4%
Comment: The ROE 0.124 means that Sonali Bank earned 12.4 percent return on owners’ equity.
Net Working Capital Ratio:
Net Working Capital Ratio = Net Working Capital / Net Assets
= 3596151916319 / 72858908619
= 49.36%
Comment: Sonali Bank Limited has 49.36% net working capital on its net assets.
Tools of credit analysis:
Credit analysis is an important tool for analyzing bank performance. In other way we can say the analysis of the loans of different customers in prospect of repayment of the loan. There are two techniques of credit analysis-
6 C’s of Credit analysis
6 C‘s of Credit analysis-For a person who is considered a good credit risk usually meets six basic qualifications. These qualifications include character (credit reputation), capacity, capital, conditions, collateral, and common sense.
1. Character: – The first thing the lender judges will focus on is customer’s character and dependability. Customer’s character should exemplify trustworthiness and he should have no unlawful financial disputes in his history, and the customer must ensure that all previous debts and credits have been fully paid. The key factors for character include:
- A proper account of the business owner.
- No involvement in unlawful activities.
- Reference and resources.
- No outstanding debts.
2. Capacity: – A customer must prove his capability to the lender when he request for credit and assuring them of his ability to run a successful business. Good marketing and promotional skills can help a great deal in this regard. If the customers have limited experience, getting credit can be a relatively difficult task. The factors that need to be considered here are:
- The successful promotion of expertise.
- Effective advertising skills.
- Marketing mechanism.
3. Capital: –Investors are always interested in the reliability of a customer before issuing him any credit. Customer must fully figure out the capacity of his business and its potential impact before seeking any kind of credit. Failure to prove the credibility of the business of a customer can result in the rejection of getting loan.
4. Conditions:-All other existing debts, stability of employment, personal factors, and other factors that might affect a person’s ability or desire to meet financial obligations are important conditions to be considered. For example, a person who has moved six times during the past year might not be considered a good risk because of living conditions that indicate some type of problem.
5. Collateral: – Collateral is necessary for banks to give credit. Most of the time the collateral will be personal belongings which have some financial value such as a car or a house. Many banks want the collateral to be large to cover the losses if customer’s business fails to return the money owed.
6. Common sense:-A person’s inner ability to make wise decisions is often referred to as common sense. A loan officer or credit manager would determine that customer (who is seeking loan) have good common sense based on how customer answer questions (either orally or in writing). Good decisions are reflected in answers such as reasons for leaving employment, number and types of credit cards and balances outstanding, or references listed on an application.
CAMPARI Model:
The CAMPARI Model:
- Charter- Willingness to pay vs. ability to pay.
- Ability to Pay- Adequacy of cash to repayment.
- Margin of Finance- The client must contribute a certain margin as commitment.
- Purpose- The purpose of loan must be defined.
- Amount- The amount the financier is willing to contribute to the client.
- Repayments terms- The structure and terms of repayment.
- Insurance- In the event of borrower dies, the loan can be settled from insurance proceeds.
For doing the credit analysis of Sonali Bank Limited here CAMELS rating will be used.
CAMELS rating for credit analysis:
CAMELS rating for credit analysis-The CAMEL’s rating is a US supervisory rating of the bank’s overall condition. This is the modern and most uses techniques of credit analysis. This rating is based on financial statements of the bank.
Capital Adequacy:-The capital requirement is a bank regulation, which sets a framework on how banks and depository institutions must handle their capital. The categorization of assets and capital is highly standardized so that it can be risk weighted. Internationally, the Basel Committee on Banking Supervision housed at the Bank for International Settlements influence each country’s banking capital requirements. Internationally the Basel committee has declared that the capital adequacy ratio for banks is 8%, which is the sum of tire-1(Core Capital) and tire-2(Supplementary capital) capital and separately both has to be 4%.
Capital Adequacy Ratio ≤ 8% is undercapitalized.
Capital Adequacy Ratio ≥ 8% is well capitalized.
Asset Quality:-Asset management is related to the left hand side of the bank balance sheet. Bank managers are concerned with the quality of their loans since that provides earnings for the bank. Loan quality and asset quality are two terms with basically the same meaning. Government bonds and T-bills are considered as good quality loans whereas junk bonds, corporate credits to low credit score firms etc. are bad quality loans. A bad quality loan has a higher probability of becoming a non-performing loan with no return.
