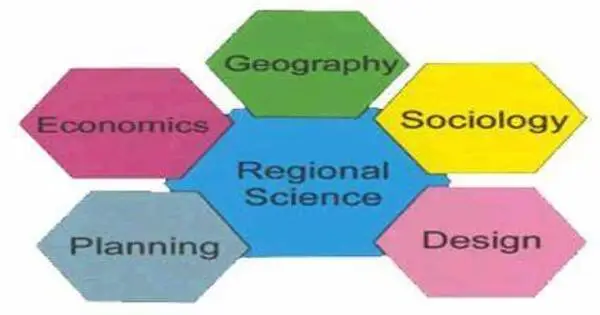
Regional science is an interdisciplinary branch of study that focuses on the investigation of geographical, economic, and social regions. It is a social science subject focused with analytical approaches to problems that are specifically urban, rural, or regional in nature. To comprehend the spatial characteristics of many phenomena, it incorporates components of economics, geography, urban planning, sociology, and other relevant disciplines.
Regional science tries to describe and forecast the regional distribution of various economic, social, and environmental phenomena and their consequences. Regional science topics include, but are not limited to, location theory or spatial economics, location modeling, transportation, migration analysis, land use and urban development, interindustry analysis, environmental and ecological analysis, resource management, urban and regional policy analysis, geographical information systems, and spatial data analysis.
Key concepts and areas of study within regional science include:
- Spatial Analysis: Regional scientists investigate the spatial distribution of economic activity, population, transportation networks, and land use patterns using a variety of instruments and approaches. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) are essential in this analysis.
- Regional Economic Analysis: This branch of regional science is concerned with the economic performance and growth of specific geographic areas, taking into account aspects such as employment, income, industry clusters, and regional inequities.
- Urban and Regional Planning: Regional science contributes to urban and regional planning by giving information on land use, infrastructure development, transportation systems, and resource allocation within specified regions.
- Migration and Demography: Studying population movements, immigration, and demographic changes is essential for understanding how regions evolve over time.
- Transportation and Infrastructure: Analyzing transportation networks and infrastructure systems helps researchers and policymakers make informed decisions about regional development and accessibility.
- Environmental and Sustainability Studies: It is increasingly concerned with environmental issues, including sustainability, land use, and the impacts of climate change on regions.
- Regional Disparities: Understanding and correcting regional differences in economic development, employment opportunities, and quality of life is a major emphasis of regional science.
Regional science is vital to governments, industries, and communities because it gives useful insights into regional growth, planning, and policy-making. Researchers in this subject employ a variety of data sources, statistical methodologies, and modeling techniques to address complex spatial challenges and promote more sustainable and equitable regional development. Regional scientists are interested in any social science investigation that has a spatial dimension.