Introduction :
Bangladesh is a less developed country, whose economy is agro based. The Agricultural system is primitive and frequently affected by natural disaster. Poverty is the main problems of this country. About 47.6% of its population is living bellow the poverty line whoever as about 18% of the population is living blows the hard core poverty line (with less then 1800 calories per head per day).
After the devastating flood 1998-1999, the economic activities of the country resumed by taking various rehabilitation program and bumper production in the agriculture sector helps to recover that blow. Bangladesh economy has faced severe set back again after the terrorist attack on world trade center of USA on September 11,2001 and Afgan war. This even has changed the world economic scenarios and caused global economic recession. This global recession has severely affected export system & Bangladesh economy like ready made garments industry, Frozen food, Manpower export hotel and tourism sector etc. Due to global recession foreign financial assistance also severely affected.
To overcome this situation government has taken various sector based reform plan (closer of Adamjee Jute Mill is an example of it). Govt. also prepares the current fiscal year’s budget to decrease the foreign aid dependency. Although global recession has caused the ever lowest foreign currency reserve of US$1057n million in October,2001, which is increased to US$1478 million in April,2002 by various positive steps taken by the Government money laundering law, emphasis on remittance through proper banking channel.
According to Bangladesh economic analysis (2002) of ministry of finance, income is increased by 1.73% and population is increased 1.71%. per capita GDP, GNI and NNI is shown in the following table :
Fiscal Year | GDP | GNI | NNI | |||
| US$ | Taka | US$ | Taka | US$ | Taka | |
| 2001 | 363 | 19595 | 377 | 20332 | 349 | 18809 |
| 2002 | 362 | 20673 | 375 | 21448 | 347 | 19805 |
Overview of Financial Institutions of Bangladesh:
Financial institutes play an important role for the economic development of any country. The objective of these institutions is to accumulate the scattered deposit and invest it in a productive manner for economic emancipation.
There are 51 schedule banks (January 2001) operate in Bangladesh. Of them 4 nationalized commercial banks, 5 specialized banks, 30 private commercial banks and 12 foreign banks. The number of branches of those banks is 6242. Of which 2511 (40.2% of total) are in urban areas and rest 3731 (59.8% of total) are in rural areas.
Up to February 2002, of fiscal 2001-2002, total deposit and loan of all banks is taka 85259.8 and Taka 69392.6 Cr. Respectively.
For proper monitoring the operations of banks, Bangladesh bank introduces “Problem Bank Monitoring Division” in addition to CAME RATING. To increase the economic activities Bangladesh bank reduces the bank rate to 6% from 7%.
To increase customer services banks are using various modern techniques like on line banking, ATM, Money Gram, Credit Card etc.
List of Banks operating in Bangladesh:
Nationalized Commercial Banks (NCBS):
Sonali Bank.
Janata Bank.
Private Commercial Bank (PCBS):
Agrani Bank.
Rupali Bank.
Pubali Bank Ltd.
Uttara Bank Ltd.
Arab Bangladesh Bank Ltd.
National Bank Ltd.
The City Bank Ltd.
International Finance Investment and Commerce Bank Ltd.
United Commercial Bank Ltd.
Eastern Bank Ltd.
National Credit and Commerce Bank Ltd.
Prime Bank Ltd.
South East Bank Ltd.
Dhaka Bank Ltd.
Dutch-Bangla Bank Ltd.
Mercantile Bank Ltd.
Standard Bank Ltd.
One Bank Ltd.
Mutual Trust Bank Ltd.
First Security Bank Ltd.
The Trust Bank Ltd.
Premier Bank Ltd.
Bank Asia Ltd.
Bangladesh Commerce Bank Ltd.
Export and Import Bank Ltd. (EXIM).
Shahajalal Bank Ltd.
Jamuna Bank Ltd.
Brac Bank Ltd.
Islami Bank Bangladesh Ltd.
The Oriental Bank Ltd.
Al-Arafa Islami Bank Bangladesh Ltd.
Social Investment Bank Ltd.
Foreign Commercial Banks :
American Express Bank.
Standard Chartered Bank.
Habib Bank Ltd.
State Bank of India.
Credit Agricole Indosuez.
National Bank of Pakistan.
Muslim commercial Bank.
Citi Bank NA.
Shamil Bank of Bahrain E.C.
The Hongkong & Shanghai Banking Corporation (HSBC).
Specialized Bank:
Bank of Small Industries & Commercial Bangladesh Ltd.
Bangladesh Shilpa Bank.
Bangladesh Shilpa Rin Shonghstha.
Bank of Small Industries & Cottage.
Bangladesh Krishi Bank.
Rajshahi Krishi Unnayan Bank (RAKUB).
Role of Private Commercial Bank in Economic Development of Bangladesh
A bank is usually defined as a financial institution which deals in money. Today, however, the functions of a bank have increased so much that it is considered a very vital agent of development in country like ours. Because of their positive involvement in trade, industry, business finance and a host of other allied services, banks today form a very important part of an economy.
A bank like private commercial Bank helps to develop economy as follows:
Finance
Payment services
Resources mobilization
Resource allocation
Specialization Economies of
Scale
Real savings
Real investment
Economic Growth
Chart – 1
The nationalized banks, countries margin operational banking units, could not demonstrates and achieve optimistic results in terms of overall economic growth. The gloomy picture of nationalized banks is mainly due to –
Lack of quality of services.
Minimum of commitment toward institutions.
Management inefficiency.
Excessive intervention of collective bargaining agent (CBA).
Lack of security.
Documentation of loans and advances debarring legal action in case of default.
Slow rate of recovery of loan.
Lack of supervision and monitoring of loans and advances.
Directive loans.
Political instability.
Transitional inconsistency while formulating policy issues on banking.
Due to inefficient and continuous loosing concern of public sector, the main objective of privatization policy was –
To reduce deficit of the Govt. to meet continuous loss of public enterprises.
To improve operative efficiency of enterprises.
To introduce competitiveness in all spheres of economic activities except few areas where Govt. control of economic activities was unavoidable.
It was increasingly felt that a number of PCBs night have improved their position patting nationalized banks into competition. The launching of PCBs has finally created a significant impact in quality of services in banking. Banking being a service industry, it is not easy to quantity to performance of this sector like manufacturing. The performance of the banking sector in terms of generating of profit, expansion of bank branches, mobilization of deposits, deployment of advances, involvement in foreign trade and generating of employment.
It is revealed from the loan operations of banks. The PCBs provide operation mainly for trading (Internal trading, export and import trade) and construction while the NCBs are providing Finance for priority areas like agriculture, industry, and export/import tasks.
PCBs have shown some efficiency in terms of branch expansion, employment generation, and mobilization of deposits and deployment of advances but their activities remained concentrated in city areas. They could not provide finance for priority sector like agriculture.
The key to success of private sector banks is identified as a professional efficiency in choosing various risk assets, personalized quality of services, result oriented business strategy and achievement against stipulated target. But by rapidly issuing fresh licenses to the promoters of private banks, the quality of entrepreneurs is not being ensured and developed. As a result too many banks are chasing same customers/entrepreneurs within limited deposit base.
Now a day, the banking business exclusively depends on quality of services in terms of new innovative strategies for boozing banking operations compatible to international standard. Modern technology, equipment and innovation like computerized money counting machine automatic teller machine (ATM) etc. are being utilized to a great extent for survival and to face competitors.
PCBs have already explored new financial products by introducing master card, credit card to attract customer/entrepreneurs. Many PCBs have implemented various attractive schemes acceptable to the existing and prospective customers such as the customer credit scheme, marriage and educational scheme, micro credit scheme and small loan scheme etc. In this respect PCBs are keen for development of human resources to train and equip their manpower with new ideas and products to enable them to contribute to the greater innovation. The PCBs are taking part in stimulating foreign exchange reserve by financing 100% export oriented RMG industries. Neutrally 65% of export earnings of Bangladesh is generated by this sector.
The PCBs are participating and financing in various types of medium and long-terms industries either wholly or partly through consortium arrangement among the member banks. The PCBs are also general investor and recently a package program has been devolved to stabilize the countries capital markets by launching merchant’s banks, which will extend loans to the brokers and general investors.
The nationalized banks are taking advantages of restrictions imposed on non-nationalized banks while mobilizing deposits from government, autonomous and semi-autonomous bodies. Out of total available funds of Govt. sector, the PCBs are restricted to the range of 25% to 40% of these funds only. Such dual practice is not desirable when we are hoping the theory of free market economy.
Above all, PCBs. Have been playing and indispensable role in the money market for the growth and development of our economy along with all nationalized specialized and foreign banks. The better performance of PCBs will finally be recognized still when they offer better quality of service based on new ideas/products. We foresee a good future for the PCBs. They are expected to develop their lending role in the near future in financial market. The importance of variant economic refers to the due attention to a sound financial system. The base of financial services in Bangladesh is quite narrow. By improving only the financial structure and financial super structure, our financial system can be made sound.
