Introduction
A credit card is part of a system of payments named after the small plastic card issued to users of the system. It is a card entitling its holder to buy goods and services based on the holders promise to pay for these goods and services. The issuer of the card grants a line of credit to the consumer (or the user) from which the user can borrow money for payment to a merchant or as a cash advance to the user. A credit card is different from a charge card, where a charge card requires the balance to be paid in full each month. In contrast, credit cards allow the consumers to ‘revolve’ their balance, at the cost of having interest charged. Most credit cards are issued by local banks or credit unions, and are the same shape and size as specified by the ISO 7810 standard.
Credit cards are issued after an account has been approved by the credit provider, after which cardholders can use it to make purchases at merchants accepting that card.
When a purchase is made, the credit card user agrees to pay the card issuer. The cardholder indicates his/her consent to pay, by signing a receipt with a record of the card details and indicating the amount to be paid or by entering a Personal identification number (PIN). Also, many merchants now accept verbal authorizations via telephone and electronic authorization using the Internet, known as a ‘Card/Cardholder Not Present’ (CNP) transaction.
1.1.1 Special Feature of the credit card
As well as convenient, accessible credit, credit cards offer consumers an easy way to track expenses, which is necessary for both monitoring personal expenditures and the tracking of work-related expenses for taxation and reimbursement purposes. Credit cards are accepted worldwide, and are available with a large variety of credit limits, repayment arrangement, and other perks (such as rewards schemes in which points earned by purchasing goods with the card can be redeemed for further goods and services or credit card cash back).
Some countries, such as the United States, the United Kingdom, and France, limit the amount for which a consumer can be held liable due to fraudulent transactions as a result of a consumer’s credit card being lost or stolen.
Credit card security relies on the physical security of the plastic card as well as the privacy of the credit card number. Therefore, whenever a person other than the card owner has access to the card or its number, security is potentially compromised. Merchants often accept credit card numbers without additional verification for mail order purchases. They however record the delivery address as a security measure to minimize fraudulent purchases. Some merchants will accept a credit card number for in-store purchases, whereupon access to the number allows easy fraud, but many require the card itself to be present, and require a signature. Thus, a stolen card can be cancelled, and if this is done quickly, will greatly limit the fraud that can take place in this way. For internet purchases, there is sometimes the same level of security as for mail order (number only) hence requiring only that the fraudster take care about collecting the goods, but often there are additional measures. The main one is to require a security PIN with the card, which requires that the thief have access to the card, as well as the PIN.
1.1.2History
The concept of using a card for purchases was described in 1887 by Edward Bellamy in his utopian novel Looking Backward. Bellamy used the term credit card eleven times in this novel.
The modern credit card was the successor of a variety of merchant credit schemes. It was first used in the 1920s, in the United States, specifically to sell fuel to a growing number of automobile owners. In 1938 several companies started to accept each other’s cards. Western Union had begun issuing charge cards to its frequent customers in 1921. Some charge cards were printed on paper card stock, but were easily counterfeited.
The Charga-Plate was an early predecessor to the credit card and used during the 1930s and late 1940s. It was a 2 1/2″ x 1 1/4″ rectangle of sheet metal, similar to a military dog tag, which was embossed with the customer’s name, city and state (no address). It held a small paper card for a signature. It was laid in the imprinter first, and then a charge slips on top of it, onto which an inked ribbon was pressed. Charga-Plate was trademarks of Farrington Manufacturing Co. Charga-Plates were issued by large-scale merchants to their regular customers, much like department store credit cards of today. In some cases, the plates were kept in the issuing store rather than held by customers. When an authorized user made a purchase, a clerk retrieved the plate from the store’s files and then processed the purchase. Charga-Plates speeded back-office bookkeeping that was done manually in paper ledgers in each store, before computers.
The concept of customers paying different merchants using the same card was invented in 1950 by Ralph Schneider and Frank X. McNamara, founders of Diners Club, to consolidate multiple cards. The Diners Club, which was created partially through a merger with Dine and Sign, produced the first “general purpose” charge card, and required the entire bill to be paid with each statement. That was followed by Carte Blanche and in 1958 by American Express which created a worldwide credit card network.
Bank of America created the BankAmeriCard in 1958, a product which, with its overseas affiliates, eventually evolved into the Visa system. MasterCard came to being in 1966 when a group of credit-issuing banks established MasterCharge; it received a significant boost when Citibank merged its proprietary Everything Card, launched in 1967, into Master Charge in 1969. The fractured nature of the U.S. banking system meant that credit cards became an effective way for those who were traveling around the country to move their credit to places where they could not directly use their banking facilities. In 1966 Barclaycard in the UK launched the first credit card outside of the U.S.
There are now countless variations on the basic concept of revolving credit for individuals (as issued by banks and honored by a network of financial institutions), including organization-branded credit cards, corporate-user credit cards, store cards and so on.
In contrast, although having reached very high adoption levels in the US, Canada and the UK, it is importance to note that many cultures were much more cash-oriented in the latter half of the twentieth century, or had developed alternative forms of cash-less payments, such as Carte bleue or the Euro card (Germany, France, Switzerland, and others). In these places, the take-up of credit cards was initially much slower. It took until the 1990s to reach anything like the percentage market-penetration levels achieved in the US, Canada, or the UK. In many countries acceptance still remains poor as the use of a credit card system depends on the banking system being perceived as reliable.
In contrast, because of the legislative framework surrounding banking system overdrafts, some countries, France in particular, were much faster to develop and adopt chip-based credit cards which are now seen as major anti-fraud credit devices.
The design of the credit card itself has become a major selling point in recent years. The value of the card to the issuer is often related to the customer’s usage of the card, or to the customer’s financial worth.
1.1.3 International Credit Card in Bangladesh
The central bank has liberalized foreign exchange transaction rules to some extent for exporters, foreign investors and other foreign currency users in the context of comfortable foreign currency reserve condition. The Bangladesh Bank September 23, 2008 issued two separate circulars to this effect and allowed all banks to issue international credit to foreign currency users. As per the liberalized rules, roaming mobile phone bill can be paid through the cards and in some cases currency can be remitted abroad without prior permission from the central bank. A Bangladesh Bank senior official said “The central bank has taken the steps to make the foreign exchange transaction rules more liberalized and time befitting”. According to one of the Bangladesh Bank circulars, banks now can issue international credit card against the balances held in the exporters’ retention quota foreign currency account. The bank can also issue international cards in favor of up to three top level executives of an exporting firm or organization holding relation quota foreign currency accounts, the circular said. An exporting firm or organization can avail of the card facility from a card issuing company. The bank may issue international credit card or pre-paid card against the annual personal travel quota entitlement. The international credit or pre-paid cards may be issued favoring private sector participants for attending seminars, conference and workshops abroad arranged by recognized international bodies. However while issuing the cards the banks shall endorse an amount not exceeding the entitlement on the passport. The bank can issue international debit or pre-paid cards to the private sector Hajj agencies to meet food.
1.2.0 Findings of Major Financial Institutions in Bangladesh:
Asia is still an untapped market as far as the credit card industry is concerned. Lafferty Financial Consultancy Group, for example, estimated that in 2000, Consumers in Australia, Hong Kong, India, Japan, Korea, Singapore and Taiwan had disposable incomes totaling S$4.46 trillion, not much less than Europe’s S$5.01trillion. However, only 7.3 percent of that sum was spent through credit cards in Asia compared to 35 percent in the United States. This, coupled with the liberalization of the financial sectors in this part of the world, has resulted in the rapid proliferation of 4credit card companies and financial companies providing other types of consumer credit.
In Hong Kong, HSBC is offering Palm Pilots and Standard Chartered is offering DVD players to those who sign up for a credit card. One can also get up to HK$15,000 in just 30 minutes through the “Cash in a Flash” service provided by AeonCredit. In Japan, it is even more convenient — just visit one of 1,500 ATMs run by consumer finance companies like Takefuji. By standing in front of the camera and entering personal details, a loan will pop out of a debt-vending machine in less than 10 minutes (Yoon, 2001).
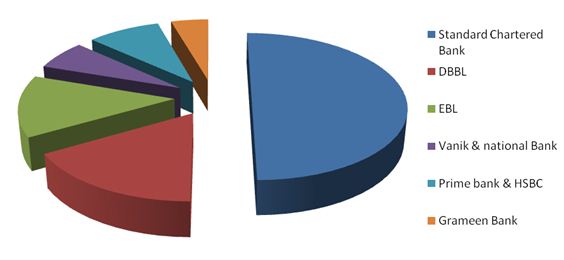
Standard Chartered Bank, Eastern Bank, Dutch-Bangla Bank Limited, Lanka Bangla- these are four major banks who play a vital role in credit card market of Bangladesh which are as follows.-
1.2.1 Standard Chartered bank
Former ANZ Grindlays Bank, now Standard Chartered Grindlays Bank, took a pioneering role in introducing credit card in Bangladesh. It started acquiring Visa and MasterCard nearly 10 years back. In the first few years, its operational area was very limited and concentrated only on the large hotels and restaurants. In 1997 the bank decided to launch full-scale card operation and very realistically brought a wide range of people under its service system. It is now giving a wide range of card services through multifarious quality facilities.