Management:-Management of a bank should be highly active to accomplish desired goals and objectives. Management of a bank must be assessing its customer in a proper way so that after giving loan to a customer the customer is not found as a defaulter.
Earnings:-Earnings are the consumption and savings opportunity gained by an entity within a specified time frame, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. But in bank it means that the earning efficiency on their loan. That is how much they can earn on their loan.
Liquidity:- In banking, liquidity is the ability to meet obligations when they come due without incurring unacceptable losses. Managing liquidity is a daily process requiring bankers to monitor and project cash flows to ensure adequate liquidity is maintained. For an individual bank, clients’ deposits are its primary liabilities (in the sense that the bank is meant to give back all client deposits on demand), whereas reserves and loans are its primary assets (in the sense that these loans are owed to the bank, not by the bank).
Sensitivity to market risk: – Market risk is the risk that the value of a portfolio, either an investment portfolio or a trading portfolio, will decrease due to the change in value of the market risk factors. The four standard market risk factors are stock prices, interest rates, foreign exchange rates, and commodity prices.
Capital Adequacy:
Bangladesh Bank has declared a Capital Adequacy Ratio for all of the commercial banks of Bangladesh. The ratio is 10%. Sonali bank has maintained a capital adequacy ratio for year 2010 is 11.12%.
The scenario for CAR is as follows for the beginning year-
Year | CAR | Position |
2008 | 10% | Well Capitalized |
2009 | 10% | Well Capitalized |
2010 | 11.12% | Well Capitalized |
Asset Quality analysis:
Sonali bank has a good control over management of its assets. If we see the last 3 years Return on Assets ratio then we can be able to understand about the asset quality of Sonali Bank Limited.
Return on Total Assets (ROA) – This ratio is a measurement for overall effectiveness of bank in generating profits with its available assets.
ROA = Net profit after Tax / Total Assets
Year | ROA |
| 2008 | 973580120 / 461964232939 = 0.0021 or 0.21% |
| 2009 | 2311114502 / 492964148318 = 0.0047 or 0.47% |
| 2010 | 3761530336 / 532560805129 = 0.0071 or 0.71% |
So we have seen that the ROA ratio of Sonali bank limited is increasing though it is poor.
- Average Assets-
Average Assets= [Total Assets (2008) + Total Assets (2009) + Total Assets (2010)]/3
= [461964232939+492946148318+532560805129]/3
= 1487471186386/3
=495823728795 Tk. Or 495.82 billion.
So we have seen that the bank has 495.82 billion Tk. as average assets.
Management quality of Sonali bank for analyzing credit:
The management body of Sonali bank has observed various operations for giving loan to customer. The governing body of the has declared few rule for seeking loans-
- Customer must have an account and the duration of the account must be 6 months
- In the time of getting loan customer must keep his assets which is equivalent to his loan amount as mortgage. The loan seeking customer must need a guarantor for getting loan if there is any problem the Sonali bank ltd. call the guarantor.
- If the customer has any previous bad record about bank transaction then that will be the first obligation for getting loan.
- For house-building loan customer must keep the land property (where the building is going to built) as mortgage.
- Customer (account holder of any one of the special savings schemes e.g.-SDS, EDS, MDS, MES, and MSS etc.) can get loan also against his deposit account in the bank. He can apply for 80% loan on his account.
- If any customer can not be able to repay loan or don’t want to repay then after six month from the starting of loan payment Sonali bank ltd. send notice for pay the loan properly. Even after if any customer doesn’t want to pay loan then the loan money is collect from the mortgage of the customer by selling it with proper bidding.
Earnings:
Earning is important for every commercial bank against loan from their customer. A banks earning is measured by the following ratios which Sonali bank ltd. do follows-
Return on Equity (ROE): – ROE measures the return earned on the owner’s investment.
ROE= Net Profit after tax/Shareholders equity
ROE (2008) = 973580120/21741728899 = 0.448 or 4.48%
ROE (2009) = 2016019588/24417714137 = 0.0825 or 8.25%
ROE (2010) = 3761530336/30438890224 = 0.123 or 12.3%
Earnings per Share (EPS):- Earning per share is generally considered to be the single most important variable in determining a share’s price.