THE TRUST BANK LIMITED
CORPORATE REVIEW
Historical Background:
The Trust Bank Ltd is schedule commercial bank, which conducts its operation as per the rules and regulations of Bangladesh Bank. The Army Welfare Trust (AWT) is the main sponsor of the bank, and it is expected that the bank would soon float public shares in the capital market for its conversion into a public limited company. The bank started its operations in November 29, 1999. At present the bank has 12 branches across the country. It renders all types of personal, commercial and corporate banking service to its customers within the purview of the Bank Companies Act, 1991 and in line with the directives and policy guidelines laid down by the Bangladesh Bank.
In addition to ensuring quality customer services related to general banking the bank also deals in Foreign Exchange transactions. In the mean time the bank has extended credit facilities to almost all the sector of the country’s economy. The bank has plans to invest extensively in the country’s industrial and agricultural sectors in the coming days.
It has also plans to promote the agro-based industries of the country. The bank has already participated in syndicated loan agreement with other banks to promote textile sectors of the country. Such participation would continue in the future for greater interest of the overall economy. Keeping in mind the client’s financial and banking needs the bank is engaged in constantly improving its services to the clients and launching new and innovative products to provide better services towards fulfillment of growing demands of its customers.
Capital:
The Trust Bank Ltd is very recent bank in this time. In present time as per the Bangladesh Bank rule that a bank’s paid-up capital must have 100 crore when any one want to open a bank. So at the present the bank do not have 100 crore in their paid-up capital structure but they have a huge fund which is given by The Army Welfare Trust. In recent the bank increase their paid-up capital from 25 crore to 35 crore but it is not signed by the board of directors.
The Trust Bank Ltd aims at optimizing profit with a view to allowing good returns on the investors’ money. Within two years of its operations bank has strengthened its capital base by increasing reserve and retained earnings. The Capital Adequacy Ratio as on December 31, 2001 was 17% against the standard of 8% and the crore capital ratios was 16% as against standard of 4%
The authorized capital of the bank is Taka 1000 million. Total shareholders equity at the end of the December 2001 stood at Taka 276.31 million. Out of Taka 276.31 million, paid-up capital is Taka 250 million, Statutory Reserve is Taka 10.97 million and Retained Earnings is Taka 15.34 million. The paid-up capital is indicative of the face value of 250000 ordinary shares of Taka 1000/= each fully subscribed by the shareholders. As at the close of business on December 2001 the capital adequacy ratio was 17% against the standard of 8%. The core capital ratio was 16% against the standard of 4%.
Number of Branches:
In this time the bank has already 13 branches in many different places in Bangladesh. Most of the branches are inside the cantonment area, because when they start their operation there main purpose was to serve the army. But with the current demand they try to go for vast banking. So for meeting up the demand they try to increase the number of brunches all over the Bangladesh.
Management Structure:
The management structure of the company has shown below through the organization structure diagram:
Organizational Management Structure
Employees:
An institution cannot run without manpower. So it is not accepted for The Trust Bank. In current they have 169 officers’ level employee and 50 as a causal worker.
Profit & Operating Result:
Total operating income of the bank in the year 2002 was Taka 190.34 million against a total operating expenditure of Taka 85.47 million. Total profit before provision stood at Taka 104.71 million during 2001. After keeping Taka 15.71 million as provision against classified loans & advances, Taka 2.52 million as provision against unclassified loans (1%) and Taka 34.00 million as provision for income tax, the net profit stood at Taka 52.48 million during the year 2001. Net profit after income tax in the year 2000 posted by the bank, was Taka 25.96 million. There is a significant increase in profit in 2002 over the preceding year 2001. The earning per share was Taka 199.45 in the year 2001. The retained earnings increased to Taka 50.53 million in 2002 from Taka 15.34 million in 2001.
Expansion of Branches:
The TBL has taken up a programme to expand its branches. The bank has already 13 branches in many different places in Bangladesh; most of them are inside the different cantonments. The management is filling that they need more branches all over the Bangladesh. So very recent they will open a branch in Dhanmondi. As per Bangladesh Bank circular that if any bank opens a branch in Dhaka then they have to be open a branch in out side Dhaka.
Information Technology & Automation:
All the branches of the TBL are fully computerized. New software is now in use to provide faster, accurate and efficient service to the clients. The bank is continuously striving for better services through extensive automation of its branches. We are soon going to launch “One Branch Banking” through on-line connectivity. The bank has set up a full-fledged IT division to keep abreast of the latest development of IT for better service in the days to come.
Foreign Correspondents:
Foreign correspondent relationship facilities foreign trade operation of the bank, mainly in respect of export, import and foreign remittance. The number of foreign correspondents and agents of the bank in the year 2002 stood at 244, which covers important business and trade centers of the world. The bank maintains excellent relationship with the leading international banks, for handling all foreign correspondent and maintaining all foreign business there is an International Division, which is called ID.
Human Resources Development:
The bank’s work force is composed of personnel having rich academic background with vast experience in banking. The human resources development means to create an environment by dynamic, enthusiastic and vigorous participation of all individuals. We would like to be consistent and transparent in their decisions and actions. The total number of executives and officers of the bank stood at 138 and others number of employees are 50 as on April 2003. To make their personnel knowledgeable and truly professional they arrange training for them at Head office of the bank, BIBM and other institutions. The management of the bank sits with the branch managers and departmental heads in regular meetings. The meetings provide scope for open discussion, which help in formulating new strategies for achieving “targets” of the bank.
Social Commitment & Future Prospect:
It has been all most three years science the stepped in to the banking arena. They are not yet past of their formative stage. It would be only a matter of time for them to testify that they are equally committed to the social upliftment of the country. They would stand by the people through philanthropic activities whenever any crisis and disaster confront them. They will not keep their social welfare activities restricted to one area only. It will be diversified in the days ahead of us as they are planning to award students of exceptional academic performance with scholarship in different educational institutions. They expect to launch soon school banking by extending their services, which would encourage parsimony in the students. It would also help in the creation of savings, which could be utilized for pursuing higher studies in future. Keeping in mind their social commitment would soon launch “Educational” and “Hajj” loans. Agriculture, being the only means of subsistence for innumerable people in rural areas of the country, needs more attention. They have plans to manufacturing agricultural equipments in the Bangladesh Machine Tools Factory Ltd., which would be distributed among their farmers at an affordable price.
SWIFT:
The bank will soon itself as a member of SWIFT Alliance Access, a sophisticated, fraud proof secured financial messaging system provided by the Society for Worldwide Inter-bank Financial Telecommunication (SWIFT), Belgium. With the installation of the SWIFT system the bank would ensure and reliable transmission of L/C, funds transfers, outgoing and incoming massages and other financial services.
Web Page:
The introduction of Internet has change the traditional concept of world trade and commerce. As the time is progressing its necessity is being felt more in the prevailing competitive since no organization can afford to remain in isolation with the rest of the world for its survival. In order to provide up-to-date information on the bank at fingertips to the trade and business communities of the world, their own IT team has developed a web page for the bank. It can be accessed to under the domain: www.trustbankbd.com.
FOREIGN EXCHANGE
Introduction:
Foreign trade can be easily defined as a business activity, which transcends national boundaries. These may be between parties or government ones. Trades among nations are a common occurrence and normally benefit both the exporter and importer. In many countries, international trade accounts for more than 20% of their national incomes.
Foreign trade can usually be justified on the principle of comparative advantage. According to this economic principle, it is economical profitable for a country to specialize in the production of that commodity in which the producer country has the greater comparative advantage and to allow the other country to produce that commodity in which it has the lesser comparative advantage. It includes the spectrum of goods, services, investment, technology transfer etc.
This trade among various countries causes for close linkage between the parties dealing in trade. The bank which provides such transactions is referred to as rendering international banking operations. International trade demands a flow of goods from seller to buyer and of payment from buyer to seller. And this flow of goods and payment are done through letter of credit (L/C).
Foreign Exchange:
As more than one currency is involved in foreign trade, it gives rise to exchange of currencies which is known as foreign exchange. The term “Foreign Exchange” has three principal meanings Firstly it is a term used referring to the currencies of the other countries in terms of any single one currency. To a Bangladeshi, Dollar, Pound sterling etc. are foreign currencies and as such foreign exchange. Secondly, the term also commonly refer to some interments used in international trade, such as bill of exchange, Drafts, Travel cheque and other means of international remittance thirdly, the terms foreign exchange is also quite of ten referred to the balance in foreign currencies held by a country.
