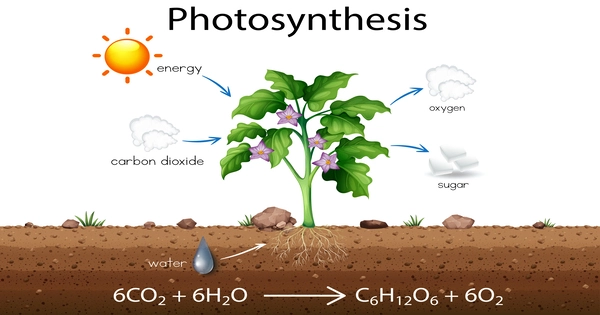
Photosynthesis is a biological process utilized by many cellular organisms to transform light energy into chemical energy, which is then stored in organic compounds and processed through cellular respiration to power the organism’s activities. It is the process by which green plants and other creatures convert light energy into chemical energy. Light energy is absorbed and used to convert water, carbon dioxide, and minerals into oxygen and energy-rich organic molecules during photosynthesis in green plants.
Typically, the phrase refers to oxygenic photosynthesis, in which oxygen is created as a byproduct, and some of the chemical energy produced is stored in carbohydrate molecules such as sugars, starch, glycogen, and cellulose, which are synthesized from the endergonic interaction of carbon dioxide with water. Photosynthesis is performed by the majority of plants, algae, and cyanobacteria; these organisms are known as photoautotrophs.
Here’s a simplified overview of the process of photosynthesis:
- Light Absorption: It is most commonly found in plant chloroplasts, specifically in chlorophyll-containing structures known as thylakoids. Chlorophyll is a green pigment that absorbs solar light energy.
- Light Reactions: Chlorophyll and other pigments absorb sunlight and use this energy to break water molecules into oxygen and protons during light-dependent processes. As a consequence, oxygen is released, and protons are utilized to form a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane.
- ATP Formation: The proton gradient formed in the thylakoid membrane causes the creation of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), an energy-storing molecule. In biological systems, ATP is the primary energy currency.
- Carbon Fixation (Calvin Cycle): In the light-independent reactions (Calvin cycle), carbon dioxide from the atmosphere is combined with the energy-rich molecules ATP and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) produced in the light reactions. This results in the formation of glucose and other organic compounds.
Photosynthesis is primarily responsible for producing and sustaining the oxygen content of the Earth’s atmosphere, as well as providing the majority of the biological energy required for sophisticated life on Earth.
The importance of photosynthesis in the survival of life on Earth cannot be overstated. If photosynthesis ceased, the Earth would soon be devoid of food and other organic stuff. Most species would die, and the Earth’s atmosphere would eventually be nearly empty of gaseous oxygen. The only creatures that can survive in such conditions are chemosynthetic bacteria, which can use the chemical energy of specific inorganic chemicals and hence are not dependent on light energy conversion.