EPS = Profit after tax/No. of share outstanding
EPS (2008) = 973580120 / 89979678 = 10.82 Tk.
EPS (2009) = 2016019588 / 90000874 = 22.40 Tk.
EPS (2010) = 3761530336 / 90010297 = 41.79 Tk.
Net Interest Margin (NIM): – Net interest margin (NIM) is a measure of the difference between the interest incomes generated by banks.
NIM = Net interest Income/Total Assets
NIM (2008) = 2336698542/461964232939 = 0.0051 or 0.51%
NIM (2010) = 8640672967/492946148318 = 0.0018 or 0.18%
NIM (2010) = 36029988710/532560805129 = 0.0677 or 6.77%
Net Bank Operating Margin:-
Net Bank Operating Margin = (Total Operating Revenues – Total Operating Expenses) / Total Assets
Year | NBOM |
2007 | (4246998619-3417856428)/461964232939 = 0.0018 or 0.18% |
2008 | (1616884090-11038246741)/49296418318 = -0.0191or -1.91% |
2009 | (3761530336-3308194007)/532560805129 = 0.0071 or 0.71% |
Economic Value Added (EVA): – Economic Value Added is a financial performance method to calculate the true economic profit of a corporation.
| EVA (2007) | 8962089341-(5%×88890899351) = 4517544373 or 4.51 Billion |
| EVA (2008) | 13101861774-(7%×95093241199) = 6445334890 or 6.44 Billion |
| EVA (2009) | 82369760517-(10%×104785960953) = 71891164421 or 7.19 Billion |
Earning Spread (ES):-
ES = (Total Interest Income/Total Earning Assets)-(Total Interest Expenses/Total Interest Bearing Liability)
Year | ES |
2008 | [(8962089341/206347592413)-{(6625390799)/241945186259}] = 0.0043- (0.027) = 0.0313 or 3.13 % |
2009 | [(13101861774/231166579465)-{(13965929070)/265590447542}] = 0.057 – (0.053) = 0.11 or 11% |
2010 | [(82369760517/231631896553)-{(8530059402)/396242643319}] = 0.36 – (0.022) 0.382 or 38.2%
|
Liquidity measurement:
Liquidity is another important instrument for measuring bank credit strength. The following ratios are necessary for measuring the liquidity for every bank which Sonali bank also follows-
Current Ratio- Current ratio is a measurement of the bank’s ability to meet its short term obligations. Scenario of current ratio for the last 3 years as follows-
Current Ratio = Current Assets / Current Liabilities
Year | Current Ratio |
2008 | 341137514499/335987250854 = 1.02:1 |
2009 | 357131987581 / 364931926622 = 0.97:1 |
2010 | 399247337979 / 396321463480 = 1.007:1 |
Quick Ratio- Quick ratio is the measurement of overall liquidity of a bank.
Quick Ratio (Acid test Ratio) = (Current Assets – Inventory) / Current Liabilities
Year | Current Ratio |
2008 | (341137514499-0)/ 335987250854 = 1.02:1 |
2009 | (357131987581-0) / 364931926622 = 0.97:1 |
2010 | (399247337979-0) / 396321463480 = 1.007:1 |
Cash Ratio- The cash ratio is an indicator of a company’s liquidity that further refines both the current ratio and the quick ratio by measuring the amount of cash.
Cash Ratio = (Cash + Marketable Securities) / Current Liabilities
Year | Cash Ratio |
2008 | (23407815028 + 0)/ 335987250854 = 0.070 or 7.0 % |
2009 | (20641592198 +0) / 364931926600 = 0.0566 or 5.66% |
2010 | (53209336915 + 0) / 396321463480 = 0.1343 or 13.43% |
Sensitivity to market risk:
Market risk can be measured by the following ratios for a bank. So the market risk of Sonali Bank is as follows-
Interest Rate Risk:
Interest Rate Risk = Interest Sensitive Assets / Interest Sensitive Liabilities
Year | Interest Rate Risk |
2008 | 269637071065/204923457791 =1.32% |
2009 | 303277625224 / 219764640512 = 1.38% |
2010 | 314726567831 / 221680427354 = 1.41% |
Market Value Added:
MVA = Book Value of Assets / Market Value of Assets
Year | MVA |
2008 | 461964232939 / 791944232938 = 0.58% |
2009 | 492964148318 / 793946148317 = 0.62% |
2010 | 532560805129 / 733530805128 = 0.72% |
Credit risk measurement:
For measuring credit risk the following ratio can be used.