In terms of section 2(d) of the foreign exchange regulations 1947, as adopted in Bangladesh, Foreign Exchange means foreign currency and includes any instrument drawn, accepted made or issued under clause (13) of article 16 of the Bangladesh Bank order, 1972, all the deposits, credits and balances payable in any foreign currency and draft cheque, letter of credit and bill of exchange expressed or drawn in Bangladesh currency but payable in any foreign country.
In exercise of the power conferred by section 3 of the foreign exchange regulation, 1947, Bangladesh Bank issues license to schedule bank to deal with exchange. These banks are known a Authorized Dealers. Licensees are also issued by Bangladesh Bank to persons or firms to exchange foreign currency instruments such as T.C, currency notes and coins. They are known as Authorized money changers.
Functions of Foreign Exchange Department:
Exports:
Pre-shipment advances.
Purchase of foreign bills.
Negotiating of foreign bills.
Export guarantees.
Advising/Confirming letters – letter of credit.
Advance for deferred payments exports.
Advance against bills for collection.
Imports:
Opening of letter of credit (L/C)
Advance bills.
Bills for collection.
Import loan and guarantees.
Remittances:
Issue of DD, MT, TT etc.
Payment of DD, MT, TT etc.
Issue and enhancement of traveler’s cheque.
Sale and enhancement of foreign currency notes.
Non-resident accounts.
The Most commonly used documents in Foreign Exchange:
Documentary Letter of Credit.
Bill of exchange.
Bill of Lading.
Commercial Invoice.
Certificate of origin of goods.
Inspection certificate.
Packing List.
Insurance Policy.
Proforma Invoice / Indent.
Master receipt.
GSP Certificate.
Documentary Credit:
In simple terms a documentary credit is a conditional bank undertaking a payment. Expressed more fully, it is a written undertaking by a bank (issuing bank) given to seller (beneficiary) at the request, and in accordance with the instructions of the buyer (applicant) to effect payment (that is, by making a payment, or accepting or negotiating bill of exchange) up to a stated sum of money, with in a prescribed time limit and against stipulated documents. The customary clauses contain in a L/C are the followings:
A clause authorizing the beneficiary to draw bills of exchange up to certain on the opener.
List of shipping documents, which are to accompany the bills.
Description of the goods to be shipped.
An undertaking by the opening bank that bills drawn in accordance with the conditions will be dully honored.
Instructs to the negotiating banks for obtaining reimbursement of payments under the credit.
Parties to a Letter of credit (L/C):
The parties to a Letter of Credit are:
Importer / Buyer.
Opening Bank/Issuing Bank.
Exporter/Seller/Beneficiary.
Advising Bank/Notifying Bank.
Negotiating Bank.
Confirming Bank.
Paying / Reimbursing Bank.
Bill of Lading:
A bill of leading is a document that is usually stipulated in a credit when the goods are dispatched by sea. It is evidence of a contract of carriage, is a receipt for the goods, and is a document of title to the goods. It also constituted a document that is, or may be, needed to support an insurance claim.
The Details on the bill of Leading should include:
A description of the goods in general terms not inconsistent with in the credit.
Identify marks and numbers, if any.
The name of the carrying vessel.
Evidence that the goods have been loaded on board.
The ports of shipment and discharge.
The names of shipper, consignee, and name and address of the notifying party.
Whether freight has been [paid or is payable at destination.
The number of original bills of lading issued.
The date of issuance.
A bill of lading specifically states that goods are loaded for ultimate destination specifically mentioned in the credit.
Commercial Invoice:
A Commercial Document is the accounting document by which the sellers change the goods to the buyer. A commercial invoice normally includes the following information:
Date.
Name and address of the buyer and seller.
Order of contract number, quantity and description of the goods, unit price and the total price.
Weight of the goods, number of the package, shipping marks and numbers.
Terms of delivery and payment.
Shipment details.
Certificate of Origin:
A certificate of origin is a signed statement providing evidence of the origin of the goods.
Inspection Certificate:
This is usually issued by an independent inspection company located in the exporting country certifying or describing the quality, specification or other aspects of the goods, as called for in the contract and the L/C. the inspection company is usually nominated by the buyer who also indicates the types of inspection he wishes the company to undertake.
Insurance Certificate:
The Insurance Certificate documents must –
Be that specified in the credit.
Cover the risks specified in the credit.
Be consistent with the other documents in its identification of the voyage and description of the goods.
Unless otherwise specified in the credit.
Be a document issued and / or signed by an insurance company or its agent, or by underwriters.
Be dated on or before the date of the date of shipment as evidenced by the shipping documents.
Be for an amount at least equal to the CIF value of the goods and in the currency of credit.
Import:
Importation is foreign goods and services purchased by customer, firms and Governments in Bangladesh.
An importer must have import registration certificate (IRC) given by chief controller of import and exports (CCI & E) to import any thing from other country. To obtain import registration certificate (IRC) the following certificates are required:
Trade License.
Income Tax clearance certificate.
Nationality certificate.
Banks solvency certificate.
Asset certificate.
Registration partnership deed (if any).
Memorandum and Article of association.
Certificate of incorporation (if any)
Rent receipt of the business premises.
Import Procedure :
To import through The Trust Bank Limited a customer/client requires –
Bank Account.
Import registration certificate.
Tax paying identification number.
Proforma Invoice/Indent.
Membership Certificate.
L/C application form duly attested.
One set of IMP Form.
Insurance Cover Note with money receipt.
Others.
Import Mechanism:
To import, a person should be competent to be an importer. According to import and Export control Act, 1950, the office of chief controller of Import and Export provides the registration certificate (IRC) to the importer. After obtaining this person has to secure a letter of credit authorization (LCA) from Bangladesh Bank and then a person becomes a qualified importer.
He is the person who requests or instructs the opening bank to open an L/C. He is also called opener or applicant or the credit.
Importer’s application for L/C limit / margin:
To have an import L/C limit, an importer submits an application to the department of (TBL) furnishing the following importation:
Full particulars of bank account.
Nature of business.
Required amount of limit.
Payment terms and conditions.
Goods to be imported.
Offered security.
Repayment schedule.
A credit officer scrutinizes this application and accordingly prepares a proposal (CLP) and forwards it to the head office credit committee (HOCC). The committee, if satisfied, sanctions the limit and returns back to the branch. Thus the importer is entitled for the limit.
Opening of Letter of Credit (L/C) by Bank:
Opening of L/C means, at the request of the applicant (importer) issuance of a L/C in favor of the beneficiary (Exporter) by a bank. the bank which open or issue L/C is called L/C opening bank or issuing bank.
On receipt of the importer’s L/C application supported by the firm contract (Indent / Proforma Invoice) and Insurance Cover Note the bank scrutinize the same thoroughly and fix up a margin on the basic of banker – customer relationship.
Before opening a L/C, the issuing bank must check the following:
L/C application properly stamped, signature verified and margin approved and properly retained.
Indent / Proforma Invoice signed by the importer and Indenter / supplier.
Ensure that the relevant particulars of L/C application correspond with those stipulated in Indenter / Proforma Invoice.
Validity of LCA entitlement of goods, amount etc. conforms to the L/C application.
Conversion and rate of exchange correctly applied.
Charges like commission, FCC, Postage, Telex charge, SWIFT charge, if any recovered.
Insurance Cover Note – in the name of issuing bank – A/c importer covering required risks and voyage route.
Incorporation of instruction for Negotiating Bank as per banks existing arrangement.
Reimbursement instructions for reimbursing bank.
If foreign bank confirmation is required, necessary permission should be obtained and accordingly advising bank is advised as per banks existing arrangement.
If add confirmation is required on account of the applicant charges should be recovered from the applicant.
In case of usance L/C, mention rate of interest clearly in the letter of credit.
Liability of Issuing Bank:
As per Article 9(a) of UCPDC 500, An Irrevocable Credit constitute a definite undertaking of the issuing Bank, provided that the stipulated documents ——— comply with the terms and conditions of the credit.
Advising of Letter of Credit:
Advising means forwarding of a Documentary Letter of Credit received from the issuing bank to the beneficiary (Exporter).
Before advising a L/C the advising Bank must see the following:
Signature of Issuing Bank officials on the L/C verified with the specimen signatures book of the said bank when L/C received.
If the export L/C is intended to be an operative cable L/C Test Code on the L/C invariably be agreed and authenticated by two authorised officers.
L/C scrutinized thoroughly complying with the requisites of concerned UCPDC provisions.
Entry made in the L/C Advising Register.
L/C advised to the Beneficiary (Exporter) promptly and advising charges recovered.
Advising Bank’s Liability:
Advising bank’s liability is fixed up in uniform customs and practice for documentary credits, publication 500.
Article 7(a): A credit may be advised to a beneficiary through another bank (the “Advising Bank”) without engagement on the part of the advising bank, but that bank, if it elects to advise the credit shall take reasonable care to check the apparent authenticity of the credit which it advises. If the bank elects not to advise the credit, it must inform the issuing bank without delay.
