Rainwater Harvesting
All living things including, plants, animals, and human beings need water to live and to carry out different cellular activities. Rainwater harvesting (RWH) the collection and storage of rain, rather than allowing it to run off. It is the simple process or technology used to conserve Rainwater by collecting, storing, conveying, and purifying Rainwater that runs off from rooftops, parks, roads, open grounds, etc. for later use. It is a sustainable process that helps in preserving water for future needs.
Rainwater Harvesting systems range from simple rain barrels to more elaborate structures with pumps, tanks, and purification systems. It is a sustainable process that helps in preserving water for future needs.
Rainwater is collected from a roof-like surface and redirected to a tank, cistern, deep pit (well, shaft, or borehole), aquifer, or a reservoir with percolation. The rainwater harvesting system is one of the best methods practiced and followed to support the conservation of water. Dew and fog can also be collected with nets or other tools.

The advantages of rainwater harvesting are –
- It is cost-effective
- Conserves water
- A source of water for landscape irrigation
- It is a simple method and easy to practice
- It reduces soil erosion and pollution of water bodies due to fertilizers and pesticides
Rainwater harvesting differs from stormwater harvesting as the runoff is collected from roofs, rather than creeks, drains, roads, or any other land surfaces. These systems range from simple rain barrels to more elaborate structures with pumps, tanks, and purification systems. Its uses include watering gardens, livestock, irrigation, domestic use with proper treatment, and domestic heating. The harvested water can also be committed to longer-term storage or groundwater recharge.
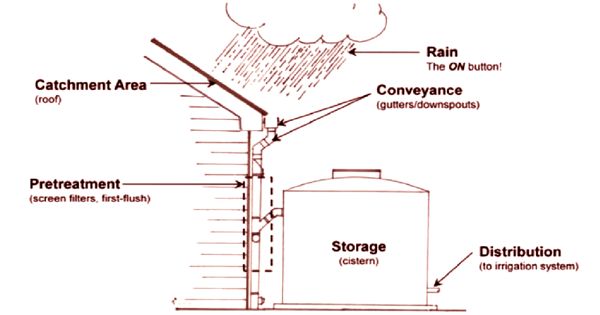
Rainwater harvesting systems consists of the following components:
- Catchment- Used to collect and store the captured Rainwater.
- Conveyance system – It is used to transport the harvested water from the catchment to the recharge zone.
- Flush- It is used to flush out the first spell of rain.
- Filter – Used for filtering the collected Rainwater and remove pollutants.
- Tanks and the recharge structures: Used to store the filtered water which is ready to use.
Today, scarcity of good quality water has become a significant cause of concern. Rainwater harvesting is one of the simplest and oldest methods of self-supply of water for households, and residential and household-scale projects usually financed by the user. However, Rainwater, which is pure and of good quality, can be used for irrigation, washing, cleaning, bathing, cooking, and also for other livestock requirements.
In addition to the great advantages, the rainwater harvesting system has a few disadvantages like unpredictable rainfall, unavailability of the proper storage system, etc. However, larger systems for schools, hospitals, and other facilities can run up costs only able to be financed by companies, organizations, and governmental units.