The bank has Visa Silver, MasterCard Silver and MasterCard Gold card. MasterCard Gold is targeted to high-end customer base that have a higher income. Silver cards have lower credit limits. The minimum income requirement for Silver is Tk. 10,000 per month and for Gold is Tk. 55,000 per month. The income of the applicant along with other financial data is the preliminary consideration in deciding the limit of credit. Standard Chartered Grind lays Bank offers air travel accidental
Insurance to its cardholders and this is maximum of Tk. 1, 00,000 for Silver and a maximum of Tk. 5, 00,000 for Gold. The bank has ATM machines in Dhaka, Chittagong and Khulna. Several more new machines will be installed in phases. Standard Chartered Grind lays Bank has initiated for the cardholders’ benefit that a cardholder can withdraw maximum 50% of his card’s limit in cash on 30% interest. Earlier a cardholder could withdraw only 20% of his card limit on the same interest.
Gold card and Silver cards
Gold Cards are for people with a higher level of income and with affluent lifestyles. Some of the attribute differences of the gold and silver cards are,
Table: – 1 Fees and charges of Gold card and Silver cards.
| Criteria | Gold Card | Silver Card |
| Minimum monthly income | BDT 55,000 | BDT 10,000 |
| Minimum Credit Limit | BDT 100,000 | BDT 10,000 |
| Maximum Credit Limit | BDT 500,000 | BDT 90,000 |
| Annual Fees (Primary Card) | BDT 3500 | BDT 1750 |
| Annual Fees (Supplementary | ||
| Card) | BDT 2000 | BDT 1000 |
| Card Replacement Fee, PIN | ||
| Replacement Fee, Over-limit | ||
| Charge & Late Payment Fee | ||
| (Per cycle) | BDT 500/Card + VAT | BDT 200/Card + VAT |
Fees and charges are subject to frequent changes to adjust with market condition and business priorities.
Local and International cards
Some of the attributable differences of the Local and International cards are,
Table: – 2 Attributable differences of the Local and International cards.
| International Cards | Local Cards | |
| Use | Can be used outside Bangladesh for purchases other currencies. | To be used only in Bangladesh for purchases only in BDT |
| Security | Issued against the deposits of an RFCD Account or an Export Retention quota | Issued fully unsecured
|
| Account Charge Currency | Charges are all in USD. | Charges are in BDT |
| Operator | VISA only | VISA and MasterCard both.
|
1.2.2 DBBL bank
▪ Started providing credit card:
DBBL commenced its card operation in August 2004. Dutch-Bangla Bank Limited has started issuance of DBBL-NEXUS Gold and Silver Cards with OD facility since June 2006.
▪ Type of cards provided by DBBL:
DBBL provides NEXUS Silver OD card (credit); NEXUS Gold OD card (credit), NEXUS VISA credit card.
▪ Cards in hand of cardholders:
At present there are over 150,000 + cards in the hands of the customers.
▪ the percentage of market share in credit card market:
At the moment, the total card market size (approx.) in Bangladesh is 7 lac. Among these, DBBL is having around 20% market share with 150,000+ DBBL NEXUS cards.
▪ Exceptional Facilities Provided by DBBL:
With a view to extending its online banking services to every corner of the country, the bank install 200 more ATMs within this year, making the total number of ATM at 350. It also installs a total 3000 POS Terminals in this year to make the bank’s services more available & convenient for the customers.
▪ Provision to have a credit card:
The applicant has to be an accountholder of Dutch-Bangla Bank Limited. They should belong to any of the following categories:
• Employees of different corporate bodies that have salary account with DBBL.
• Government Service Holders.
• Valued clients of DBBL.
• Employees of Banks, Financial Institutions, Multinational Companies, Telecommunication Companies, University / College/ School/ Autonomous Companies, Pharmaceuticals Companies, Professionals, Defense, CIP, VIP;.
• DBBL borrowers, SB or CD account holders.
▪ The Fees & Charges system for Card Products:
With this card, the cardholders can avail an OD facility from Tk.10, 000/- (ten thousand) up to Tk.2, 000,000/-(twenty lac) depending on credit worthiness. Cardholders have to pay late payment charges (specific percentage) or other charges if fails to maintain the requirements.
▪ Employment of Credit Card Company:
DBBL use both Master and Visa card to provide their Credit Card.
▪ Future Plan:
• The bank has adopted a focused marketing strategy with its goal to achieve a card base of 1 million by 2010.
• In the near future the bank is going to issue MasterCard International & VISA International’s credit cards. Therefore, the bank shall be offering a complete card product range starting from proprietary debit/credit, OD cards to international branded debit/credit cards.
• The bank is going to get the principal membership of MasterCard International for issuing and acquiring (in POS Terminals) of credit cards.
1.2.3 EBL bank
▪ Started providing credit card:
EBL commence its card operation in 2006.
▪ Type of cards provided by EBL:
The bank provided VISA card of four categories- Local Classic, Local Gold, Dual Classic, and Dual Gold that depends on the range of credit limit.
▪ Cards are in the hand of cardholders:
It has already crossed the mark of issuing 35,000 credit cards within a couple of years.
▪ The percentage of market share in credit card market:
As the total card market size (approx.) in Bangladesh is 7 lac. Among these, EBL is having around 5 % market share with 35,000+ cards.
▪ Exceptional Facilities Provided by EBL:
When a person become a member of EBL SIMPLE Card Services family, he/she become a part of an exclusive club – entitled to first class financial advice, priority treatment and a growing range of courtesy services. Some unique services that only provided by this bank are as follows:
• Balance Transfer: They introduced Balance Transfer for the first time in Bangladesh. Here the card holder has the option to transfer current outstanding balance of other banks at a much cheaper rate to the EBL Credit Card. Also, EBL is offering to switch balances at 8% less interest then other banks.
• Card Cheque: Through EBL Credit Card, one can enjoy a full-fledged cheque book facility through making payment (account payee only) to any person or organization. EBL is offering the “FIRST CHEQUEBOOK FREE”. There is a charge for subsequent Cheque books.
▪ Provision to have a credit card:
To avail EBL Credit Card services, one needs to pay the Issuance/Joining/Subscription/ Annual Fee only once. After that there is no annual fee for them as long as they transact at least 18 times in a whole year.
▪ The Fees & Charges system for Card Products:
Table:- 3 Fees & Charges excluding VAT, all in BDT.
| ITEMS | LOCAL CLASSIC | LOCAL GOLD | DUAL CLASSIC | DUAL GOLD |
| Card Issuance Fee | 1,300 | 2,500 | 1,300 | 2,500 |
| Finance Charge on all Transactions (per month) | 2.50% | 2.50% | 2.50% | 2.50% |
| Balance Transfer Interest (per month) | 1.83% | 1.83% | 1.83% | 1.83% |
| Interest on Excess of Limit Amount (per month) | 2.92% | 2.92% | 2.92% | 2.92% |
| Certificate Fee | 200 | 200 | 200 | 200 |
▪ Employment of Credit Card Company:
EBL use Visa card to provide their Credit Card. they named their credit card as Simple card.
▪ Future Plan:
Their future plan is to Introduce “EBL SIMPLE Credit Cards” as a complete Credit Card with every benefit possible, and still offering something extra to the cardholders.
1.2.4 Lanka Bangla credit card
▪ Started providing credit card:
By launching the Vanik Classic and Gold Credit Cards in 1998 they became the only issuer in the market to have introduced a private label card accepted at a merchant network of around 3000 establishments across Dhaka, Chittagong and Cox’s Bazaar.
▪ Type of cards provided by Lanka Bangla:
The bank has successfully launched the Lanka Bangla MasterCard Gold and Classic Cards.
▪ Cards in hand of cardholders:
It has already crossed the mark of issuing 6,000 credit cards within a couple of years.
▪ The percentage of market share in credit card market:
As the total card market size (approx.) in Bangladesh is 7 lac. Among these, Lanka Bangla is having around 0.85 % market share with 6000+ cards.
▪ Exceptional Facilities Provided by Lanka Bangla:
• 5% discount on Master Health Check at Apollo Hospital
• Auto enrolment in “Infinity” program of Agora
• 50% discount on Price Club Wholesale Membership Fee
• “Have Wings, Will Fly” – 6 months Interest Free Installment plan at Wings Classic Travels
• 10% discount at Athena Furniture and Home Décor
▪ Provision to have a credit card:
The minimum income requirement for Silver is Tk. 10,000 per month and for Gold is Tk. 55,000 per month. The income of the applicant along with other financial data is the preliminary consideration in deciding the limit of credit.