Article 7(b): If the advising bank cannot establish such apparent authenticity it must inform, without delay, the bank from which the instructions appear to have been received that it has been unable to establish the authenticity of the credit and if it elects nonetheless to advise the credit it must inform the beneficiary that it has not been able to establish the authenticity of the credit.
Adding Confirmation:
Adding Confirmation is done by the confirming bank confirming bank is a bank which adds its confirmation to the credit and it is done at the request of the issuing bank the advising usually does not do it if there is not a prior arrangement with the issuing bank. By being involved as a confirming agent the advising bank undertakes to negotiate beneficiary’s bill without recourse to him.
Issue L/C and request to add confirmation.
Review the L/C terms.
Provide reimbursement.
Drafts to be drawn on L/C opening bank.
Availability of credit facilities.
Line allocation from the business and ownership units in the importer’s country.
Confirm and advise L/C.
Amendments to Letter of Credit:
After issuance and advising of a L/C, it may be felt necessary to delete, add or alter some of the clauses of the credit. All these modifications are communicated to the beneficiary through the same advising bank of the credit. Such modifications to a credit are termed as amendment to a letter of credit.
There may be some of the conditions in a credit are not acceptable by the beneficiary. In that cases beneficiary contact applicant and request for amendment of the clauses. On receipt of such request applicant approaches his bank that is issuing bank with a written request for amendment to the credit. The issuing bank scrutinizes the proposal for the amendment and if the same is not in contravention with the exchange control regulation and bank’s interest, the bank may then process for amendment there can be more than one amendment to a credit. All the amendment forms an integral part of the original credit.
L/C amendments are to be communicated by SWIFT or mail. If there are more than one amendment to a credit, all the amendment must bear the consecutive serial number so that the missing the any amendment can be identified by the advising bank or by the beneficiary.
What is to be done by the issuing bank before advising amendments?
The issuing bank has to –
Obtain written application from the applicant of the credit duly signed and verified by the bank.
In case of increase of value, applications for amendment are to be supported by revised Indent/Proforma Invoice evidencing consent of the beneficiary.
In case of extension of shipment period, it should be ensured that relative LCA is valid/revalidated/increased up to the period of proposed extension.
Amendments an increase of credit amount and extension of shipment period both the cases amendment of Insurance Cover Note also be submitted.
Proper recording and filing of amendment is to be maintained.
Amendment charges (if an account of applicant) will be recovered and necessary voucher is to be passed.
The following clauses of L/C are generally amended:
Increase/decrease value of L/C and increase/decrease of quality of goods.
Extension of shipment/negotiated period.
Terms of delivery i.e. FOB, CFR, CIF etc.
Mode of shipment.
Inspection clause.
Name and address of the supplier.
Name of the reimbursing bank.
Name of the shipping line etc.
Settlement of Letter of Credit :
Settlement means fulfillment of issuing bank in regard to affecting payment subject to satisfying the credit terms. Settlement to may be done under three separate arrangements as stipulated in the credit.
Settlement by Payment :
Here the seller presents the documents to the nominated bank and the bank scrutinizes the documents. If satisfied, the nominated bank makes payment to the beneficiary and in case this bank is other than the issuing bank, then sends the documents to the issuing bank and claim reimbursement as per arrangement.
Settlement by Acceptance :
Under this arrangement, the seller submits the documents evidencing the shipment to the accepting bank (nominated by the issuing bank for acceptance) accompanied by draft down on the bank at the specified tenor. After being satisfied with the documents, the bank accepts the documents and the draft and if it is a bank other than issuing bank, then sends the documents to the issuing bank stating that it has accepted the draft and at maturity the reimbursement will be obtained in the pre-agreed manner.
Settlement by Negotiation :
This settlement procedure starts with the submission of documents by the seller to the negotiating bank. in a freely negotiate documents and if negotiation restricted by the issuing bank, only nominated bank can negotiate the documents. After scrutinizing that the documents meet the credit requirement, the bank may negotiate the documents and give value to the beneficiary. The negotiating bank then sends the documents to the issuing bank as usual; reimbursement will be obtained in the pre-agreed manner.
Accounting Treatment:
Sundry Deposit L/C Margin A/C Dr.
PAD A/C Cr.
(Margin amount transferred to PAD A/C)
Customer A/C Dr.
PAD A/C Cr.
(Customer A/c debited for the remaining Amount)
PAD A/C Dr.
Head Office A/C + Exchange Trading A/C Cr.
Income A/c interests on PAD Cr.
(Amount given to Head Office ID and interest credit)
Reversal Entries:
Banker’s Liability Dr.
Customer’s Liability Cr.
(When lodgment is given)
After realizing the telex charge, service charge, interest (if any), and the shipping documents is then stamped with PAD number & entered in the PAD Register. Intimation is given to the customer calling on the bank’s counter requesting retirement of the shipping documents. After passing the necessary vouchers, endorsements is made on the back of the bill of Exchange as “Receipt Payment” and the Bill of Lading is endorsed to the effect “Please deliver to the order of M/s………………………. under two authorized signatures bank’s officer’s (P.A. holder). Then the documents are delivered to importer.
Payment procedure of the Import Documents:
This is the most sensitive task of the import department. The officials have to be very much careful while making payment.
Date of Payment: Usually payment is made within 7 days after the documents have been received. If the payment is become deferred, the negotiating bank may claim interest for making delay.
Preparing Sale Memo: A sale memo is made at BC rate to the customer. As the TT & DD rate is paid to the ID, the difference between these two rates is exchange trading. Finally, an Inter Branch Exchange Trading Credit Advice is sent to ID.
Requisition for the foreign Currency: For arranging necessary fund for payment, a requisition is sent to the International Department.
Transmission of Telex: A telex is transmitted to the correspondent bank ensuring that payment is being made.
Export:
Practically by the term Export we mean out carrying of anything from one country to another. As banker we define export as sending of visible things outside the country for sale. Export Trade plays a vital note in the development process of an economy. With the caring we meet out import bills.
Although export trade is always encouraged, any body cannot export anything to any place. Like importer the exporters are also required to get them registered before entering into export trade. Export registration certificate (ERC) given by CCI & E is required for this purpose. The required documents to obtain ERC are also same as IRC.
When a bank (Authorized dealer) receives a L/C (cable or original) it ascertains the correctness of the test number and the authorized signature. Then the bank sends the original copy of the L/C to the beneficiary.
The exporter presents the relative documents to the negotiating bank after the shipment of the goods. The L/C issuing bank undertakes to honor is obligation only if the beneficiary fulfills the conditions stipulated in the L/C, may namely, the submission of stipulated documents with in the stipulated time. Even a slide deviation of the documents from these specified in the L/C may give an excuse to the negating bank. so the negotiating bank must be careful, promote, systematic and bias-free while scrutinizing the tender documents after careful and through examination of the documents, the banker has to list out the discrepancies which may be classified as major or minor, irremovable or removable. The removable discrepancies can be corrected by the tendered or future losses, which may arise due to non-repatriation of proceeds.
The following types of discrepancies may be noted while the negotiating bank examines the documents:
1. L/C expired.
2. Late shipment.
3. Amount drawn in excess of the L/C.
4. Bill of exchange not properly drawn.
5. Descriptions of goods differ.
6. Bill of Lading or Airway Bill state.
7. Bill of Lading classed.
8. Insurance Cover Note as per terms L/C.
9. Insurance Cover obtained after the Bill of Lading or Airway Bill date.
10. Enough number of copies not submitted as required by L/C.
11. Negotiation under L/C restricted.
12. Packing List and certificate of analysis not as per the L/C.
13. Documents not properly endorsed in favor of the bank.
14. Full shipment not effective and part shipment prohibited.
15. Gross Weight and Net Weight shown in different documents differ.
16. Same of the documents required by L/C not submitted and
17. Documents inadequately stamped.
Documents with major discrepancies, which could not be negotiated, should be sent on collection basis with the permission of the exporter.
Export Procedure:
The Export and Importer trade in our country are regulated by imports and exports (control) Act, 1950. Under the Export Policy of Bangladesh the exporter has to get the valid Export Registration Certificate (ERC) from chief controller of Import & Export (CCI & E). The ERC is required to renew every year. The ERC number is to be incorporated on EXP Forms and other papers connected with exports.
