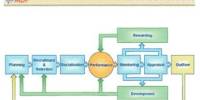
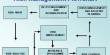
Executive Summary
This report is prepared as a requirement of the internship of MBA Program of the Stamford University of Bangladesh. This paper is aimed at reviewing the recruitment and selection procedure of Resource Integration Center (RIC); an NGO in Bangladesh.
In the course of the three months working experiences in RIC on Recruitment and Selection Procedures, a clear concept on human resources practices of the organization has been developed. In this report, I have discussed the recruitment and selection procedures that are already in place in the organization and the gaps that can be resolve by the organization for its betterment.
For this paper, data have been collected from both primary and secondary sources in different ways; key informant interview (KII), document the secondary data and observation of few procedures were mainly involved. Key informants were asked regarding the mission, vision, goal and objectives of the organization. They were also been asked about the existing selection and recruitment procedure, gaps within the procedure and how to resolve those gaps for this organization.
This report has dealt with the detail description of recruitment and selection procedure of HRD of RIC. While preparing this report it has been tried to reveal the insights of the HRD program of the developer & a few recommendations and suggestions were also prescribed based on the observations and findings. At the same time for easier understanding of the report, supporting topics and terms are explained in light of textbooks and regulatory guidelines.
Some key findings of this report are as followed: organization did not have any detail written policy on the requirements of various positions. A standing committee regarding recruitment was found inactive; the organization had very little interest in new generation worker; publication of vacancy announcements in news paper or internal notice board was very rare; sometimes recruitment was done by only verbal communication rather than any written or viva exam; no specific committee were found for selection procedure and no specific criteria were found for some positions as well.
The information is valuable for future strategic decision in the workplace. The result of this study may have higher implications for other organizations as well. The study encourages the authority to take initiatives to develop, improve and update the recruitments policy and procedure according to the current situation and demand.
“Recruitment & Selection Procedures of Resource Integration Center (RIC), a National NGO in Bangladesh”
Introduction
Human Resource Management (HRM) is concerned with the “people” dimension in management. One of the most important activities of human resource management is to develop and implement an effective Human Resource (HR) policy .HR policies are generalized guidelines and principles, which help management in decision making with regard to human resources. HR policy includes recruitment, leave, staff transition, policies related to salary & other financial benefits, staff development (through training, motivation etc.). The policies truly belong to the organization as well as to the employee. From the broader areas of HR policies I like to work with staff recruitment. I believe by developing and implementing a suitable and proper recruitment policy and procedures, primarily we can ensure to place the right person to the right place at the right time. This paper aimed at identifying the problem based on literature review, rationale of the study, objectives together with relevant methodologies, and expected outcomes etc.
Objective of the Study:
Main Objective:
This paper aimed at reviewing the recruitment and selection procedure of RIC an NGO in Bangladesh.
Specific objectives:
To investigate the original procedure regarding selection and recruitment of the selected organization.
To understand the current practice of selection and recruitment procedure of the selected organization.
To find out the gaps between original and current procedure and to conclude with an appropriate explanation.
Scope of the Study:
This report has been prepared based on only one particular organization of Bangladesh. It focused on the nature, types and functions of recruitment and selection of the organization, accounts & audit and as wells the service department, operated by the head office of Resource Integration Centre.
Methodology of the study:
The information gathered for this report through the use of primary and secondary sources. Initial contacts with key persons have been made through personal communication. Sub sequent interviews with the concerned officials have been used for collecting information. Additional secondary information has been collected from company’s published yearly publications. Data and information are collected through the following ways:
► Primary sources of data:
- Interviews both formal and informal were taken from the officers of RIC
- This study was designed according to surveys and both directed and undirected questions type of descriptive surveys.
- Observing the procedure of company’s activities followed by each department.
- Face to face interview with the respective officers of the office and MIS data has been analyzed.
► Secondary sources of data:
- Various Operating Manuals, journals of RIC
- Reading various relevant files.
Deskwork: during the practical orientation I worked different desk in different time.
Limitations of the Study:
Every project has some limitation. During the course of my practical orientation I faced some usual constraints.
- Time frame for the research was very limited. The actual survey was done within a month.