▪ The Fees & Charges system for Card Products:
When a cardholder receives his monthly statement, he can either choose to pay in full or just the minimum due amount shown on the statement. For the Gold Card Taka 3,000 is to be paid as annual fee while Taka 1,500 for the Classic. Interest per month is 2.5% on carried forward amount for both the cards. No interest is charged if he pays in full within the payment due date (interest free credit period is maximum 45 days). There are many sorts of service charges like – annual fee, additional fee, replacement fee, late payment fee, excess limit penalty, return cheque fee etc. If a cardholder accumulates 20,000 Prime Bank Bonus Points for his Gold Card or 10,000 Bonus Points for his Silver Card in a year then he will enjoy card facilities without fee ($ 1 purchase equivalent to 1 Bonus Point).
▪ Employment of Credit Card Company:
In 2005 they have obtained license from MasterCard International to introduce its globally recognized card products.
▪ Future Plan:
Now Lanka Bangla providing credit cards by covering only Dhaka city and it has a plan to spread its services to different parts of Bangladesh.
Findings of Other Financial Institutions:
There are some other financial institutions which are not the major player in Credit Card Market in Bangladesh, but still they have a significant role in Credit Card Market in Bangladesh. They are described as follows:
1.2.5 National Bank
National Bank burst into the world of credit card in October 1997.There are different types of cards provided by this Bank like Gold International, Gold Local, Silver International, Silver Local. The special facilities provided by National Bank is like-
• For example, a high-ranking government official may achieve a Gold Card though he does not fulfill the condition of income.
• It is now dealing with more than 6,000 clients. As the National Bank believe that “The cards are for a section of people, not for the commoners”, so, the issuance of credit cards is on the rise.
1.2.6 Prime Bank
Prime Bank opened its business of credit card in November 1999. The bank has Gold International and Gold Local, and Silver International and Silver Local. Prime Bank inserts the client’s photograph on the credit card. The bank has listed about 3,500 members for their cards. The special facilities provided by Prime Bank is like-
• When a cardholder receives his monthly statement, he can either choose to pay in full or just the minimum due amount shown on the statement. No interest is charged if he pays in full within the payment due date.
• If a cardholder accumulates 20,000 Prime Bank Bonus Points for his Gold Card or 10,000 Bonus Points for his Silver Card in a year then he will enjoy card facilities without fee ($ 1 purchase equivalent to 1 Bonus Point).
• If a cardholder accumulates 10,000 Prime Bank Bonus points for Gold Card or 8,000 Bonus Points for Silver Card in a year then he will enjoy Card facilities without fee. (Tk. 50- purchase equivalent to 1 Bonus point).
The highest Prime Bank Bonus Point Holder can enjoy free air ticket of Dhaka-Bangkok-Dhaka (Business Class).
1.2.7 Grameen Bank
The Grameen Bank is set to introduce its own version of credit cards for rural people. The Bank has taken up initiatives to bring the country’s rural masses, initially its members, under its IT network to facilitate their daily transactions and other business activities smoothly and bring about a qualitative change in their lifestyle through its ‘smart card’ project. The ‘smart card’ will provide facilities like Banking, utility and insurance to members of the Bank’s micro-credit program. The users use ‘smart card’ to facilitate their business and other needs. At every POS terminal, there is a smart card that preserves data of all off-line transactions. The card is expected to be introduced this year in greater Dhaka zone of Grameen network. Later, different villages across the country will be brought under the network of the smart card services.
1.2.8 HSBC bank
HSBC’s co-branded credit card with Prime Bank gives the freedom to pay for goods and services without the hassle of carrying cash. The card is accepted anywhere in Bangladesh displaying the MasterCard logo. One can enjoy between 20 to 50 days of interest free credit from the date of each transaction. Also, after receiving your monthly statement, one can either choose to pay full or a minimum of 8% of the current balance shown in the statement or BDT 500 whichever is higher; Interest is 2.5% per month and credit limit range from BDT 50, 000 to BDT 200, 000.
1.2.9 Ready Cash Card of Janata Bank
The Ready Cash Card (debit card) was introduced in Bangladesh by Janata Bank in October 1999. Its operation has not expanded well yet. The Ready Cash cards will be used as an alternate to cash transaction. The bills of telephone, electricity, WASA will be brought under the card payment system. People can pay the gas bill by Ready Cash Card. The water and sewerage bills in the capital and Narayanganj can now be paid by ‘Ready Cash’ card through one stop service from July 1, 2001. An agreement to this effect was signed between WASA and American International (Bangladesh) Limited on May 16, 2001. The cardholders will be able to pay the bills, including the utility bills easily and without any risk. Arrangements will be made soon for payment of telephone and electricity bills by using the Ready Cash cards. The Mercantile Bank and Dhaka Bank have introduced Ready Cash Card in limited scope.
1.2.10 Bank Asia Credit Card
ACCEPTANCE:
Bank Asia Credit Card is accepted more than 3,500 merchant outlets around the country. Our wide range of merchants include hotels, restaurants, airlines, & travel agents, shopping malls and departmental stores, hospitals & diagnostic centers, jewelers, electronics & computer shops, leather goods mobiles & internet service providers, petrol pumps and many more. This number is increasing everyday to cater to your needs. Last of all wherever you will see “MasterCard” logo you will be able to use your card.
CREDIT FACILITY:
Bank Asia Credit Card offers you free credit facility up-to 45 days & minimum 15 days without any interest; you can also pay 8.33% of your billing amount or current dues every month and thus have the flexibility to plan your payments.
CASH ADVANCE:
Bank Asia MasterCard gives you facility to draw cash up to 50% of the credit limit against your local MasterCard and you can enjoy this facility by using any ATM’s across the country which shows ‘’MasterCard” logo Beside this you can also withdraw cash from any of our branch.
1.2.11 BRAC Bank Credit Card Loan
When you have a credit card sky is your limit with BRAC Bank. Now, a credit card is all you need to get a loan from BRAC Bank. Loan can be used for any reason from buying consumer goods, automobile to vacation expenses. Just decide what to do and start planning for it.
Eligibility
• A one-year-old local credit card with any institution
• A minimum of 12 months of satisfactory credit card relationship with any credit card issuer in Bangladesh
Additional Salaried:
• Letter of introduction pay slip
• Latest 3 months Bank statement
Business Person
• TIN Proof of 5 years in business Permanent address in the area where you operate
• Company and personal Bank statement 6 months (latest)
Maximum Amount
• 5 times of credit card limit with a maximum of TK 1,000,000
Features
• Any Purpose Loan Status of the facility in just 72 hours
• Flexible repayable plan in equal monthly installment
What do you need to apply?
• Copy of credit card Last 3 month’s credit card statements Proof of 1 year of credit card history
• Personal guarantee of immediate family member
1.2.12 Dhaka bank
Credit Card Services
Reasons for Preferring Dhaka Bank VISA Credit Card
• Substitute of Cash- Zero Cash Handling ensures Security
• Wide Range of Local & International Products (Classic, Gold)
• Hassle Free Documentation
• No Joining or Processing Fee
• Flexible Credit Limit Enhancement Based on Usage & Regular Payment
• Flexible Payment through Cash, Cheque or Dhaka Bank account debit
• Auto Debit Payment facilities for DBL account holders
• Auto Renewal of card before expiry date
• Competitive Fees & Charges
• Supplementary Cards for dear ones
• Separate Limits for Supplementary Cards
• Cash Advance facility up to 50% of Credit Limit
• Dedicated Sales Team and Customer Service Desk at your service
• International Card against RFCD account & ERQ
• International Card- Accepted Worldwide for Purchase & Cash Withdrawals
What you can do with your Dhaka Bank VISA Credit Card
Everything you would expect from a credit card. You can use it at all the merchant locations that display the VISA Card sticker. That’s not all. You can also use it at all the locations that display the Card sticker. And that’s a whopping 7,000 merchants and more than 400 ATMs.
Free Supplementary Card
Your dear one needs a card too for everyday use. That is why we offer cards to your dear ones absolutely FREE. Your spouse can enjoy the same facilities as you do. So, you won’t have to worry about whether either of you are carrying enough cash.
Convenience
Unlike other cards, all branches of Dhaka Bank Ltd. can accept your bill payments and handle your card service requests. You may open an account as well with any of these branches to conduct all your banking and card service requirements under one roof.
Flexible Repayment Options
Dhaka Bank VISA Credit Card offers you credit facility absolutely FREE up to a maximum of 45 days. You get 15 days time from the date of statement to repay your dues. You can pay in full within 15 days (and save money; no interest accrued, no payout) or in part. The minimum amount required to pay is 1/20th of the total amount or Tk. 500 (whichever is higher). The revolving credit line of your card allows you to select payment terms to suit your other financial commitments.
Quick Replacement
If your card has been lost or stolen, don’t worry. A replacement will be sent to you within a couple of days. But remember to report the loss as soon as you have detected it. Once reported, there will be no liability on fraudulent charges.