Registration of Exporters:
For obtaining ERC indenting Bangladeshi exporters are required to apply to the Controller / Joint Controller / Deputy Controller / Assistant Controller of Imports and Exports, Dhaka / Chittagong / Khulna / Mymensing / Sylhet / Comilla / Barishal / Bogra / Rongpur / Dinajpur in the prescribed Form along with the following documents:
1. Nationality and assets certificate.
2. Memorandum and Articles of Association and certificate of Incorporation in case of limited company.
3. Bank certificate.
4. Income tax certificate.
5. Trade license etc.
Securing the Order:
After getting the ERC (Export Registration Certificate) the exporter may proceed to secure the export order. He/she can do this by containing the buyers directly or through agent. In this purpose exporter can get help from:
Liaison Office.
Buyer’s local agent.
Export Promotion organization.
Bangladesh mission abroad.
Chamber of Commerce (Local & Foreign)
Trade fair etc.
Signing the contract :
After communicating with buyer exporter has to get contracted (writing or oral) for exporting exportable item(s) from Bangladesh detailing commodity, quantity, price, shipment, insurance and marks, inspection, arbitration etc.
Receiving the Letter of Credit:
After getting contract for sale, exporter should ask the buyer for letter of credit clearly stating terms and conditions of export and payment.
The following are the main points to be looked into for receiving (collecting export proceeds by means of documentary credit:
The terms of the L/C are in conformity with those of the contract;
The L/C is an irrevocable one, preferable confirmed by the advising bank;
The L/C allows sufficient time for shipment and negotiation;
Terms and conditions should be stated in contract clearly in case of other modes of payment:
Cash in advance;
Open A/C
Collection basis (documentary / clean).
(Here the regulatory frame work is URC-525, ICC Publication).
Procuring the Materials :
After making the deal and on the L/C opened in his favor, the next step for the exporter is to set about the task of procuring or manufacturing the contracted materials/merchandise.
Shipment of goods:
Then the exporter should take the preparation for export arrange for delivery of goods as per L/C and INCO-terms, prepare and submit shipping documents for Payment/ Acceptance/ Negotiation in due time. Documents for shipments –
EXP Form,
ERC (Valid),
L/C Copy,
Customer Duty Certificate,
Shipping Instruction,’
Transport Documents,
Insurance Documents,
Invoice,
Other documents,
Bill of Exchange (if required),
Certificate of Origin,
Inspection Certificate,
Quality Control Certificate,
G.S.P. Certificate,
Phyto-sanitary certificate,
Final Step :
After those, exporter submits all these documents along with a letter of Indemnity to NCCBL for negotiation. An officer scrutinizes all the documents. If the document is a clean one, NCCBL purchases the documents on the bank’s of banker – customer relationship. This is known as Foreign Documentary Bill purchases (FDBP).
Procedure for FDBP:
After purchasing the documents, NCCBL gives the following entries:
FDBP A/c Dr.
Customer A/c Cr.
(Before realization of proceeds)
Head Office A/c Dr.
FDBP A/c Cr.
(Adjustment after realization of proceeds).
A FDBP Registered is maintained for recording all the particulars.
Foreign documentary Bills for Collection:
The Trust Bank Limited forwards the documents for collection due to the following reasons –
If the documents have discrepancies.
If the exporter is a new client.
The banker is in doubt.
Foreign documentary bills for collection signify that the exporter will receive payment only when the issuing bank gives payment. The exporter submits duplicate EXP Form & Commercial Invoice. Subsequently, the value of the bill is calculated and the following accounting entries are given:
Head Office A/C Dr. @ TT Clean.
Client’s A/c Cr.(@ OD sight)
Govt. Tax A/c Cr.(@ of Invoice Value)
Postage A/C Cr.
Income A/c profit on Exchange Cr.
After passing the above vouchers, an Inter Branch Exchange Trading Debit Advice is sent for debiting the NOSTRO account. The Trust Bank Limited has NOSTRO account with its reimbursing bank. an FDBP register is maintained, where first entry is given when the documents are forwarded to the issuing bank for collection and the second one is done after realization of the proceeds.
Export Bill Scrutiny Sheet :
Bank scrutinizes the export bill on they following points –
General:
1. Late shipment.
2. Late presentation.
3. L/C expired.
4. L/C overdrawn.
5. Partial shipment or Trans shipment beyond L/C terms.
Bill of Exchange:
1. Amount of bill differs with invoice.
2. Not drawn on L/C issuing bank.
3. Not signed.
4. Tenor or B/E not identical with L/C.
5. Full set not submitted.
6. Invoice.
7. Not issued by the beneficiary.
8. Not signed by the beneficiary.
9. Not made out 1 name of the applicant.
10. Description, price, quantity, sales terms of the goods not correspond to the credit.
11. Not marked one fold as original.
12. Shipping marks differs will B/A & Packing List.
Packing List :
1. Gross weight, Net weight & Measurement, number of cartoons / packages differs with B/L.
2. Not marked one fold as original.
3. Not signed by the beneficiary.
4. Shipping marks differs with B/L.
Bill of Lading / Airway Bill :
1. Full set of bill not submitted.
2. B/L is not drawn or endorsed.
3. “B/L shipping on Board” “Freight Prepaid” or “Freight Collect” etc. notations are not marked on the B/L.
4. B/L not indicate the name and capacity of the party i.e. carrier or master, on whose behalf the agent is signing the B/L.
5. Shipped on Board notation not showing name of pre-carriage vessel/intended vessel.
6. Shipping on Board notation not showing port of loading and vessel name (Incase B/L indicates a place of receipt or taking in charge different from the port of loading).
7. Short form B/L.
8. Charter party B/L.
9. Description of goods in B/L not agree with that of Invoice/E & P/L.
10. Alternations in B/L not authenticated.
11. Loaded on deck
12. B/L bearing clauses or notations expressly declaring defective condition of the goods and/or the packages.
Others :
1. Non-negotiable documents not forwarded to buyers or forwarded beyond L/C terms.
2. Inadequate number of Invoice, Packing List & others submitted.
3. Short shipment certificate not submitted.
Settlement of Local Bill :
The settlement of Local Bill is done in the following ways:
The customer submits the L/C to The Trust Bank Limited along with the documents to negotiate.
The Trust Bank Limited official scrutinize the documents to ensure the conformity with the terms and conditions.
The documents are then forwarded.
The L/c issuing bank gives the acceptance and forward an acceptance letter.
Payment is given the customer on either by collection basis or by purchasing the documents.
Accounting treatment of or purchase of Local Bill :
Local Bill purchase documentary Dr.
Party A/c Cr.
Commission Cr.
Interest A/c Cr.
A LBPD (Local Bill purchase documentary) register is maintained to record the acceptance of the issuing bank until the acceptance is obtained, the record is kept in a collection register.
Mode of payment of export bills under L/C :
The most common methods of payment under a L/C are as follows:
1. Sight Payment Credit: In a Sigh payment credit, the bank pays the stipulated sum immediately against the exporter’s presentation of the documents.
2. Negotiation Credit : In negotiation Credit, the exporter has to present a bill of exchange payable to him in addition to other documents that the bank negotiation.
3. Deferred Payment Credit: In deferred payment, the bank agrees to pay on a specified future date or event, after presentation of the export document. No bill of exchange is involved. In TBL, payment is given to the party at the rate of D.A 60-90-120-180 as the case may be. But the Head Office is paid at T.T clean rate. The difference between the two rates is the exchange trading for the branch.
4. Acceptance Credit: In acceptance credit, the exporter presents a bill of exchange payable to himself and drawn at the agreed tenor (that is, on a specified future date event) on the bank that is to accept it. The bank signs its acceptance on the bill returns it to the exporter. The exporter can then represent it for payment on maturity. Alternatively he can discount it in order to obtain immediate payment.
Advising L/C :
When exporter L/C is transmitted to the bank for advising, the bank sends an advising letter to the beneficiary depicting that L/C has been issued.
Test Key Arrangement :
Test Key arrangement is a secret code maintained by the banks for the authentication for their telex message. It is a systematic procedure by which a test number is given and the person to when this number is given can easily authenticate the same test number by maintaining that same procedure. The Trust Bank Limited has test key arrangements with so many banks for the authentication of L/C messages and for making payment.
Back to Back Letter of Credit :
A Back to Back letter of credit is a new credit. It is different from the original credit based on which the bank undertakes the risk under the back to back credit. In this case, the bank’s main security is original credit. The original credit (selling credit) are separate instruments independent of each other and in no way legally connected – although they both from part of the same business operation.
The supplier (beneficiary of the back to back credit) ships goods to the importer and presents documents to the bank as is specified in the credit. It is intended that the exporter would substitute his own documents for negotiation under the original credit, his liability under the back to back letter of credit would be adjusted out of these proceeds. The exporter L/C is marked lien and no margin is taken.
In TBL, papers/documents required for submission for opening of back to back L/C:
A) Master L/C
B) Valid Import Registration Certificate (IRC) & Export Registration Certificate (ERC).
C) L/C application & LCA Form duly filled in signed.
D) Proforma Invoice or Indent.
E) Insurance Cover Note with money receipt.