- Large-scale research was not possible due to constraints and restrictions posed by the organization.
- In many cases, up to date information was not published.
- Getting Relevant papers and documents were strictly prohibited.
- Many procedural matters were conducted directly in the operations by the top management level, which also gave some sort of restrictions.
- To protect the organizational loss in regard of maintaining confidentiality, some parts of the report are not in depth.
Expected Outcomes of this study:
It is expected that the findings of the study will encourage the Chief Executive of the NGOs to take initiatives to develop, improve and update the recruitments policy and procedure according to the current situation and demand. It will also help to develop professionalism of the employees and make them more conscious about their human rights and finally right people will be placed in the right place at the right time.
Literature Review
In 1972, just after liberation war, Bangladesh Government tried various measures to develop the nation. It was then that Non-Government-Organizations (NGOs) began to be formed to supplement government efforts at poverty alleviation. Since hunger is the most abject denial of the fundamental human right to life, these NGOs therefore served a definite purpose. Soon these organizations branched out in other social sectors e.g. education, family planning, reproductive health care, vocational training, etc. in trying to complement the action agenda of government, which in many cases was found wanting. (PPRC, 2003).
The main purposes of the NGOs are to assist the poor and poorest people of Bangladesh to rehabilitate themselves through primary health care, agricultural and natural resource and small enterprise development. (ADB, June1995)
Around one-third populations of our country are unemployed. NGOs are playing a vital role in this regard through effective Human Resource Management (HRM) to develop and implement an effective human resource policy. NGOs have been keeping evidence of better Human Resource Planning (HRP) that increases the performance of the NGOs. (Sen, 1996 & IFAD, 1992).
These organizations are increasingly involved in more complex technologies and are attempting to function in more complex economy, political and socio-cultural environments depending on the human resource policies. (Schein, 1997).
For the better performance of these NGOs with scare resources, Human Resource Planning (HRP is “the process of getting the right number of qualified people into the right job at the right time”) has become a necessity factor for long-term survival (Hossain, 1996).
Overview of the Organization
Background of Resource Integration Centre (RIC)
RIC started with relief, rehabilitation and financial assistance program for rural woman after being established as a non-government organization in 1981, long back 29 years by some distinguished social worker to support the national development efforts. RIC’s focus was on the rural poor specially the woman. RIC has advanced through learning by doing, adjusting its strategy to prevailing circumstances.
In progress RIC diverse its activities in almost all major part of development sector, hundreds of employees, volunteers are involved in and support development assistance activities from the isolated islands to the heart of the capital city among them ethnic groups, minority groups, children and older community are mention worthy.
Vision:
RIC’s vision is to establish a happy and prosperous Bangladesh based on equal rights and strong democratic values.
Mission:
To alleviate poverty through human resource mobilization and socio-economic development in its broader sense. RIC would like to standardize the quality of life of people at the grassroots, ensure the rise of Human Development Index (HDI), and increase Human Rights (HR) and political empowerment including Gender Equity and Conservation of Congenial Environment.
Main activities:
RIC has been engaged in (i) empowering target groups through institution building, (ii) women’s development, (iii) environmental development through awareness raising, plantation and sanitation programmes, (iv) emergency disaster response and service delivery, (v) the provision of health services to women, children, adolescent and older people (vi) formal and non-formal education to underprivileged children, (vii) income generation through micro-credit operations, (viii) employment development training projects for the poor, (ix) natural disaster preparedness and risk reduction programmes, (x) empowerment of older people, (xi) agriculture development and food security, and (xii) urban governance.
RIC current Program and Project at a glance
Sector wise ongoing program and projects are as follows:
| Sectors | Ongoing projects | Funding partners |
| Human rights | 5 | IRISHAID, Manusher Jonnya foundation, European Union, HelpAge Germany, Helpage International,ILO |
| Food & Livelihood Security | 4 | WFP, European Commission, CARE- Bangladesh (USAID fund) |
| Education | 3 | Ministry of primary and Mass Education of Bangladesh Government, UNICEF |
| Health and Nutrition | 3 | CIDA, HAD, CARE- Bangladesh |
| Disaster Preparedness Response Rehabilitation and Risk reduction | 4 | UNDP, DEC, Ministry of Foreign Affairs-Germany |
| Income Generation Programs | 10 | PKSF, Sonali bank, Basic bank, Bangladesh |
1. Rights Based Programs (Women rights, child rights, older people rights)
- Targeted Citizen Initiatives to address the Identified Problem relating to Human Security and Basic Services in DhakaCity.
