Nosean, also known as noselite, is a mineral of the feldspathoid group with the formula: Na8Al6Si6O24(SO4). H2O. It is a mineral of the sodalite group, a silicate, and sulphate of sodium and aluminium. It is an uncommon member of the feldspathoid group that is closely related to Lazurite and Hauyne. It is a mineral found in igneous rock as isometric crystals. It can sometimes be very difficult to distinguish these three minerals without a complex chemical analysis.
Nosean is named after German mineralogist and chemist Karl Wilhelm Nose (1753-1835). It was first described in 1815 from the Rhineland in Germany and named after the German mineralogist K. W. Nose.
General Information
- Category: Sodalite – (Feldspathoid)
- Formula: (repeating unit) Na8Al6Si6O24(SO4)
- Crystal system: Cubic
- Crystal class: Hextetrahedral (43m) H-M symbol: (4 3m)
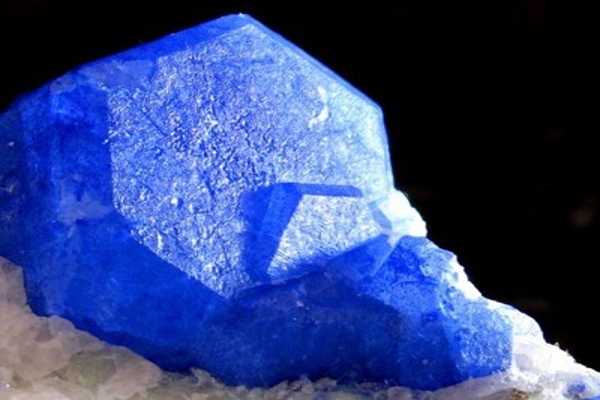
- Colour: Colorless, white, gray, gray-brown, blue, black

Physical Properties
Nosean forms colorless, white, gray, gray-brown, blue, black granular masses, crystals are rare. It has a Mohs hardness of 5.5 to 6 and a specific gravity of 2.3 to 2.4. It is fluorescent. It is found in low-silica igneous rocks. It forms isometric crystals of variable color: white, grey, blue, green, to brown. There is a solid solution between nosean and hauyne, which contains calcium.
- Lustre: Vitreous
- Transparency: Transparent, Translucent
- Hardness: 5½ on Mohs scale
- Tenacity: Brittle
- Cleavage: Poor/Indistinct Indistinct on {110}
- Fracture: Irregular/Uneven, Conchoidal
- Density: 2.3 – 2.4 g/cm3 (Measured); 2.21 g/cm3 (Calculated)
Occurrences: In silica-de¯cient alkalic volcanic rocks, principally phonolites.
The mineral is rare but widespread, found in such diverse localities as ocean islands (e.g., Tahiti) and the La Sal Range in Utah.
Nosean forms a solid solution series with Hauyne, where Hauyne contains calcium in place of some of the sodium, whereas Nosean lacks any calcium and has water in its chemical structure.
Association: Sanidine, mica, leucite, magnetite, ilmenite, titanite, zircon.