F) IMP Form duly signed.
In addition to the above the following papers/documents are also required for export oriented garments industries while requesting for opening back to back letter of credit –
Textile permission.
Valid bonded warehouse license.
Quota allocation letter issued by Export Promotion Bureau (EPB) in favor of the applicant in case of quota items.
In case the factory premises is a rented one, letter of disclaimer duly executed by the owner of the house/premises to be submitted.
Detective points or clauses appears in the Master L/C:
Issuing bank is not reputed.
Advising Credit by the advising bank without authentication.
Port of destination absent.
Inspection clause.
Nomination of specific Shipping/Airline or nomination of specified vessel by subsequent amendment.
B/L to blank endorse, to third bank, to be endorsed to buyer or third party.
No specific reimbursing clause.
UCP clause not mentioned.
Shipment / presentation period is not sufficient.
Original document to be sent to buyer or nominated agent.
FCR or HAWB consigned to applicant or buyer.
“shippers’ Load and Count is acceptable”.
L/C shall expire in the country of the issuing bank.
Negotiation is restricted.
Payment of back to back Letter of Credit:
In case of back to back as 60-90-120-180 days of maturity period, deferred payment is made. Payment is given after realizing export proceeds from the L/C issuing bank.
Accounting treatment for back to back L/C:
When the document is arrived, the following vouchers are passed:
Customer’s A/c Dr.
Commission on Acceptance Cr.
While payment, if the fund is at hand, the accounting entry is –
Sundry deposit margin on acceptance Dr.
Customer’s A/c Cr.
If the party is paid in foreign currency, B.C. rate is applied in this regard. International department takes the T.T. OD. Rate. If the payment is made to ID in local currency in national rate, T.t. clean rate is followed by ID. When the party is paid O.D sight rate is followed.
If the fund is not available to make the payment, the following vouchers are to passed –
OAP Dr.
Customer’s A/c Cr.
Under the back to back concept, the seller, as beneficiary of the credit, offer it as security to the advising bank for the issuance of the second credit. As application for this second credit the seller is responsible for reimbursing the bank for payment made under it regardless of whether or not be himself is paid under the first credit. There is, however, no compulsion for the bank to issue the second credit, and in fact, many banks will not do so.
Foreign Exchange Remittance :
Remittance means sending of fund. The word remittance we understand sending/ transferring of fund through a bank from one place to another place which may be within the country or between two countries, one in abroad is called Foreign Remittance.
“Foreign Remittance” means purchase and sale of freely convertible foreign currencies as admissible “Foreign Exchange Regulations Act-1947” and “Guidelines for Foreign Exchange Transaction – VOL. 1&2 of the country. Purchase of foreign currencies constitutes inward foreign remittance and sale of foreign currencies constitutes out ward foreign remittance.
So we see that there are two types of Foreign Remittance:
1. Foreign inward remittance.
2. Foreign outward remittance.
Inward Remittance:
The remittances which are received from abroad are called inward remittance.
Purpose of inward remittance:
Family maintenance.
Indenting commission.
Donation.
Gift.
Foreign investment.
Export proceeds.
Others.
Mode of inward remittance:
Telegraphic Transfer (TT)
Mail transfer (MT)
Foreign Demand Draft (FDD)
Payment order (PO)
Travelers cheque (TC)
Foreign Currency Notes.
Outward Remittance:
Remittances which are made from our country to abroad is called outward remittance.
Mode of outward remittance:
Foreign Telegraphic Transfer (FTT)
Foreign Mail Transfer (FMT)
Foreign Demand Draft (FDD)
Travelers Cheque (TC)
Foreign Currency Notes.
Present limit of outward remittance fixed by Bangladesh Bank :
Travel:
For Private Travel : Private travel quota entitlement of Bangladesh national total US$3000 per calendar year for visit to countries other than SAARC (India, Pakistan, Nepal, Bhutan, Srilanka, Maldives) and Myanmar.
Quota for SAARC countries and Myanmar is US$1000 for travel by Air and US$500 for travel by land. At a time bank can issue full amount of above quota if required. Case dollar may be issued maximum US$600 per passport per travel. The amount of travel quota mentioned above are prescribed for adults only. The minors are eligible for 50% of the annual ceilings of adults.
Business Travel :
(1) Subject to an annual upper limit of US$5000 importers are entitled to business travel quotas 1% of their imports settled during the previous financial year.
(2) Subject to an annual upper limit of US$5000 non exporting producers are entitled to business travel quotas 1% of their turnover of the preceding financial year as declared in their tax return.
a) For Exporters: New exporters are entitled to a quota for US$ 6000 annually and old exporters can use FCAD expanse retention quota A/c as per their requirement.
b) For Foreign Nationals : The Authorized Dealers may issue foreign currency TCS to foreigners without any limit and foreign currency notes up to US$300 or equivalent per person against surrender of equivalent amounts in foreign currencies.
Education:
Foreign exchange may be remitted for studies abroad by Bangladesh National in all regular courses (Subject to being consistent with the education policy of the Bangladesh Govt.) in recognized institutions. Authorized dealer has to open file for the individual student. Application and papers required for this purpose as follows:
Application duly filled in.
Original and photocopy of admission letter issued by the educational institution in favor of the student.
Original and photocopy of estimate relating to annual tuition fee, board and lodging incidental expenses etc. issued by concerned institution.
Attested copies of educational certificates of the applicant.
Valid passport.
Seminar / Workshop / Conferences:
Up to US$250 per dicer and US$200 per days receptively may be issued by Authorized Dealers to private sector participants for attending seminars, conferences and works hops arranged by recognized international bodies in SAARC member countries or Myanmar and in other countries without prior approval of the Bangladesh Bank. Foreign exchange may be released only for the actual period of the seminar, workshop and conference to be held.
Medical Treatment:
Foreign currency up to US$10000 our equivalent may be released by the ADS on the basis of the recommendation of the medical Board set up by the health directorate and the cost estimate of the foreign medical institution. Application for release of exchange exceeding US$10000 should be forwarded along with supporting documents to Bangladesh Bank for prior approval.
Fees:
The Ads may release foreign exchange towards remittance of membership fees of foreign professional and scientific institutions and fees for application, registration, admission, examination (TOEFL, SAT, etc). In connection with admission into foreign educational institutions on the basis of written application supported by demand notice / letter from the concerned foreign institution showing the amount to be –
Family Maintenance:
a) Bangladesh National: Outward remittance may be made to family members / dependent parents, spouses and children living abroad with the permission from Bangladesh Bank. a certificate issued by relevant Bangladesh embassy regarding residency of the beneficiary extend of income abroad along with the embassies recommendation as required for this purposes.
b) Foreign Nationals: Foreign Nationals who are resident in Bangladesh and who have an income in Bangladesh are permitted to make monthly remittances to the country of their domicile out of their current savings up to 50% of their income to cover their commitments abroad.
Foreign Shipping Lines / Air Lines / courier Services Company:
These companies may remit their income after adjustment of the amount shipment for local disbursement and tax payable.
Dividend/ Gain of Foreign Companies/ Shareholders:
Dividend, Profits, Gains may be remitted abroad to the owner, shareholders without prior approval of Bangladesh Bank.
Hajj:
The Govt. of Bangladesh announces each year the scale at which foreign exchange may be issued to intending pilgrims for performing Hajj. Release of foreign exchange for this package should be made as per instruction, to be issued for this purpose by Bangladesh Bank each year.
Remittance of Salaries and Savings by Expatriates:
Expatriates working in Bangladesh with the approval of the Govt. may remit through an Authorized Dealer 50% of salary and 100% of leave salary as also actual savings and admissible pension benefits. No prior Bangladesh Bank approval is necessary for such remittance.
Expenses of office opened abroad:
Remittance of up to US$3000 or equivalent may be made annually meet current expenses of such offices opened abroad by a commercial or industrial concern. Such remittance may only be made in the names of concerned offices, subsidiary companies abroad.
Remittance of Royalty and Technical Fees:
No prior permission of Bangladesh Bank or BOI is required by the enterprises for entering into agreement involving remittance of royalty, technical know how or technical assistance fees. Operational services fees, marketing commission etc. if the total fees and other expenses connected with technology transfer do not exceed the following limit:
For new projects, not exceeding 6% of the cost of imported Machinery.
For ongoing concerns not exceeding 6% of the previous years sales as declared in the income tax return.
Operating Expense of Bangladesh Shipping Corporation & Bangladesh Biman:
Bangladesh shipping corporation and Bangladesh Biman are allowed to make remittances to meet bonafide disbursements in foreign ports, foreign station without approval of Bangladesh Bank.
Remittance against Export Claims:
The Authorized Dealers may remit export claims not exceeding 10% of the repatriated export proceeds on the following counts:
a) Short weight claims.
b) Quality claim.
c) Part shipment.