- Realizing the Rights of the Marginalized and Vulnerable Older People (RROP) Program
- Promoting Older People’s Participation in Development in Rural Bangladesh
- Coordinated assistance for the older women in Bangladesh.
- Sponsor A Granny (SAG)
- Prevention and Elimination of worst form of Child labour
2. Food & Livelihood Security
- Vulnerable Group Development Program (VGD)
- Vulnerable Group development of Ultra Poor (VGDUP)
- Strengthening Household Ability to Respond Development Opportunities- (SHOUHARDO) Program
3. Education
- Post Literacy For Continuing Education Program
- Formal Education for Vulnerable and Marginalized Community People Program
- Basic Education for Hard to Reach Urban Working Children (BEHTRWC) Project
4. Healths and Nutrition
- Health and Home Care for Older People components under the RROP and SAG Program.
- Community based health support for the older people
- Mother and Child Health and Nutrition Program
5. Disaster Preparedness, Response and Rehabilitation
- Rehabilitation of the Flood-Effected Weavers of Nowabgonj Upazilla Project
- International and Inclusive Humanitarian support for cyclone affected older people and their family members.
- Enhancing Disaster Risk Reduction Capacity of Older person in cyclone SIDR affected areas
6. Income Generation Programs
- Mainstream Microfinance (Rural and Urban) Program
- Microfinance for Micro Enterprise Development Program
- Micro-credit for Hard core Poor Program
- Financial Support for the Poorest (FSP) Program
- Microfinance for Small and Marginal Farmers (MFMSF) Program
- Microfinance for Older People Program
- Microfinance for the parents of the Working Children Program
- Livelihood Restoration Program (LRP)
- SHAHOS
- RESCUE
7. Microcredit:
RIC financial assistance program focuses on the poor and ultra hard-core poor of rural women. Besides, RIC has urban credit program from which we are covering the whole Dhaka city. The major classification of microcredit supports are mainstream microcredit program, micro enterprise, financial support for the poorest, micro finance for marginal & small farmers, micro finance for the older people and financial support for the parents of the children involved in hazardous form of child labor with the partnership of PKSF, Sonali Bank, Basic Bank, Bangladesh Bank and ILO. RIC is operating its financial support program in Dhaka, Munshigonj, Pirojpur, Cox’s Bazar, Gazipur, Narayangonj, Noakhali, Naogoan and Norshindi district. Rate of recovery is almost 99%.
8. Good Governance:
RIC started urban governance project at 25 ward of DhakaMetropolitanCity in the current year with the assistance of Manusher Jonno to ensure peoples participation with the local govt and essential service providers so that people’s opinion can reflect in the decision. RIC is organizing a common body in every ward consisting service provider and consumer to ensure citizen rights.. RIC is organizing village development Committee in every working village of Moheshkhali under Cox,s Bazer district and this committee is playing the key role for project playing.
9. Organizational Structure and Human Resources:
The organizational structure is 3 tire based. The sufficient manpower is available and working in the separate and independent discipline of projects and programs. The management structure and system of management of RIC is well defined and is clearly provided in its Human Resource and Administrative manual. As per the constitution General Body (GB) consisting of 25 members is the highest body of the organization. They elect 07 members Executive Committee (EC) for two years term in Annual General Meeting. Executive Committee is responsible for day-to-day policymaking and its implementation. EC appoint a ‘Director’ who is ex-officio Member secretary and Chief Executive Officer (CEO) of the organization. Director appoints requisites number of staff with specific functional responsibilities such as Finance and Administration, Human Resource Management, Monitoring and Evaluation, Micro-Credit operation Programme and Project management. There is separate Human Resource Management Section headed by a Human Resource coordinator to look after HRM issues. An approved Human Resource Management Manual guides Human Resources management.