Great Offers
Special promotions, discount offers and prizes are announced for your card usages. They are exciting and exclusively for you. So watch for it!
Lowest interest rate in the country (2% per month)
Dual Currency Visa Credit Card
One supplementary card free of cost for lifetime (Spouse only)
Treasure point facilities including foreign part
Shortest process for Dual Currency card, only 24 hours
Roaming Mobile Phone bill payment facilities
Use of additional 142 ATM’s Booth and 600 POS of Dutch-Bangla Bank
1.2.13 NCC Bank Visa Credit Card
NCC Bank has launched its Visa Credit Card Service on August 22, 2005 and we are offering three types of cards which are Visa Classic, Visa Gold (Local) and Visa Dual Currency Card (Globally and locally). Since then were able to reach 5000 cards, both corporate and general.
Why NCC Bank Credit Card?
Our Commitments
We promise the followings in our services:
Wide Range of Acceptance
NCC bank Visa Credit Card is accepted at over 5,000 merchant outlets around the country. Our wide range of merchants include Hotels, Restaurants, Airline and Travel Agents, Shopping Malls, Hospitals, Jewellery Shops, Mobile Phone and Internet Service Providers, Petrol Pumps and many more! Now NCC Bank Visa Credit Cards can also be used at all 142 ATM’s Booth and 600 POS (Point of Sale) of Dutch-Bangla Bank.
Instant Cash Advance
You do not need to carry cash any more if you have a NCC Bank Credit Card. You can withdraw cash up to 50% of your credit limit from any ATM across the country that shows Visa logo.
Credit Facilities
NCC Bank Visa Credit Card offers you free Credit facility up to 45 days and minimum of 15 days without any interest (Purchase only).
Supplementary Card
NCC bank Visa Credit Card holder can also enjoy spouse Credit Card free of cost for lifetime and issue more Supplementary card.
Reward Programs
As a NCC Bank Visa Credit Card holder, you will accumulate Treasure points for every purchase made by using Visa Credit Card. For every Tk. 50 and USD 1 spent on your Credit Card, you will earn 1 and 1.5 Treasure Point accordingly and be closer to redeeming the reward of your choice.
Flexible Payment Option
With the NCC Bank Visa Credit Card, you have the convenience to pay as little as 5% of your outstanding (or Tk. 500, whichever is higher) on the Card account every month, thus having the power and flexibility to plan your payments.
Auto-Debit Payment Facility
With the NCC bank Credit Card, you no longer have to stand in long queues for paying your monthly bill. You can pay your monthly bill through NCC Bank Account by instruction Auto-Debit.
Corporate Visa Credit Card
Corporate is characteristic of individuals acting together; “a joint identity”; “the collective mind”; “the corporate good”. The new dimension of NCC Bank Visa Credit Card is Corporate Credit Card which has already started to benefit the Corporate Houses.
Fast and Accurate Services
Effective Communication
Attractive Pricing (Annual fee 50% discount on card fee)
Strong Communication
Smiling faces of the Bankers
Good Ambience in the Bank
Objective of Corporate Customers
Table: – 4 NCC bank Corporate Offer
| Particular | Small (10-100) | Medium (101-500) | Large (500 above) |
| Card Fee | 50% | 50% | (Negotiable) |
| Rate of Interest | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Cash Withdrawal | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Purchase | 2% | 2% | 2% |
| Maximum period of interest free | 45 Days | 45 Days | 50 Days |
| Replacement Card Fee | Charges | Charges | Free |
| Late Payment Charge | Charges | Charges | Free |
| Excess Over Limit Charges | Charges | Charges | Free |
Balance Transfer Facilities
If anyone holds other Bank Credit Card, then NCC Bank will issue a credit card with equivalent limit and will issue a pay order by debiting card A/C from balance transfer option for the equivalent amount of total outstanding in order to full settlement and cancellation of other Bank A/C.
1.2.14 Southeast Bank VISA Credit Cards
Financial Freedom
at Your Fingertips be a member of the Southeast Bank (SEBL) VISA Cardholder family and enter a world free from everyday financial worries.
Dual Card : We would like to introduce our dual card. SEBL VISA dual card offers you the facility to access both your local and international spending limit through a single plastic. Therefore, there is no need to carry separate local and international credit cards.
Acceptance : An International / Dual card is accepted at millions of establishments across the world and a Local/ Dual VISA Card is accepted at 10,000 outlets across the country including shops, restaurants, 5 star hotels, hospitals, departmental stores etc. Whenever you see a VISA Logo at any merchant shop window or payment counter you will be able to use your card.
Credit Facility: Southeast Bank VISA Credit Card offers you free credit facility up to 50 days without any interest; you also have the option of paying a minimum of 5% of your billing amount every month and thus have the flexibility to plan your repayment.
Cash Advance: Southeast Bank Visa Credit Card gives you the facility to draw cash up to 50% of the credit limit against your local VISA Card. You can withdraw cash from all our branches and ATMs having VISA Logo Besides, Cash Facilities can also be taken from any of our branches across the country.
Supplementary Cards: You may apply for Supplementary Cards. While each supplementary member will have his / her own independent usage, the expenses will be charged to your (Principal Cardholder’s) account.
SMS Push Pull Service: Through SMS Push Pull Service you can enquire your card account any time.
Card Cheque: You can draw cheque up to the available balance in your card account
In Case Of Lost Card : If your card is lost or stolen you just need to call our Customer Service Center at Card Division which is open 24 hours a day 365 days a year and will get a replacement card on submission of written application and payment of prescribed fees.
Table: – 5 Fees and Charges for Southeast Bank VISA Credit Cards.
| Gold Card | Classic Card | |||
| I) | Principal Card Annual/Renewal Fee: | |||
| Local | Tk. | 1200.00 | 600.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 60.00 | 30.00 | |
| ii) | Supplementary Card Annual Fee/ Renewal Fee : | |||
| Local | Tk. | Free | Free | |
| iii) | Replacement Card Fee : | |||
| Local | Tk. | 300.00 | 300.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 10.00 | 10.00 | |
| iv) | Late Payment Fee : | |||
| Local | Tk. | 350.00 | 200.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 10.00 | 10.00 | |
| v) | Return Cheque Fee : | |||
| Local | Tk. | 350.00 | 250.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 10.00 | 10.00 | |
| vi) | Statement Retrieval Fee: | |||
| Local | Tk. | 50.00 | 50.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 5.00 | 5.00 | |
| vii) | Charge Slip Retrieval Fee : | |||
| Local | Tk. | 250.00 | 200.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 10.00 | 10.00 | |
| viii) | Outstation Cheque Collection Fee : | |||
| Local | Tk. | 100.00 | 100.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 15.00 | 15.00 | |
| ix) | Personal Identification Number (PIN) Re-issuance Fee : | |||
| Local | Tk. | 500.00 | 500.00 | |
| International/dual | USD. | 10.00 | 10.00 | |
| x) | Excess Limit Charge : | |||
| Local | Tk. | Nil | Nil | |
| International/dual | USD. | Nil | Nil | |
Repayment:
01 A monthly Card Account Statement is issued to you if there is any balance outstanding in your card account.
02 If you repay the entire amount within the payment due date as shown on your monthly Card Account Statement, you need not pay any interest and thus you have the option of enjoying a free credit facility from 20 to 50 days depending on the date of posting of your transaction to your Card Account Statement. However, this condition is not applicable for cash withdrawal.
03 If you repay the Minimum Payment Amount as shown on your Card Account Statement within the payment due date then you need not pay any late payment fee.
Minimum Payment Amount is calculated as under:
01 When the current balance in the statement is less than or equal to your approved credit limit, the minimum repayment for the current month is:
a) For International Card: 5% of the current balance or USD 25 whichever is higher. If your current balance is less than USD 25, it must be paid in full.
b) For Local Card: 5% of the current balance or Tk. 500.00 whichever is higher. If your current balance is less than Tk.500.00, it must be paid in full.
02 When the current balance in the Card Account Statement is more than the credit limit, the minimum payment is: 5% of the credit limit plus the amount in excess of credit limit.
03 Any overdue amount (i.e. minimum payment amount carried forward from the previous statement) must be paid immediately. Thus the total minimum payment amount is: the minimum payment amount of the current Card Account Statement balance plus the minimum overdue amount from the previous statement.
Interest:
01 Any amount outstanding after the Payment Due Date will attract an interest @2.50% per month calculated on a daily basis from the date the transaction until the amount is paid in full.
02 In case of cash advance, the interest @ 2.5% per month will be charged from the date the transaction until cash advance transaction is paid in full. Cash Advance Fee @2% or Tk. 100.00 whichever is higher for local card or @ 2% or USD. 3 whichever is higher for International Card will be charged on the cash drawn amount.
The above fees and charges are subject to change by the Bank at any time at its discretion. Auto Debit facility for Grameen Phone Post Paid Subscribers:
Southeast Bank VISA Credit cardholders can settle their Grameen phone post paid bills giving Auto Debit instruction to Southeast Bank Card Division.
