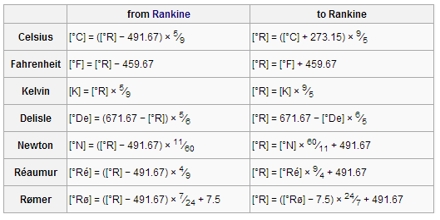
The aim of this lecture is to present on Rankine Scale. Rankine is a thermodynamic (absolute) temperature scale named after the Scottish engineer and physicist William John Macquorn Rankine, who proposed it in 1859. The symbol is R. As with the Kelvin scale (symbol: K), zero on the Rankine scale is absolute zero, but the Rankine degree is defined as equal to one degree Fahrenheit, rather than the one degree Celsius used by the Kelvin scale. A temperature of -459.67 °F is exactly equal to 0 R.
Presentation on Rankine Scale