RIC has well infrastructure & decentralized organ gram to ensure transparent management system and accountability. The entire department is leading by competent personnel having adequate academic background and professional skill. . At present there are 2015 staff (Female 677 and Male 1338) among them 749 are permanent staff and rest 1266 are different project based staff. All most all of the staff is working for long time with RIC. Key positions are hold by the personnel having long outstanding experience in the development field and have adequate skill and knowledge. Besides there are some consultant and advisor are also associate with the organization to provide technical support on specific issues.
10. Office Set-ups and Logistics Support
RIC has office set –up at Dhaka, which is Central Office, another 15 office set-up those are called Area office located in project areas of RIC.RIC also have 79 branch offices and 44 project offices in its operational areas. All offices are supported with all sorts’ necessary office equipments. All officers at the central have access to individual email accounts and have a Local Area Network (LAN) for better communication and sharing. All officers at Central and Area Office level have been provided with cell phone for quick communication. All Area office has adequate numbers of Motor cycle and Bi- cycle for field monitoring.
Recruitment and selection
The important function of Human Resource Management (HRM) is Recruitment & Selection, Performance appraisal, Evaluation, training need assessment. Recruitment and Selection procedure is one of the major parts of the HRM. The main objective of this process is to recruit & select right people to the right jobs. Most of the organizations try to follow some principles in the recruitment & selection process. Those are:
- Merit & Skill basis recruitment
- First priority to qualification & experience
- Transparency in the whole recruitment Process.
Recruitment Process
An Organization will want to staffing, than assuming, that demand for certain skill, knowledge and abilities is greater than the current supply is recruiting. Recruiting is the process discovering potential candidates for actual or anticipated organizational vacancies it is a linking activity that bring s together those with jobs to fill and those seeking jobs.
According to David A. DeCenzo & Stephen P. Robbins, “The more applications received, the better the recruiter’s chances of finding an individual best suited to the job requirement.” Edwin B. Flippo prescribes recruitment as, “A process of searching for prospective employees and stimulating them to apply for job in the organization”. William B. Werther and Keith Davis observe recruitment as, the process of finding and attracting capable applicants for employment. This process begins when recruits are sought and ends when their applications are submitted.
From the above-mentioned definition we can find some characteristics of recruitment as follows:
- Human resource Recruitment is a continuous process in a big organization.
- Human resource Recruitment process is very complex and costly.
- Human resource Recruitment process is done in the light of recruitment planning.
- Human resource Recruitment is a process between recruitment planning and selection.
- Human resource Recruitment process increases organizational image and assists to bring goodwill to general people.
After this discussion we can say that, human resource recruitment is a process for searching qualified people for the new and vacant posts in an organization and to influence them to apply for the job. It is important to know that perfect human resource came out from this applicant. It depends on organizational image, Job attractiveness, internal organizational polices, government influence recruiting costs.
Recruitments process:
Once the organization has an idea of its future human resource needs, the next phase is recruiting new employees. Recruiting, the process of attracting qualified persons to apply for jobs that are open. Recruitment can be in two ways; internal and the external recruitments.
Sources/Methods considering at the time of recruitment:
- Current employees
- Former employees
- Referrals
- Walk-in candidates
- Executive recruiters
- University recruiters
- Customers
Selection Process
According to Heinz weihrich and Harold Knootz, “Selection is the process of choosing from the candidates, from within the organization or outside, the most suitable person for the current position or for the future position. Dale Yoder said that, “Selection is the process by which candidates for employment are divided into two classes those who will be offered employment and those who will not.” David A. DeCenzo & Stephen P. Robbins, stated that “Selection process typically consists of eight steps: 1) initial screening interview, 2) completing the application form, 3) employment tastes, 4) comprehensive interview, 5) background investigation, 6) conditional job offer, 7) medical or physical examination and, 8) permanent job offer.”
Recruitment is the process of finding and selecting capable applicants for employment. The process begins when new recruits are sought and ends when their applications are submitted. The result is a pool of applicants from which new employees are selected. Recruitment is concerned with reaching out and attracting a supply of people from which qualified candidates can be selected for the job vacancies.