2.1.0 Introduction to the research:
The concept of using a card for purchases was described in 1887 by Edward Bellamy in his utopian novel Looking Backward. Bellamy used the term credit card eleven times in this novel.
The modern credit card was the successor of a variety of merchant credit schemes. It was first used in the 1920s, in the United States, specifically to sell fuel to a growing number of automobile owners. In 1938 several companies started to accept each other’s cards. Western Union had begun issuing charge cards to its frequent customers in 1921. Some charge cards were printed on paper card stock, but were easily counterfeited.
The concept of customers paying different merchants using the same card was invented in 1950 by Ralph Schneider and Frank X. McNamara, founders of Diners Club, to consolidate multiple cards. The Diners Club, which was created partially through a merger with Dine and Sign, produced the first “general purpose” charge card, and required the entire bill to be paid with each statement. That was followed by Carte Blanche and in 1958 by American Express which created a worldwide credit card network.
Bank of America created the Bank America in 1958, a product which, with its overseas affiliates, eventually evolved into the Visa system. MasterCard came to being in 1966 when a group of credit-issuing banks established Master Charge; it received a significant boost when Citibank merged its proprietary Everything Card, launched in 1967, into Master Charge in 1969. The fractured nature of the U.S. banking system meant that credit cards became an effective way for those who were traveling around the country to move their credit to places where they could not directly use their banking facilities. In 1966 Barclaycard in the UK launched the first credit card outside of the U.S.
In contrast, although having reached very high adoption levels in the US, Canada and the UK, it is importance to note that many cultures were much more cash-oriented in the latter half of the twentieth century, or had developed alternative forms of cash-less payments, such as Carte bleue or the Euro card (Germany, France, Switzerland, and others). In these places, the take-up of credit cards was initially much slower. It took until the 1990s to reach anything like the percentage market-penetration levels achieved in the US, Canada, or the UK. In many countries acceptance still remains poor as the use of a credit card system depends on the banking system being perceived as reliable.
The design of the credit card itself has become a major selling point in recent years. The value of the card to the issuer is often related to the customer’s usage of the card, or to the customer’s financial worth. This has led to the rise of Co-Brand and Affinity cards – where the cards design is related to the “affinity” (a university, for example) leading to higher card usage. In most cases a percentage of the value of the card is returned to the affinity group.
I have selected the topic because it adds a new interval to our people. And during my internship I have spent the maximum time in the card division. So it is easier for me to collect data and information about the aforementioned topic. And I also feel interested to deals with this topic. These are the reasons to select this topic.
2.1.1 Scope of the research
The report is based on the selection criteria of credit cards of MBA students in Dhaka city. This report mainly focuses how they select credit card and in which areas they prefer to select a credit card. The substance presented in this study may not be applicable anywhere outside the university.
]
2.1.2 Objective:
Broad objective:
The main objective of my research work is to identify the significant credit card group based on the age, income level, professions, and gender, according to the credit card limit & uses and in which purpose credit card holders are using credit cards.
Specific objectives
My specific objectives are given below:
• Identify the Income level of credit card users.
• Identify the main reason of using credit card.
• Find out the main benefit of using credit card.
• Find out the present position of credit card service.
• Which professionals is the highest user of credit card?
2.1.3 Data and Methodology of the research work
01 Study Design
The report was fully investigative in nature. Data have been collected from both primary and secondary sources.
02 Data Collection
This study is mainly based on primary data. In addition to these other necessary information have been collected from the daily news papers, relevant journals, Bangladesh bank, Ministry of Finance and Planning and publications of other relevant institutions have also been taken into consideration and also the various bank web site.
A survey of consumer perceptions on credit card selection was conducted in April, 2009, and the data collected via a random sample of 120 cardholders from the university in Dhaka city. Questionnaires were distributed to these individuals who then completed them on site.
In addition to asking the questions used to identify the respondents’ credit cards and demographic profiles, the main part of the questionnaire sought to identify the primary reasons for selecting a particular credit card over other cards. 3 questions were anchored on a Likert-type scale ranging from (1) highly unimportance to (5) highly importance. Through the review of the literature, and from our understanding of the credit card market in Bangladesh, five factors were identified as potentially “importance” reasons for credit card selection in Bangladesh. They were economic reasons, reputation of the card, convenience perceived in using the card, protection offered in case of loss, and promotional activities.
Primary sources of data:
• Face to face conversation with the credit card users.
• Conversation with the bank credit card sales officers.
• Different’ manuals of Different Bank.
Secondary sources of data:
• Unpublished data.
• Different text books.
• Various bank web sites.
• Journals of different banks
• Brochures of banks
• Data from Bangladesh Institute of Bank Management (BIBM)
Methodology includes direct observation, face-to-face discussion with employees and customer of credit card. In preparing this report both primary and secondary sources of information have been used. The study requires a systematic procedure from selection of the topic to final report preparation. To perform the study the data sources are to be identified and collected, they are to be classified, analyzed, interpreted and presented in a systematic manner and key points are to be found out. The over all process of methodology is given in the following page that has been followed in the study.
03 Selection of the topic
The topic of the study was assigned by our supervisor. Before assigning the topic it was discussed with me so that a well organized internship report can be prepared.
04 Identifying data sources
Essential data sources both primary and secondary are identified which will be needed to complete and work out the study. To meet up the need of data primary data are used and study also requires interviewing the official and staffs were necessary. The report also required secondary data.
05 Analysis Techniques:
With regard to the data analysis, soft wares such as MS Excel, SPSS were used which was really supportive for me. In order to make data informative and draw inferences, both descriptive statistics (bar diagram) and inferential statistics like factor analysis were used extensively.
2.1.4 Limitations of the Report
Limitations of the report will be as follows:
Lack of comprehension of the respondents was the major problem that may created many confusions regarding verification of conceptual question.
Limitation of time was one of the most importance factors that shortened the present study. Due to time limitation many aspects could not discussed in the present study. Due to time constraints, the sample size had to be restricted to120 only.
Confidentiality of data was another importance barrier that was faced during the conduct of this study. Every organization has their own secrecy that in not revealed to others. While collecting data on Banks, personnel did not disclose enough information for the sake of confidentiality of the organization.
Rush hours and business was another reason that acts as an obstacle while gathering data.
The findings of the survey are based on customers’ response of credit card user in Dhaka City MBA students only. The results may not reflect the same for other credit card user outside Dhaka.
2.2.0 Findings and analysis:
Below presents the finding of a survey of Credit card selection criteria: A study of MBA students in Dhaka city. In the study 7 question are general for both credit card user and non user. Another 14 question for credit card user and 6 questions for credit card non user. This all 27 questions used to identifying the real selection criteria of credit card user and define customer’s satisfaction of credit card.
2.2.1 Questionnaire factor analysis & findings
Promotion
Being the fourth in terms of relative importance (62.5%), the promotional factor was determined by two variables: “special discounts in selected outlets”, and “loyalty and rewards program (FFP)”. The “loyalty and rewards program(FFP)” was found to be the most importance variable with a total mean score of 3.2143, whereas “road show with instant application approval/gift promotion” was deemed the least importance.
Reputation
Reputation (62.5% in importance) represents the symbolic aspect of credit card usage. It was interpreted as indication of prestige and was determined by only two variables, “status symbol” and “brand name”. “Brand name” was seen to be the more importance variable of the two, with a total mean score of 3.9464, followed by “status symbol”, with a total mean score of 3.8571. “Status symbol” was seen as an unimportance variable, as respondents do not consider the ownership of credit cards a form of status symbol. In fact, when respondents were asked whether they agree with the statement “Status symbol is an importance factor to look for when applying for a credit card”, their responses were mostly “highly unimportance”.
Flexibility
Interpreted as flexibility of use in Bangladesh, this factor was ranked third (53.6 percent) in importance by Bangladeshis cardholders. It was represented by one variable: “availability of supplementary cards”. With a total mean score of 3.6785, followed by “the availability of supplementary cards”.
Economics
MBA students in Dhaka city cardholders ranked Economics as the second importance factor (46.43%) in determining credit card selection. It was identified by three variables: “higher credit limit”, “level of cash advance”, “low interest rates”. ”Level of cash advance” and “credit limit” were found to be the top two most desired variables, with a total mean score of 3.5357and 3.8928 respectively.
At the time of the writing, most credit card companies and card-issuing banks in Bangladesh charged an annual interest rate of more than or equal 24%, In addition, most of them charged an annual fee for their credit cards, again with the only exceptions being.
The level of cash advance made available by the credit card companies and card-issuing banks in Singapore ranged from a conservative Standard Charted Bank even offered a 50% of credit limit for the first 6 months.