Subscriptions to Foreign Media Services:
On application from the local news papers, Ads may remit foreign exchange towards cost of subscriptions of news items features articles of foreign news agencies. Remittance should be made on the basis of contracts entered into between the applicant and the foreign agency and NOC of the Ministry of information Ads may remit abroad costs, fees on account of their own subscription of foreign media services such as Router monitor service without prior Bangladesh Bank approval.
Advertisement of Bangladeshi Products in Mass Media Abroad:
Ads may without prior Bangladesh Bank approval effect remittance towards cost of advertisement of Bangladeshi products on mass media abroad.
Bank charges and sundries:
The Authorized Dealers may affect remittances toward settlement of dues to foreign banks of bank charges. Cost of cables and other incidental charges arising in their normal curse of the business without prior Bangladesh Bank approval. All such remittances should be reported to the Bangladesh on forms TM along with appropriate return.
Taking out / Bringing in of Bangladeshi Taka:
Incoming, outgoing passengers may bring in/take out up to taka 500 per person in Bangladesh currency.
In all above cases for outward remittance TM form to be obtained and this will have to be reported to Bangladesh Bank Monthly basis.
Submission of Returns to Bangladesh Bank:
The Ads must maintain adequate and proper records of all foreign exchange transactions including transaction on non-resident Taka A/C in their book and furnish such particular in the prescribed statements/returns for submission to the Bangladesh Bank.
The purpose of submission of return & statements to Bangladesh Bank for keeping systematic and proper records of all dealings in foreign exchange including transactions on non-resident Taka A/Cs. Submission of the returns/statements to Bangladesh Bank is very much important. Total picture of foreign exchange transaction of the country such as reserve of FC, FCs earned through export, wage earners & other reference and FCs paid through import, treatment, education, traveling etc can be ascertained after compilation of these returns/statements submitted to Bangladesh Bank by the ADs.
Procedures for reporting transactions:
A) Export :
Export bills drawn under confirmed and/or irrevocable L/Cs:
Transactions in respect of export bills negotiated by the Ads should be reported as purchase only at the time entries are made in the currency account duly supported by EXP form and schedule:
a) EXP Original reported by Custom Authority to Bangladesh Bank at the time of shipment/export.
b) EXP . duplicate : To be reported by the Ads to Bangladesh Bank within 14 days of shipment.
c) Exp. Triplicate : To be reported after repatriation of the export proceeds.
Export bills drawn on Collection basis :
Sometimes ADs also purchase export bills drawn on collection/CAD basis. Transactions relating to such export bills should be reported as outright purchases against “export” in the summary statement on receipt of advice of realization of the export proceeds.
Export bills pertaining to Head Office or branch maintaining independent currency account:
When export bills are re-discounted with the Bangladesh Bank the transactions should be reported as purchase in the Summary statement supported by Schedule A and Exp Form and the contra entries should be reported on schedule D as sales to Bangladesh Bank.
Export bills pertaining to branch not maintaining its own currency account :
As and when the exports are re-discounted with the Bangladesh Bank the branch concerned will report the transactions as purchase in the summary statement supported by Schedule A-1/0-1 and Exp. Form.
B) Other Receipts :
Purchase of DD, TT and MT etc. should be reported to Bangladesh Bank only when the transactions are put through the currency accounts.
C) Imports :
Foreign currency A/Cs of ADs are debited at the time of negotiation of import documents by their foreign corespondent drawn under the L/Cs established by the ADs. Sale of this F.C. should be reported on receipt of negotiated import documents and not on the basis of retirement of bills by the importer.
All sales on account of imports are required to be supported by the original copy of the IMP form.
Import bills received on collection/CAD basis, the transactions will be reported on Schedule E-2 supported by original IMP Form.
D) Other payment :
Transactions relating to DD, TT, MT etc issued by the Ads should be reported only at the time of entries are made in the currency accounts.
Transactions in non-resident Taka accounts of foreign banks should also be reported by the ADs.
Coding of Transactions:
AD will give code numbers for all receipts and payments transactions on the relevant forms and schedules as per code list provided by Foreign Exchange Policy Dept. Bangladesh Bank (2000 edition) and. AD will use the HS Code number form the HS Code Guide titled “The Harmonized commodity Description and Coding System” exports and imports in the relevant schedules.
Reporting Procedure for cash transaction:
Ads shall report to the Bangladesh Bank particulars of all their foreign exchange transactions i.e. all outward and inward remittances effected. Whether through their accounts in foreign currencies or through the Taka accounts of non-resident banks. The original copies of statement / schedules to be sent directly to the Statistics Dept. Bangladesh Bank Head Office, Dhaka the duplicate copies along with the relevant forms should be endorsed to the concerned area office of Bangladesh Bank. these monthly statement / schedules to be sent to Bangladesh Bank by the 5th day of the following month.
Compilation of summary statement:
Each summary statement will be an abstract of the Ads ledger A/c and will consist of totals under specified heads. Opening and closing balances should be added making each summary a complete and balance statement.
Supporting schedules and forms of the summary statement:
Every summary statement must be accompanied by schedules and the relative forms as indicated in the summary statements.
Preparation of schedules:
Schedule A-1 :
When EXP form is certified against purchase of FCS the transaction must be listed in schedule A-1 in triplicate showing the number of EXP form and the amount.
Schedule A-2:
a) Advance receipt for goods to be exported this is to be reported through “Advance Receipt Voucher” (A[ppendix-19 Vol-2)
b) Where the duplicate EXP form has already been lodged with the Bangladesh Bank and the triplicate is not available at the time when proceeds are received. This is to be reported through “EXP form not attached voucher” (Appendix 20-Vol-2).
Schedule A-3:
Schedule A-3/0-3 is used to report purchase of F.C. against export to Myanmar under Bangladesh – Myanmar Border Trade Arrangement.
Schedule –C :
Currencies purchased from other Ads or branches in Bangladesh to be reported in schedule – C to be attached with relative S-1, S-2 and S-6 statement.
Schedule – G:
Currencies sold to other Ads or branches in Bangladesh to be reported in schedule-G to be attached with S-1, S-2, and S-6.
Schedule – D:
FCs purchased from and sold to Bangladesh Bank to be reported as Schedule-D.
Schedule – E-2/P-2, E-3/P-3 and EL 1/2/3:
All import transactions to be reported schedule E=2/P-2 and the charges (interest reimburse etc.) there against and other sales other than import Traveling, Treatment, Service/Technical charges etc in schedule E-3/P-3. Transactions relating to Loans/Grants will be reported through EL-1/2/3.
Reporting of Inland L/C settlements:
Payment against inland L/Cs in foreign exchange will be reported in summary statement S-1 or sales side as “Payment against Inland L/C” and the recipient AD will report the receipt on the purchase side of S-1 as “Receipt in settlement of Inland L/C”.
Date of submission of statements to Bangladesh Bank:
Schedule Time
| 1. Operations on private non-resident Taka accounts of non-bank clients. | Quarterly with 12th day of following month. |
| 2. Monthly statement of outstanding payment commitments abroad | By 15th of following month |
| 3. Commodity wise statement of imports L/Cs outstanding as on each month end. | 10th of the following month |
| 4. Monthly statement of outstanding exports bills as of each month end. | 15th of the following month. |
Currency wise daily position statements should be kept ready for immediate submission to Bangladesh Bank as and when called for.
Performance of The Trust Bank Limited
Introduction:
The Trust Bank Limited has diversified activities in retail banking, corporate banking and international trade. From the very beginning it has obtained a solid foundation in respect of foreign trade. The bank is now moving forward for the better future position in the field of foreign exchange and in the money market of the Bangladesh.
Performance at a Glance:
The performance of the Trust Bank Limited for last three years depicted a true success story of the bank. The deposits indicated the increase of its performance and reliability of the bank to the customer. It has controlled its loans and advances with a significant way of banking. The amount of investment shows the higher upscale line through the year. The final figure has projected when we look at the profit amount of those three years. The amount sharply goes double in these three years.