Credit Risk Measurement = Nonperforming Loans / Total
Year | Credit Risk |
2008 | 25601420699 / 2069347592413 = 0.124 or 12.4% |
2009 | 22982195440 / 231166579465 = 0.0994 or 9.94% |
2010 | 21691289675 / 231631896553 = 0.094 or 9.4% |
SWOT Analysis
SWOT Analysis of Sonali Bank:
| Strength: Ñ Huge capital fund. Ñ Efficiency of Fund Management. Ñ Govt. own bank. Ñ Diversification | Weakness: Ñ Lengthy process. Ñ ROA is too low. Ñ Lacking on assessing people in case of giving loan. |
| Opportunities: Ñ Better financial products & services. | Threats: Ñ Non-payment of loan. |
FINDINGS & RECOMMENDATION
Findings:
As a largest commercial bank and the agent of Bangladesh bank Sonali bank has to do various types of work without thinking about the profit. For this reason I have seen that in some cases bank doing loss, but for this loss I directly cannot say that bank is going down, this is happening only for helping the nation.
Some other important factors-
- The banks profit increasing rate is poor but increasing.
- The bank is highly liquid and earns much profit on owner’s equity.
- Bank’s operating efficiency is good.
- Price of share is increasing.
- Sonali banks earning spread is also increasing. That means the earning efficiency is good.
- The banks average net working capital is 3596.15 million which makes a good sign.
- In the year 2009 the CAR of the bank is 11.12% against the requirements of 10% by Bangladesh Bank.
- The bank Return on assets is less than 1% but it is increasing.
- The banks assess its customer before giving any kinds of loan, but though there are some customers are found defaulter. From a reliable source it is found that among the defaulters most of them are political person.
- About 88% respondent has identified that Sonali Bank is a well Capitalized Bank.
- It seems to about 68% respondents that Sonali Bank should help other banks as a nationalized commercial bank.
- It seems to about 90% of the respondent that ROA & ROE is the key indicator of profitability.
- Properly measuring liquidity measures the overall financial position of Sonali Bank Limited.
- Most of the respondent identified that EPS is a growth driver of Sonali Bank Limited.
- 52% of the respondent identified that remittance helps development of economy of a country and by providing this Sonali bank increase its profitability it seems about 50% of the respondent.
- About 86% respondents’ things that Sonali Bank has to maintain bad debt.
- By providing Foreign Remittance service Sonali Bank helps the country to earn more tax.
So after all I can say that as a nationalized commercial bank Sonali Bank Limited is a bank which earns better than other nationalized Banks.
Recommendation:
- To increase the profit Sonali banks needs to increase interest rate on various types of loan.
- To increase ROA Sonali Banks needs to increase its net profit.
- Sonali Banks needs to properly assess the customer to operate its operation efficiently and also take needs to take action on those customers.
- To increase employment in the different Branches for fulfilling vacancy of the post.
CONCLUSION
As a bank Sonali Bank Ltd. has to do a lot of things for the betterment of the country. The Bank is strongly positioned in the market and with its core strengths it can match shareholders’ expectations and thus raise their wealth in future through ethical banking and best pricing. Thus, it has to take initiatives so that it can fulfill the desire of the govt. as well as people. It will enhance more public services and build up working teams to provide the best services to its valuable customers. It must be run in organized way and discipline must be ensured in all sphere of its performance. Efficient export team, import team and remittance team must be formed and perform duties properly. More training, computerization, data collection, market analysis and swiftness in servicing are essentially required. To do these the recommended suggestions can be used. Although it is theoretical suggestions, it is not valueless. It has great impact on the banking business and other sectors of the economy. For this, government’s help is essential and it is expected that govt. will broaden its hand for implementing the recommendations for the welfare of the people of Bangladesh.