Convenience/Protection
The combination of convenience and protection of the credit card was found to be the importance factor (27.14%) in determining credit card selection of MBA students in Dhaka city. It was determined by five variables: “wide acceptance in Bangladesh”, “wide acceptance overseas”, “acceptance in most modern establishments”, “protection when the card is lost or stolen”, “provision of insurance when traveling”, and. Among these five, the “protection when the card is lost or stolen” and “wide acceptance in Bangladesh” was found to be the top two most desired variables.
What age group do you fall in (user and non user)?
Table:-6 Age group of the respondent in percentage
| Age group | Figure in %both user | Figure in % user | Figure in % non user |
| Below 30 | 53.8% | 35.7% | 63.5% |
| 30-35 | 20% | 42.9% | 5.8% |
| 35-40 | 11.2% | 10.7% | 13.5% |
| 40-45 | 13.8% | 7.1% | 17.3% |
| 45-50 | 1.2% | 3.6% | 0% |
| Above 50 | 0% | 0% | 0% |
FIGURE-1 Age group of the respondent (1st user and non user both, 2nd only user, 3rd non user)
53.8% respondent are under the age of 30 of and this age group is higher then others,30-35 age are 20%,35-40 age are 11.2%,40-45 are 13.8%, 45-50 age are 1.2% and above 50 are 0% respondent, maximum respondent of MBA students in Dhaka city are under the age group bellow 30.
42.9% user respondent are age of 30-35 of and this age group is higher then others, under age of 30 are 35.7%, 35-40 age are 10.7%,40-45 are 3.6%, 45-50 age are 0% and above 50 are 0% user respondent, maximum user respondent of MBA students in Dhaka city are under the age group 30-35.
65.3% non user respondent are under the age of 30 of and this age group is higher then others,30-35 age are 5.3%,35-40 age are 13.5%,40-45 are 17.3%, 45-50 age are 0% and above 50 are 0% non user respondent.
Which profession do respondents fall in?
Table:-7 Profession of the respondent in percentage
| Profession | Figure in %both user | Figure in %user | Figure in %non user |
| Business | 11.2% | 25% | 3.8% |
| Private service | 60.0% | 71.4% | 51.9% |
| Public service | 12.5% | 3.6% | 17.3 |
| Retried person | 0% | 0% | 0% |
| Others | 16.2% | 0% | 26.9% |
FIGURE-2 Profession of the respondent (1st user and non user both, 2nd only user, 3rd non user)
The occupations of 60.0% user and non user respondent are private service, 12.5% are public service, 16.25% are others (students), and 11.2% are business man. But there are no retried people.
The occupations of 71.5% user respondent are private service, 3.6% are public service, 0% is others (students), and 25% are business man. But there are no retried people.
The occupations of 51.9% non user respondent are private service, 17.3 are public service, 26.9% are others (students), and 3.8% are business man. But there are no retried people.
Which income group do you fall in?
Table:-8 Income level of respondent in percentage.
| Income level per month | Figure in %both user | Figurer in %user | Figure in %non user |
| Less than 30000 taka | 60% | 32.1% | 75% |
| 30000-50000 taka | 26.2% | 39.3% | 19.2% |
| 5000-70000 taka | 6.2% | 17.9% | 0% |
| 70000-90000 taka | 6.2% | 7.1% | 0% |
| 90000-110000 taka | 0% | 0% | 5.8% |
| More than 110000 taka | 6.2% | 3.6% | 0% |
FIGURE-3 Income level of respondent in (1st user and non user both, 2nd only user, 3rd non user)
Below 30000 taka income per month is 60% user and non user respondent, 30000-50000 are the 26.2% respondent,50000-70000 6.2% of the respondent ,70000-90000 are the 6.2%,,90000-110000 are the 0% of the respondent and above 110000 are 1.2%
Below 30000 taka income per month is 32.1% user respondent, 30000-50000 are the 39.3% respondent,50000-70000 17.9% of the respondent ,70000-90000 are the 7.1%,,90000-110000 are the 0% of the respondent and above 110000 are 3.6%
Below 30000 taka income per month is 75% non user respondent, 30000-50000 are the 19.2% respondent,50000-70000 0% of the respondent ,70000-90000 are the 0%,,90000-110000 are the 5.8% of the respondent and above 110000 are 0%.
Marital Status of the respondent:
Table: – 9 Respondent Marital Status in percentage.
| Marital Status | Figure in %both user | Figurer in %user | Figure in %non user |
| Married | 56.25% | 75% | 46.15% |
| Single | 42.5% | 21.4% | 53.85% |
| Divorced | 1.20% | 3.6% | 0% |
| Others | 0% | 0% | 0% |
Figure:-4 Marital status of the respondent (1st user and non user both, 2nd only user, 3rd non user)
56.25% of my respondent are married, 42.5% respondent are single, and only 1.25% are divorced. There are no other categories.
75% of my respondent are married, 21.4% respondent are single, and only 3.6% are divorced. There are no other categories.
46.15% of my respondent are married, 53.85% respondent are single, and only 0% are divorced. There are no other categories.
Gender of the respondent:-
Table10 Gender group of the respondent in percentage.
| Gender:- | Figure in %both user | Figurer in %user | Figure in %non user |
| Male | 75% | 75% | 75% |
| Female | 25% | 25% | 25% |
Figure:-5 Gender group of the respondent (1st user and non user both, 2nd only user, 3rd non user)
75% of my user and non user respondents are male and rest of 25% are female.
75% of my user and respondents are male and rests of 25% are female.
75% of my non users respondents are male and rest of 25% are female.
Using credit card?
Table:-11 Credit card user and non user in percentage.
| Are you using credit card? | Figure in % |
| YES
| 35% |
| NO
| 65% |
Figure:-6 Credit card user and non user.
65% of MBA respondents are credit card non user and 35% of MBA respondents are credit card user.
Relation between credit card user age and occupation.
Figure: – 7 Relation between credit card user age and occupation.
100% of Public Service holder falls in 25-30 age groups. Private Service holder only 25% fall in 25-30 age group 55% fall in 30-35 years age group. Rest of 20%fall in 35-40 years and 40-45 years age group 15% and 5% respectively. Business man who use credit card 57.1% fall in 25-30 age group 14.3% fall in 30-35 years age group. Rest of 28.6%fall in 40-45 years and 45-50 years age group 14.3% and 14.3% respectively. There is no MBA student’s age of more than 50 use credit card.
Relation between credit card user occupation and monthly income.
Figure:-8 Relation between credit card user occupation and monthly income.
Monthly income level of Business man credit card users are respectively 44.4% less than 30000, 40% 50000-70000, and rest of 50% 70000-90000. 11.1% of credit card user income level less than 30000 is public service holders. 100% of 30000-50000 monthly income groups come from Private Service category.44.4% of less than 30000 monthly income groups come from Private Service category. 60% of 50000-70000 monthly income groups come from Private Service category. 100% of more than 110000 monthly income groups come from Private Service category.
Relation between credit card user age and marital status.
Figure:-9 Relation between credit card user age and marital status.
Single credit card user, 83.3% are below 30 years age and 16.7% are in 30-35 years age group. Married credit card user 23.8% are below 30 years age group, 52.3% are 30-35 years age group, rest 23.8% are from 35-40, 40-45 years age group 14.3% and 9.5% respectively. 100% of divorced group at the 45-50 years age group.
Relation between credit card user monthly income and monthly credit card limit.
Figure:-10 Relation between credit card user monthly income and monthly credit card limit.
Credit limit less than 50000 Out of 100%, 58.3% have monthly income less than 30000,16.7% monthly income 30000-50000 also 16.7% monthly income 70000-90000, and rest of 8.3% have monthly income 70000-90000. Credit limit more than 50000-100000 Out of 100%, 18.2% have monthly income less than 30000, 63.6% monthly income 30000-50000 and rest 18.2% monthly income 70000-90000. Credit limit more than 100000-150000 Out of 100%, 33.3% monthly income 30000-50000 also 33.3% monthly income 70000-90000, and rest of 33.3% have monthly income 70000-90000. Credit limit more than 150000 Out of 100%, 50% monthly income 30000-50000 and rest of 50% has monthly income more than 110000.
Reason of why credit card holders start to using credit card?
Figure: – 11 Reason of why credit card holders start to using credit card?
21.4% of credit card user start to using credit card because of getting the credit facility.14.3% of credit card user start to using credit card because of online shopping.7.1% of credit card user start to using credit card because of reducing the carrying cash risk.28.6% of credit card user start to using credit card because of shopping and substitute for money. Rest 14.4% of credit card user start to using credit card because of credit facility and online shopping, getting extra facility, foreign visit, financial facility equally 3.6%.
• How many credit cards are you using?
Table: – 12 Number of credit cards using by Individual credit card user in percentage.
| Number of credit card | Figure in % |
| One | 67.9% |
| Two | 28.6% |
| Three | 3.6% |
| More than three | 0% |
Figure: – 12 Number of credit cards using by Individual credit card user.
67.9% of MBA credit card user uses only one credit card, 28.6%two credit card, and only 3.6% have three credit card. In here we can see that most of the credit card holders use only one credit card.