Particulars | 2000 | 2001 | 2002 |
| Authorized Capital | 1000 million | 1,000 million | 1000 million |
| Paid-up Capital | 2,00,000,000 | 250,000,000 | 350,000,000 |
| Statutory Reserve | 123,555 | 10,852,396 | 28,273,070 |
| Deposits | 1,111,177,724 | 2,478,816,542 | 2,975,731,164 |
| Loans & Advances | 525,743,315 | 1,603,951,250 | 1,897,629,064 |
| Investments | 201,998,900 | 363,112,500 | 493,187,300 |
| Operating Income | 34,153,596 | 115,932,783 | 190,343,764 |
| Operating Expenditure | 28,316,615 | 45,422,491 | 85,473,392 |
| Net Profit (After Tax) | 370,665 | 25,965,648 | 52,485,597 |
Net Interest Income:
Year | Net Interest Income (Taka) |
| 2000 | 3,098,859 |
| 2001 | 82,991,374 |
| 2002 | 106,012,056 |
Findings and Analysis
SWOT Analysis of The Trust Bank Limited:
SWOT Analysis is an important tool for evaluating the companies Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats. It helps the organization to identify hoe to evaluate its performance and can scan the macro environment, which is turn would help the organization to navigate in the Turbulence Ocean of competition. Following is given the SWOT analysis of The Trust Bank:
Strengths:
1. Top Management:
The top management of the bank, the key strength for The Trust Bank has contributed heavily towards the growth and development of the bank. The top management officials are army’s highest position holder, so they have a good idea about the current situation.
2. Company Reputation:
The Trust Bank has created a good reputation in the banking industry of the country. Their main customers are army persons. The popularity of this bank is increase day by day also in the general public area.
3. Sponsors:
The Trust Bank has founded by The Army Welfare Trust. The main sponsors for this bank is Sena Klyan Sangstha. The chairperson of this bank is Chief of Army Staff and directors are also appointed by the sangstha, that’s why the sponsor does not have any problem for the fund.
. Modern Facilities and Computer:
From the very beginning The Trust Bank tries to furnish their work surroundings with modern equipment and facilities. For speedy service to the customer, The Trust Bank had installed money-counting machine in the teller counter. The bank has computerized banking operation under software called PC banking. More over computer printed statements are available to internal use and occasionally for the customers. The Trust Bank is equipped with telex and fax facilities.
5. Stirring Branches:
From the formative stage of The Trust Bank tried to furnish their branches by the impressive style. Their well-decorated branches gets attention of the potential customer, this is one kind of positioning strategy. The Sena Klayan Bhaban Branch is also impressive and is comparable of foreign banks.
6. Interactive Corporate Culture:
The corporate culture of The Trust Bank is very much interactive compare to other local organization. This interactive environment encourages the employee to work attentively. Science the banking jobs is very much routine work oriented and lovely environment boots up the work capability of the employees.
Weakenesses:
1. Limitation of Information System (PC Bank):
PC bank is not comprehensive banking software. It is desirable that a more comprehensive banking system should replace PC bank system.
2. Hierarchy Problem:
The hierarchy problem treated as a weakness for The Trust Bank, because the employee will not stay for a long. So there will be a chance of brain drain from this bank to other bank.
3. Advertisement Problem:
There is another weakness for The Trust Bank is advertisement. Their media coverage is so much low that people do not know the bank thoroughly.
Opportunities:
1. Diversification:
The Trust Bank can pursue diversification strategy in expanding its current line of business. They do not serves not only the army but also the general people.
Threats:
1. Contemporary Banks:
The contemporary banks of The Trust Bank like: Dhaka Bank, Dutch Bangla Bank, National Bank, Mutual Trust Bank, Mercantile Bank are its major rivals. They are carrying out aggressive campaign to attract lucrative clients as well as big time depositors. The Trust Bank should remain vigilant about the steps taken by these banks, as these will in turn affect The Trust Bank strategies.
2. Multinational Bank:
The Rapid expansion of multinational bank poses a potential threat to new PCB’s. Due to the booming energy sector, more foreign banks are expected to operate in Bangladesh. Moreover, the existing foreign banks such as HSBC, AMEX, CITI N.A, and Standard Chattered Grindlays are now pursing an aggressive branch expansion strategy. Since the foreign banks have tremendous financial strength, it will pose a threat to local bank to a certain extant in terms of grabbing the lucrative clients.
3. Default Culture:
Default culture is very much familiar in our country. For a bank, it is very harmful. As The Trust Bank is new, it has not faced it seriously yet. However as the bank grows older it might become big problems.
Major drawbacks of The Trust Bank Limited:
In the middle of twenty first century here we are facing a heavy competition with each other. Here everyone is competing with each and every single point. So today’s business institution are moving forward to remember this concept. If any one has a week point than the rival party will take the opportunity and make a problem for the week intuition.
After complete my internship in The Trust Bank I realized that there are many problems and this may be a cause of huge loss or create a barrier for the future prospect. So the bank should take care on this problems very seriously.
Advertisement Problem:
Today’s world is very much depend on the media, so if the intuitions are not think about the advertisement or any kind of activities which is related some kind of advertisement then it will not earn so much popularity. A media can rise or fall an institution within very short time. So if we see to other developed country then we can find that every business intuition has a huge budget for the advertisement purpose. They do not take this expanse as an expanse; they always take it as a huge investment, because if the people do not know about my organization then how they will do business with us (it dose not matter which type of organization is this), it may be big manufacturing company or a bank. Here I realized for The Trust Bank that they do not have any kind of vast advertisement or any kind of social activities, so most of the people do not have any idea about The Trust Bank. In this case when any one asks that “where are you working?” then if any one say that in The Trust Bank then people reply at first that “is this Mutual Trust”. So for his or her kind information they have to say no there is a bank called The Trust Bank and it is a bank for the army. This bank is also serving the general people but it is not so much popular, because of advertisement. People thought that this bank’s purpose is to serve only army people. That’s why the bank is not go for a vast banking.
Hierarchy Problem:
This is another big problem for The Trust Bank, because in the beginning level there are so many ranks to become a principal officer that it may be the cause of brain drain from this bank to other bank.
Absence of Online Banking:
Today’s world is modern world, so here every one wants that they will do banking from their own house. The Trust Bank does not have this kind of facilities. So if they implement online banking than they will gain huge popularity.
Limited Number of Branches:
The Trust Bank has only 12 branches allover the Bangladesh. So if they want to do a vast business then they have to increase the number of branches.
Limited Power to the Managers:
The managers and other high officials have no power for decision-making. The branch managers have no power to sanction loans. In every bank there is a certain amount that a branch manager can sanction, but in this bank if anyone wants to take a single Taka for loan then the manager has to for the head office approval. Some times it may be the cause of losing customer, because it will take time to sanction a loan.
Recommendations:
Through conducting this study I have acquired some practical knowledge about export import business in Bangladesh & and other relevant matters. Now I would like to provide some recommendation which may be helpful to promote the export import business of The Trust Bank Limited as well as Bangladesh. As per earnest observation some suggestions for improvement of the situation are given below:
For attracting more clients The Trust Bank Limited has to create a new marketing strategy which will increase the total export import business.
Effective and efficient initiative is necessary to recover the default loans.
Attractive incentive package for the exporter will help to increase the export and accordingly it will diminish the balance of payment gap of The Trust Bank Limited.
Introduction of attractive WES which will increase the remittance.
For the foreign exchange officials long terms training very much essential.
For a sound and stale foreign exchange operation, The Trust bank Limited should give more emphasis on the foreign exchange department.
Foreign exchange operation of other renowned commercial banks is more dynamic and less time consuming. The Trust Bank Limited should take some initiative to compete with those banks.
Bank can provide foreign market reports which will enable the exporter to evaluate the demand for their products in foreign countries.
Conclusion:
Proper financial system of a country can contribute towards the development of that country’s economy. In our country Bangladesh, banks have a leading power to its financial system. For this reason, the banks should have a potential role to make our financial system. In this arena, private commercial banks are playing a vital role in the development of our economy. But Govt. and Bangladesh Bank play a crucial role to the private commercial banks through imposition of deposit restriction, lending role and other banking operations. In recent years of banking business, The Trust Bank Limited has shown better performance comparing with other first generation banks.
We expect the The Trust Bank Limited may hold its prospect in future and can play a vital role in the socio-economic development of our country.

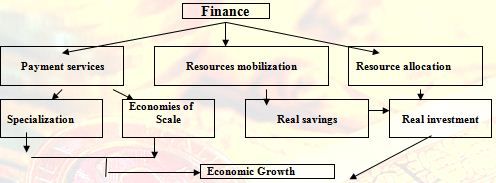
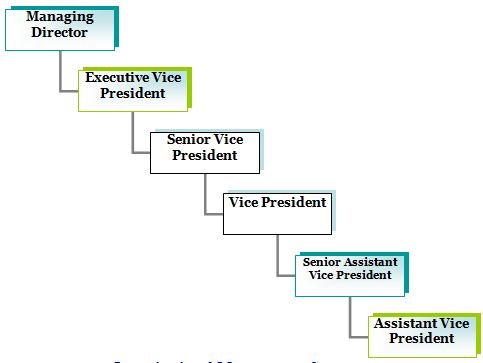



![Internship Report on Security Watching All the Time (S.W.A.T.) [Part- 2]](https://assignmentpoint.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/04/Security-Watching-All-the-Time-200x100.jpg)











