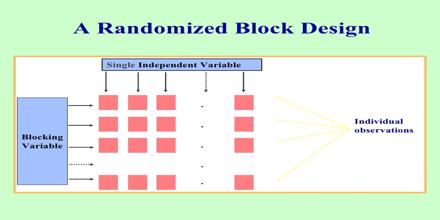
In a Randomized Block Design, the experimenter divides subjects into subgroups called blocks, such that the variability within blocks is less than the variability between blocks. This is intended to eliminate possible influence by other extraneous factors. Like stratified sampling, randomized block designs are constructed to reduce noise or variance in the data. The experimenter will typically need to spend some time deciding which nuisance factors are important enough to keep track of or control, if possible, during the experiment.
Randomized Block Design