Credit limit
Table:-13 Credit limit of credit card user in percentage.
| Credit limit | Figure in % |
| Less than 50000 | 42.9% |
| 50000-100000 | 39.3% |
| 100000-150000 | 10.7% |
| More than 150000 | 7.1% |
Figure: – 13 Credit limit of credit card user.
Out of 100% 42.9% have credit limit of 50000,39.3% have more than 50000-100000 credit limit,10.7% have more than 100000-150000 credit limit, and rest of 7.1 have more than 150000credit limit,
Number of credit card used by family member of each individual credit card holders.
Table: – 14 credit card used by family member in percentage.
| Number | Figure in % |
| One | 37.7% |
| Two | 50% |
| Three | 14.3% |
| More than three | 0% |
Figure: – 14 credit card used by family member
35.7% credit card holders only one family member use credit card,50% credit card holders two family member use credit card, 14.3% credit card holders three family member use credit card.
2.2.3.0 Level of satisfaction at cash back facility.
Table: – 15 Level of satisfaction at cash back facility in percentage.
| Level of satisfaction | Figure in % |
| Very unsatisfied | 7.1% |
| Unsatisfied | 21.4% |
| Moderate | 32.1% |
| Satisfied | 28.6% |
| Very satisfied | 10.7% |
Figure: -20 Level of satisfaction at cash back facility
7.1% of credit card user are very un satisfied 21.4% of credit card user are un satisfied, 32.1% of credit card user are moderate satisfied, 28.6% of credit card user are satisfied, 10.7% of credit card user are very satisfied about cash back facility provided by credit card company.
Level of satisfaction at substitutes for currency facility.
Table: – 16 Level of satisfaction at substitutes for currency facility in percentage.
| Level of satisfaction | Figure in % |
| Very unsatisfied | 0% |
| Unsatisfied | 0% |
| Moderate | 14.3% |
| Satisfied | 39.3% |
| Very satisfied | 46.4% |
Figure: -16 Level of satisfaction at substitutes for currency facility
14.3% of credit card user are moderate satisfied, 39.3% of credit card user are satisfied, 46.4% of credit card user are very satisfied about substitutes for currency facility provided by credit card company.
Levels of satisfaction at Frequent fly program facility.
Table: – 17 Levels of satisfaction at Frequent fly program facility in percentage.
| Level of satisfaction | Figure in % |
| Very unsatisfied | 0% |
| Unsatisfied | 25% |
| Moderate | 28.6% |
| Satisfied | 39.3% |
| Very satisfied | 7.1% |
Figure: -17 Levels of satisfaction at Frequent fly program facility
25% of credit card user are unsatisfied, 28.6% of credit card user are moderate satisfied, 39.3% of credit card user are satisfied, 7.1% of credit card user are very satisfied about Frequent fly program facility provided by credit card company.
Level of satisfaction at protection facility.
Table: – 18 Level of satisfaction at protection facility in percentage.
| Level of satisfaction | Figure in % |
| Very unsatisfied | 3.6% |
| Unsatisfied | 7.1% |
| Moderate | 21.4% |
| Satisfied | 39.3% |
| Very satisfied | 28.6% |
Figure: – 18 Level of satisfaction at protection facility.
3.6% credit card user are very unsatisfied, 7.1% of credit card user are unsatisfied, 21.4% of credit card user are moderate satisfied, 39.3% of credit card user are satisfied, 28.6% of credit card user are very satisfied about protection facility provided by credit card company.
Level of satisfaction at level of cash advance facility.
Table: – 19 Level of satisfaction at level of cash advance facility in percentage
| Level of satisfaction | Figure in % |
| Very unsatisfied | 0% |
| Unsatisfied | 0% |
| Moderate | 28.6% |
| Satisfied | 64.3% |
| Very satisfied | 7.1% |
Figure: – 19 Level of satisfaction at level of cash advance facility
28.6% of credit card user are moderate satisfied, 64.3% of credit card user are satisfied, 7.1% of credit card user are very satisfied about level of cash advance facility provided by credit card company.
Level of satisfaction at availability of supplementary cards facility.
Table: – 20 Level of satisfaction at availability of supplementary cards facility in percentage
| Level of satisfaction | Figure in % |
| Very unsatisfied | 0% |
| Unsatisfied | 0% |
| Moderate | 39.3% |
| Satisfied | 53.6 % |
| Very satisfied | 7.1% |
Figure: – 20 Level of satisfaction at availability of supplementary cards facility
39.3 % of credit card user are moderate satisfied, 53.6% of credit card user are satisfied, 7.1% of credit card user are very satisfied about level of availability of supplementary cards facility provided by credit card company.
Level of satisfaction at insurance provision when traveling facility.
Table: – 21 Level of satisfaction at insurance provision when traveling facility in percentage
| Level of satisfaction | Figure in % |
| Very unsatisfied | 0% |
| Unsatisfied | 0% |
| Moderate | 46.4% |
| Satisfied | 46.4 % |
| Very satisfied | 7.1% |
Figure: – 21 Level of satisfaction at insurance provision when traveling facility
46.4 % of credit card user are moderate satisfied, 46.4% of credit card user are satisfied, 7.1% of credit card user are very satisfied about level of insurance provision when traveling facility provided by credit card company.
2.2.4.0 Respondent opinion about level of importance on interest rate.
Table: -22 level of importance on interest rate in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 10.7% |
| less importance | 10.7% |
| Moderate | 32.1% |
| importance | 17.9 % |
| Very importance | 28.6% |
Figure: – 22 Level of importance on interest rate
10.7% of credit card user respondent are thinking interest rate is very less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 10.7% respondent think interest rate is less importance factor to open a credit card account. 32.1% think its moderate importance, 17.9 % and 28.6% of credit card user think interest rate is importance factor and very importance factor respectively to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on processing time.
Table: – 23 level of importance on processing time in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 0% |
| less importance | 7.1% |
| Moderate | 14.3% |
| importance | 53.6 % |
| Very importance | 25% |
7.1% of credit card user respondent are thinking processing time is less importance factor to open a credit card account, 14.3% think its moderate importance, 53.6 % and 25% of credit card user think processing time is importance factor and very importance factor respectively to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on service of company.
Table: – 24 level of importance on service of company in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 7.1% |
| less importance | 0% |
| Moderate | 7.1% |
| importance | 42.9% |
| Very importance | 42.9% |
7.1% of credit card user respondent are thinking service of company is very less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 7.1% think its moderate importance, 42.9 % and 42.9% of credit card user think service of company is importance factor and very importance factor respectively to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on purchase point service of company.
Table: – 25 level of importance on purchase point service of company in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 0% |
| less importance | 0% |
| Moderate | 10.7% |
| importance | 75% |
| Very importance | 14.3% |
75% of credit card user respondent are thinking purchase point service of company is very importance factor to open a credit card account, another10.7% think its moderate importance, rest 14.3% of credit card user think purchase point service of company is very importance factor to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on credit limit.
Table: – 26 level of importance on credit limit in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 0% |
| less importance | 3.6% |
| Moderate | 21.4% |
| importance | 57.1% |
| Very importance | 17.9% |
17.9% of credit card user respondent are thinking credit limit is very importance factor to open a credit card account, 3.6% of credit card user respondent are thinking processing time is less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 21.4% think its moderate importance, rest 21.4% of credit card user think credit limit of company is importance factor to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on level of cash advance.
Table: – 27 level of importance on level of cash advance in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 0% |
| less importance | 10.7% |
| Moderate | 32.1% |
| importance | 50% |
| Very importance | 7.1% |
7.1% of credit card user respondent are thinking level of cash advance is very importance factor to open a credit card account, 10.7% of credit card user respondent are thinking level of cash advance is less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 32.1% think its moderate importance, rest 50% of credit card user think level of cash advance of company is importance factor to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on wide acceptance in abroad.
Table: – 28 level of importance on wide acceptance in abroad in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 7.1% |
| less importance | 10.7% |
| Moderate | 17.9% |
| importance | 32.1% |
| Very importance | 32.1% |
32.1% of credit card user respondent are thinking wide acceptance in abroad is very importance factor to open a credit card account, 10.7% of credit card user respondent are thinking wide acceptance in abroad is less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 17.9% think its moderate importance, 32.1% of credit card user think wide acceptance in abroad is importance factor to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on wide acceptance in local.
Table: – 29 level of importance on wide acceptance in local in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 0% |
| less importance | 28.6% |
| Moderate | 3.6% |
| importance | 25% |
| Very importance | 42.9% |
Figure: – 29 level of importance on wide acceptance in local
42.9% of credit card user respondent are thinking wide acceptance in local is very importance factor to open a credit card account, 28.6% of credit card user respondent are thinking wide acceptance in local is less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 3.6% think its moderate importance, rest 25% of credit card user think wide acceptance in local is importance factor to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on brand name.