The primary purpose of any recruitment process is to find the most competent applicants and choose those individuals who are best qualified for employment and to place them in jobs for which their talents, skills, training and experience are best suited. No organization can expect successful organizational growth unless it has an effective work force.
Human Resource planning is the process by which an organization ensures that it has right number and kind of people at right place, at right time capable of effectively and efficiently competing those tasks that will aid the organization in achieving its overall objectives.
Recruitment is the process of generating a pool of candidates for a particular job. It aims to attracted qualified candidates. It pares the way for collection procedure by producing the smallest number of candidates. In order to do so, we have to consider the following procedure of recruitment and selection.
Tools of selection
- Application call
- Ability test – MCQ type
- Personality test
- Physicality test
- Interviews
Another procedure often use by the company is interview method
- Traditional interview
- Non-directive interview
- Directive interview
- Structured interview based on job analysis
- Stress interview to determine how an applicant will react to stress on the job.
Organizations consider the following steps in the interview –
- Plan: Review application and resume location of interview.
- Established Rapport: Ask non-controversial questions
- Ask Questions
- Review the interview
- Close the interview
- Some guidelines for the interviewer
- Use a structured form
- Delay the decision
- Focus on traits that are more accurately assets in interview
- Get the interviewee to talk.
Recruitment Policy of RIC
General Policies
- Any citizen Bangladesh or foreign is eligible for appointment in any post of RIC provided s/he qualify the whole interview process.
- Nobody who is below 18 years of age and not more than 60 years of age can be appointed at RIC. However, the appointing authority, in special cases, can continue a person in the service of RIC above sixty in age at contractual basis.
Recruitment Committee (RC)
A five member’s recruitment committee will be formed by the initiative of HRD which will be consulted and approved by the Director. Inclusion of Chief of the HRD section in the committee is mandatory. The committee will act as standing committee for recruitment. However, during recruitment, at least three from the recruitment committee and personnel form the concerned section/ projects/ department will be included in the recruitment committee if needed. Member from the EC may be included in the Recruitment Committee in special cases.
Recruitment Procedures
Advertisements
RIC’s policy is to give preference to appoint internal candidates provided the employee is suitable and qualified. Such appointments may be made by the way of promotion, up-gradation or transfer. If not, then as a usual procedure, job vacancies will be advertised by HRD through internal notices to the concerned offices and the National Dailies. An internal candidate can also apply based on the advertisements. Advertisements/notices should indicate the position, nature of appointment, location, major areas of responsibilities, terms and conditions such as salary, duration, minimum education qualification, work experience and special requirements.
Short Listing
After receiving the applications, the HRD will prepare a matrix then Recruitment Committee and the concerned program chief will make a short list of the applicants in consultation with the Convener of the Recruitment Committee.
However, when RIC needs to recruit a huge number of manpower at a time then instead of short listing interested candidate may be invited for ‘ Walk-in- Interview’ to expedite the recruitment process.
Interview Process for Selection
Candidates Short-listed by the Recruitment Committee will be called for written or verbal interviews or for the both. RIC will adapt a systematic interview procedure and ability/written test as deemed appropriate. Interview Board/Selection Committee will be formed comprising of Sr. staff members including senior personnel of the concerned program/project. However for appointment in the senior position a member of the EC and for the technical position external expert may be included in the selection/interview board. Upon completion of the test/interview, the interview board will prepare a final panel for appointment.
Driving Test
For appearing in the driving test for recruitment in the position of Driver the candidate must produce a valid driving license to the interview board. The Management may verify the driving licensee from License issuing authority (if needed).
Offer of Employment
The selected candidate(s) will be offered employment with RIC with all-necessary terms and conditions. Any offer of employment must be contingent upon the final reference check with the present or past employer.
I. Appointment and Joining
Appointment
The Chairperson of the EC will issue appointment letter to Director on the basis of approval of EC.
Director will issue all other letter of appointment as per on the basis of recommendations of Recruitment Committee. The appointment letter must include:
- Job title, grade/step and salary
- Nature of appointment
- Place of posting
- Name of program, section/department
- Effective date of appointment
- Probationary period, conditions of confirmation and notice period
- Ending date of employment (for contractual employment)
- Job description
- Job acceptance letter by the employee along with a joining letter
Joining
- Person(s) who is/are employed with another organization must provide clearance/release letter prior to joining RIC and shall submit a joining letter in RIC-HRD provided joining letter format during the date of joining.
- The Management may re-designate/transfer any staff for the interest of RIC. The staff concern must join the station within the given time frame after handing over his/her current charges officially to assigned staff. Failure of which, management may take any action including termination.
All re-designation in senior positions of RIC are subject to prior approval of the Director. Re-designation will not be automatic and the applicant has to go through the recruitment process and compete with other candidates who have applied for the post.
II. Probation Period and Confirmation
Probation
All appointments of RIC must have a probation period of at least 3 (Three) months from the date of joining at RIC, extendable at the discretion of the appointing authority by the recommendation of the concern/respective supervisor. In case of Director Position the EC may waive or impose probation.
Expiry of Probation
At the end of probation period, the line manager will prepare a brief performance appraisal with recommendation for confirmation, extension of probation or dismissal/discontinue to the authority.
At the end of successful completion of the probation period, the appointing authority will issue a confirmation letter to the employee from the date of confirmation. The probation period may be extended by one additional period of 3 (three) months only in the event if it is deemed necessary. If the performance level of the employee on probation is not found satisfactory, he/she may be released from service within 7 (seven) days’ notice, or otherwise, as stated in the appointment letter.
The appointing authority will inform the employee on probation, in writing, so as to his/her confirmation, termination or extension of probationary period before the end of the probation period.
- Personal Files and Records
RIC shall open a personal file for each individual employee, starting from the date of his/her appointment. This personal file should have all records starting from job application, CV, copy of certificates, licenses, interview result sheet, test related papers, reference letters, appointment letter, job description, important correspondence on leave, medical records, performance appraisal, employee’s status and salary changes including transfer (if there is any), increment, promotion, disciplinary actions and any communications with regard to his/her personal behavior, performance etc.
The personal file is treated as a confidential document and nobody will have any access to those files. These should be kept under direct control of the HRD section .On written request of an employee; Director may allow the employee to see his/her personnel documents with some restrictions. All the pages of personal file must be marked with page number, which will start from the first document.
The personal files of ex-employees, subject to the final payment are made, will be destroyed after 5-years from the date of employee’s separation. A committee should be formed by Director to destroy any document of RIC. In the event of any dispute between the employee and RIC, the concerned file can’t be destroyed until it is over.
IV. Job Orientation
Orientation is defined as the act of introducing a new employee to a job in the organization. It is the guided adjustment of the employees to the organization and their work environment. It is RIC’s policy to orient all new employees to become acquainted with their new positions within 15 days of joining.
In consultation with the director, the HRD will arrange and coordinate the orientation program depending on the level of the employee like head of a department, field or support staff and type of job to be performed by the employee like program, finance, technical, administrative or consultant. Whatever the level and the job of the employee, some important areas of orientation based on values and philosophy of RIC must be included in the orientation program for the employee.
Objectives of Orientation- The objectives of the orientation of the employees are to:
- Have an understanding of RIC’s mission, vision, values, philosophy, approach etc.
- Get an understanding of RIC activities and his/her job (Job Description or TOR)
- Develop favorable attitude towards the organization, its policies and its employees
- Develop positive attitude towards gender equity and secular values
- Install a feeling of belonging to and acceptance in the organization
- Generate enthusiasm and high moral
- Build relationships with colleagues and key staff in the organization
Contents of Orientation Program
A standard orientation program will include at least the following:
- Introduction to colleagues
- Orientation to organization structures
Provide Important RIC Documents to the employee of RIC for study
- HRD Manual
- Administrative policies
- Accounting procedures essential for them
- Program specific documents
- Annual Report (Previous + Present)
- RIC brochures etc.
- RIC publications
- Personnel policies such as: terms of employment, employee and organization’s expectation, leave and benefits, HRD process, working conditions and facilities, HRD rules and regulations and administrative rules.
- Job specific orientation, which includes the detailed duties and responsibilities, working relationship with other staff of the office.