Table: -30 level of importance on brand name in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 0% |
| less importance | 7.1% |
| Moderate | 3.6% |
| importance | 67.9% |
| Very importance | 21.4% |
Figure: – 30 level of importance on brand name
21.4% of credit card user respondent are thinking brand name is very importance factor to open a credit card account, 7.1% of credit card user respondent are thinking brand name is less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 3.6% think its moderate importance, rest 67.9% of credit card user think brand name is importance factor to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about level of importance on status.
Table: -31 level of importance on status in percentage
| Level of importance | Figure in % |
| Very less importance | 0% |
| less importance | 7.1% |
| Moderate | 14.3% |
| importance | 64.3% |
| Very importance | 14.3% |
Figure: – 31 level of importance on status
14.3% of credit card user respondent are thinking status is very importance factor to open a credit card account, 7.1% of credit card user respondent are thinking status is less importance factor to open a credit card account, another 14.3% think its moderate importance, rest 64.3% of credit card user think status is importance factor to open a credit card account.
• Respondent opinion about “service of credit card has increase from very beginning of my use”.
Table: -32 Respondent opinions about trend of service in percentage
| Opinion | Figure in % |
| Increase | 60.7% |
| No change | 28.6% |
| Decrease | 10.7% |
Figure: – 32 Respondent opinion about trend of service
60.7% of total credit card user respondent since from there using the service of credit card increase.10.7% provide the negative opinion about credit card service. They think at the beginning of there use they get better service.28.6% have provide there opinion that the service of credit card has no change over the time.
• Respondent opinion about present service of credit card.
Table: -33 Respondent opinion about present service of credit card in percentage
| Level of measurement | Figure in % |
| Excellent | 7.1% |
| Good | 53.6% |
| Fair | 28.6% |
| Poor | 10.7% |
| Very poor | 0% |
Figure: – 33 Respondent opinion about present service of credit card
53.6% of credit card user respondent are thinking present service of credit card is good, 28.6% of credit card user respondent are thinking present service of credit card is fair, 10.7% of credit card user respondent are thinking present service of credit card is poor, and rest 7.1% think present service of credit card is excellent.
Figure: – 34 Factor of importance
59.6% of non user respondent think the interest rate of credit card is the main factor that may be improve to increase the number of credit card holders.13.5% of non user respondent think the interest rate, bank service, processing time, purchase point service, credit limit, level of cash advance, wide acceptance in abroad and local all factor are need to improve to increase the number of credit card holders.
2.2.5.0 Credit card provider company analysis:
After collecting all the data we are going through an analysis which is described below:
▪ Employment of Credit Card Company:
In Bangladesh, maximum financial institutions are using Master Card as their own credit card, but some of them are using Visa Card. There is another version of card named “Smart Card” which was first introduced by Grameen Bank to help the poor people. This concept gives a new era of Credit Card market in Bangladesh. The Master card holds 62.5% of total market. And Visa and Smart card holds rest 37.5% of credit card market.
Figure: -35 Employment of Credit Card Company
▪ The percentage of market share in credit card market:
According to analysis, Standard Chartered Bank has the highest market share. They hold 50% of total market share of credit card market in Bangladesh. DBBL is the second position they hold 16.7% of total market share of credit card market in Bangladesh and EBL is in third position they hold 13.5% of total market share of credit card market in Bangladesh. And all other bank holds rest 19.8% of total market share of credit card market in Bangladesh. The brief analysis is shown below:
Figure: -36 Market Share of Each Bank in Credit Card Market
▪ Income Requirement:
Though different banks providing different types of cards but these all credit cards can be classified as – “Silver” and “Gold”. To have any of this card, a person need to have a certain amount of income which are analyzed below:
Figure: – 37 Range of Income Needed
▪ Most Focused Area of Each Bank towards Credit Card Market in Bangladesh:
Though every banks basic motto is to “Create Secure and Simple Payment System” through credit card, but according to our analysis, each bank focusing on different area to expand Credit Card Market in Bangladesh like-
• Standard Chartered Bank, DBBL, Vanik, Prime Bank Limited and HSBC Bank – these banks main focus is to create highest market share in Credit card Market in Bangladesh.
• EBL’s main focus is to introduce “EBL SIMPLE Credit Cards” as a complete Credit Card with every possible benefit.
• National Bank main focus is to create better facilities for government officials.
2.3.1.0 Suggestions
From my research I can find out some point which is importance for Credit Card Provider Company. After analyzing the credit card market in Bangladesh, the following issues are suggested:
The first and importance finding is the credit card charged high interest rate than the other conventional credit facility. At that time the conventional bank charge less than 18% per annual month, on the other hand all of the credit card provider company charged more than 24% per annual. That’s why the credit card provider company decreases the annual charge. 85% of non user thinks that interest factor is most importance factor to increase the number of credit card holder.
The age group of below 30 was the highest respondent of my research which is all most 53.8% out of 100%. The below age of 30 MBA credit card user in Dhaka city is also highest than the other age group. On the other hand non user out of 100%, 63.5%comes from the below 30 years age group. That’s why it is easy to see that the credit card provider company needs to think about the age group. Because there are the most potential future customer. To capture the future customer they need to think. And do some promotional program.
The female are almost 50% of our population. But from my finding you can see that only 25% female are using credit card. There is also having some opportunities for credit card Provider Company to capture the female future potential customer.
The private service group was the highest respondent from occupation category of my research which is all most 60% out of 100%. The private service group MBA credit card user in Dhaka city is also highest than the other age group. On the other hand non user out of 100%, 51.9%comes from the private service group. That’s why it is easy to see that the credit card provider company needs to think about the occupation group. Because they are the most potential future customer. To capture the future customer they need to think. And do some promotional program.
The married group was the highest respondent from marital status category of my research which is all most 56.25% out of 100%. The married MBA user of credit card in Dhaka city is also highest than the other single group. On the other hand non user out of 100%, 46.15% comes from the private service group. That’s why it is easy to see that the credit card provider company needs to think about the married group. They can provide more supplementary card for that group or reduce the annual fee for additional credit card holders in a family.
The credit card provider company may increase there Frequent flies program facility because the satisfaction level of this category is not so good. Only 39.3% are satisfied at Frequent flies program facility.
Almost 85% of respondent think the service of credit card is importance. So the credit card provider company may increase there service as much as possible.
They also increase the purchase point and try to increase the purchase point service.90% of credit card user think the purchase point service is importance. Only 7.1% user think present service of credit card is excellent.
They also increase the credit limit of customer as easy as possible. More than 60% of credit card users think the credit limit is importance.
The credit card provider company may decrease there charge because most of non user think it is expensive. And some are worry about hidden charge. The company may introduce credit card as a very well known and very useful financial product in front of customer.
2.3.2.0 Conclusion
A credit card is a new addition of the modern banking system. People can perform their daily activities such as shopping, payments of different bills etc. at ease and comfortably. A credit card transaction is often more secure than other forms of payment, such as checks, because the issuing bank commits to pay the merchant the moment the transaction is authorized, regardless of whether the consumer defaults on the credit card payment (except for legitimate disputes, which are discussed below, and can result in charges back to the merchant). In most cases, cards are even more secure than cash, because they discourage theft by the merchant’s employees and reduce the amount of cash on the premises. Prior to credit cards, each merchant had to evaluate each customer’s credit history before extending credit. That task is now performed by the banks which assume the credit risk.
To summarize, this study of credit card selection among MBA Students in Dhaka city found that convenience, protection, and economics were the main drivers, while the reputation of card and travel economics were less importance in determining credit card selection in MBA Students in Dhaka city. The convenience/protection attributes were found to constitute the most importance factor in determining credit card selection in MBA Students in Dhaka city. One reason for the importance placed on wide acceptance in MBA Students in Dhaka city and modern establishments might be that credit cardholders in Bangladeshis would prefer to use their cards for a large variety of purposes. When it comes to security concerns, Bangladeshis was not any different in their responses than cardholders in other countries such as Greece and Turkey (Meidan and Davos, 1994; Barker and Sekerkaya, 1992; Kaynak et al. (1995); Kaynak and Harcar, 2001). This is in contrast to a study (Chan, 1997) in Hong Kong that found economic factors, like “long interest-free repayment period” and “low annual fee”, to be the most importance deciding factors for the use of credit cards. While the prestige factor represents the symbolic aspects of credit card usage, the credit card as a status symbol was seen as the least importance of all 22 attributes. Thus, Bangladeshis tend to use credit cards for practical purposes more so than its status symbols.
Analysis by demographic factor show that the high income Bangladeshis place less value on the economic-promotional factor, when it comes to credit card selection. Bangladeshis who are older, married and professional are inclined to weight the convenience-protection factor more than the economic promotional factor. From a gender perspective, female Bangladeshis seem to value the promotional factor more, while their male counterparts showed a preference for the economic factor. In addition, our results showed that the number of credit cards owned by Bangladeshis is positively related to education, income, middle-age, and marital status. Single credit card owners stress economic factor more than the multiple card holders.