Analysis and Data Presentation
For this paper, we have collected data in different ways; key informant interview (KII), document the secondary data and observation of few procedures were mainly involved. We interviewed few key informants regarding the mission, vision, goal and objectives of the organization. Besides, we also asked them about the existing selection and recruitment procedure, gaps within the procedure and how to resolve those gaps for this organization.
Data from KII were analyzed very systematically. With these textual data content analysis was done completing the procedure from the compilation of data to identification of theme. These data helped us to identify the gaps and how can we resolve those gaps to run the organization smoothly.
From the documentation process, we reviewed the recruitment and selection procedure of the organization in systematic manure. In the beginning we reviewed overall procedure are in place and then we looked into individual level those are already employed in the organization for several years. We randomly selected 30 individuals to review their recruitment and selection process. From our observation we found that in-terms of educational qualification sometimes-original system were not followed specially in the mid level positions. On the other hand, for relatively higher position criteria in terms of experience was not followed all the times by the organization. Out of our ten observations 5 (table#1) of them were not matched in educational qualification with the existing system in the Branch Manger (BM) position. Similarly, In Area Manager (AM) position selection criteria in terms of experience were not matched with the existing rule.
Table#1
Positions | Selection Criteria | Total Observations | |||
Followed by | Not Followed by | ||||
Education | Experience | Education | Experience | ||
FO | 9 | 9 | 1 | 1 | 10 |
BM | 5 | 7 | 5 | 3 | 10 |
AM | 9 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 10 |
To know the current procedure of selection and recruitment, we observed few procedures during our data collection using a checklist. With some selected points those are indicated in the original guideline we observed few interview cases and analyzed the information accordingly. After collecting the information we organized the data and looked into the original guideline following the steps are indicated. And after completion of this observation when we found any discrepancy in the process we talked to those key informants to know the reasons and explanation so that we can easily find the gaps in the existing process.
Findings and Recommendations
Findings
In overall observation regarding recruitment procedure we found some findings:
- The organization did not have any written policy about the requirements of various positions except some position.
- There was a standing committee regarding Recruitment, but the committee found inactive, even we did not see such practical practices.
- The organization had very little interest in new generation worker.
- Sometimes the CVs with familiar reference are given importance to recruit in selected positions.
- Although any employee got terminated due to some illegal activities he or she might have gained that position again without any punishment and in those cases no rules or regulation were followed by the organization.
- Some times there was no vacancy announcements found published in news paper or internal notice board for some positions. Even sometimes respected department or their representatives were not always informed of the matter about the recruit process was going on for her department.
Regarding the selection written or viva exam was not always taken for all recruitments. Sometimes it happened only by the verbal communication. There was no specific committee found for selection procedure. There were also no specific criteria found for some positions to recruit in the organization.
Recommendations
- Criteria should be followed for every position.
- The organization should ensure right people in the right places.
- Organization should build the separate policy for requirements & selection
- The policy should be updated so that it can compete with other organization as well.
- This policy should be reviewed by external expertise /reviewer at least in every two years.
References:
1.H. Schein, Sloan Management Review Fall 1977, volume-19 Number-01
2. Zakir Hossain , Dhaka University Journal of Business Studies Vol. 17(2), 207-227, Dec 1996
3. Dr. Dilip Kumar Sen , Dhaka University Journal of Business Studies Vol. 17(1), 93-120, June 1996
4. PPRC, (a research organization) “How can the Human Rights and Governance Agenda be Best Served ” –An Analytical Overview, 2003
5.Asian Development Bank- Inception Report, June in 1995
6.NGO Affairs Bureau – Circular May, 2005
7.Social Welfare Department – Circular May, 2005
8. IFAD, The Study of World Rural Poverty, 1992
9.Chowdhury, Additte Nag, “ Let Grass root Speal-People’s Participation Reef help groups NGO’s in Bangladesh, University Press Ltd. 1989.
10.Dr.Muzaffer Ahmed, Bangladesh Business Research Report, Volume-01 (1989)
11.C.R. Kothary, Research Methodology, Second Edition
12. CARE (an International NGO), HR Policy & Procedures Manuel, 2002
13. Plan International (an International NGO), HR Manuel, 2004
14. Resource Integration Centre (a National NGO), Service & Administrative Rules, 2002